Not happy with your purchase?
Simply let us know, and you'll get a full refund, no questions asked. And you don't even need to return anything.
So that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
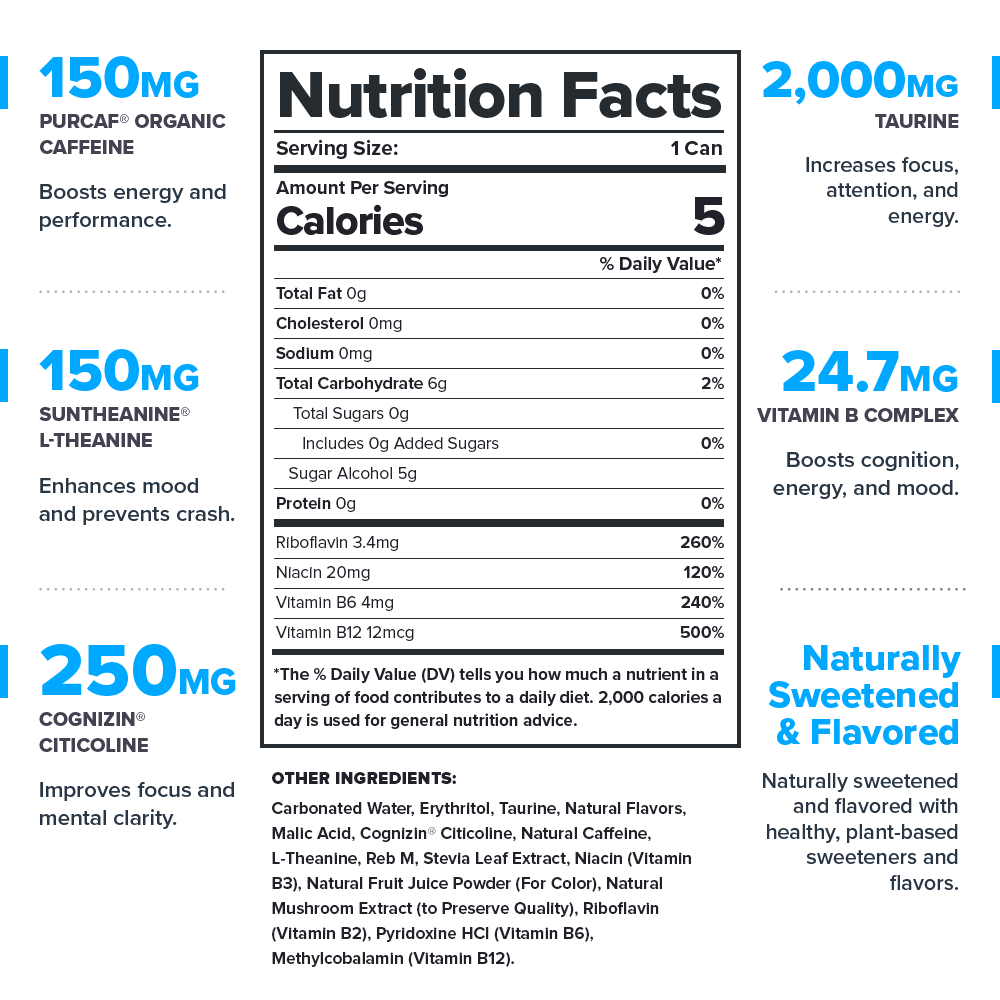
Legion Energy Drink Ingredients (3,577 milligrams per serving)
PurCaf® Natural and Organic Caffeine (150 milligrams per serving)
Caffeine is a naturally occurring substance found in many plants native to Africa, East Asia, and South America, including various kinds of tea, cocoa, and coffee.
PurCaf® is an organic, patented form of caffeine extracted from non-GMO green coffee beans using a proprietary clean-water process.
Naturally derived caffeine tastes significantly better than its synthetic counterpart, and anecdotally, many people report that it provides a "smoother" boost of energy, possibly due to beneficial compounds like chlorogenic acids and antioxidants found in natural caffeine but absent in synthetic versions.
Caffeine’s primary effects in the body are to stimulate the central nervous system and block the activity of another chemical—adenosine—that causes tiredness.
Research shows that supplementation with PurCaf® caffeine . . .
- Boosts mood and energy levels[9]
- Improves focus, drive, and wakefulness[10][11][12]
- Increases metabolic rate[13]
- Enhances strength and power[14][15][16][17][18]
- Boosts endurance[19][20][21]
- Improves anaerobic performance[22][23][24][25][26]
The clinically effective dose of caffeine for enhancing energy, focus, and performance is between 50 milligrams and 6 milligrams per kilogram of body weight.[27][28][29]

Suntheanine® L-Theanine (150 milligrams per serving)
L-theanine is an amino acid found primarily in tea that helps balance the levels of two chemicals in the brain—glutamate and GABA—that transmit nerve impulses and affect mood, cognitive performance, and more.
Suntheanine® is a patented form of L-theanine that’s the most clinically proven form on the market, with over 40 peer-reviewed studies supporting its efficacy.
Research shows that supplementation with Suntheanine® L-theanine . . .
- Reduces the effects of mental stress[30]
- Promotes relaxation[31]
- Improves mood, memory performance, and attention (when paired with caffeine)[32][33][34][35]
- Increases the production of nitric oxide (which improves blood flow)[36]
The clinically effective dose of L-theanine when combined with caffeine is between a ratio of 1:1 and 2:1 theanine to caffeine.

Cognizin® Citicoline (250 milligrams per serving)
Citicoline is a chemical that occurs naturally in the brain and increases levels of another chemical called phosphatidylcholine, which is vital for brain health and function.
Citicoline can also increase levels of a neurotransmitter known as acetylcholine, which is involved in learning and muscular contraction.
Cognizin® is a patented form of citicoline that’s the only form studied in healthy adults and supported by 16 years of clinical research.
Research shows that supplementation with Cognizin® citicoline . . .
- Improves focus and memory[37][38]
- Boosts attention and mental processing speed[39]
- Mitigates cognitive decline as we age[40][41][42]
The clinically effective dose of citicoline is between 250 and 500 milligrams.

Taurine (2,000 milligrams per serving)
Taurine is an amino acid found primarily in seafood and meat that, unlike most amino acids, isn’t used to build proteins.
Rather, it plays an important role in cardiovascular and muscle function by protecting cells from oxidative stress and regulating the release of neurotransmitters.
Research shows that supplementation with taurine . . .
- Improves focus, attention, and reasoning when combined with caffeine[43][44]
- Helps minimize unwanted side effects of caffeine (like jitters)[45]
- Helps prevent a "sugar crash" by slowing the release of glucose into the blood[46][47]
The clinically effective dose of taurine is 1-to-6 grams per day, with the majority of benefits in the range of ~1-to-3 grams.

B Vitamin Complex (27.4 milligrams per serving)
B vitamins are a category of naturally-occurring substances that cells need to turn food into energy. They also affect mood, feelings of wellness, and brain, nerve, and cardiovascular function.
Although B vitamins don’t directly increase energy levels in the same way as a stimulant like caffeine, many people report feeling more energized when supplementing with B vitamins. This is likely because B vitamins are required for many bodily processes that influence energy production, and thus, by increasing the availability of B vitamins, such processes can function more effectively.
Research shows that supplementation with B vitamins (particularly vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B12) . . .
- Reduces stress[48]
- Improves mental clarity, energy, and focus[49]
- Boosts cognitive function and memory[50][51]
- Improves mood and energy levels[52][53]
There is no established clinically effective dose of B vitamins, but the ones thought to most improve energy, mood, and cognitive function are B2, B3, B6, and B12 in the amounts contained in our energy drink.

Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.[54][55][56][57][58][59]
That's why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit instead. Research shows that these ingredients are not only safe but can also confer several health benefits, including better nutrient absorption, healthy cholesterol and inflammation levels, and more.[60][61][62][63]

No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
As with artificial sweeteners, studies show that artificial food dyes and fillers can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[64][65][66][67][68]
That’s why we use natural coloring and flavoring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for improving texture, enhancing shelf life, and facilitating the manufacturing process.

Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Our energy drink is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA and WADA safety guidelines.[69]
Made in the USA with Globally Sourced Ingredients
If you want to ensure the supplements you’re swallowing every day are safe and effective, you want to buy from a company that:
- Sources ingredients from premium suppliers around the world (great supplements require great raw materials)
- Tests all products for purity and accuracy in accredited laboratories (to conclusively verify safety and efficacy)
- Manufactures in America, which has some of the strictest regulations in the world
And that’s exactly what we do here at Legion.
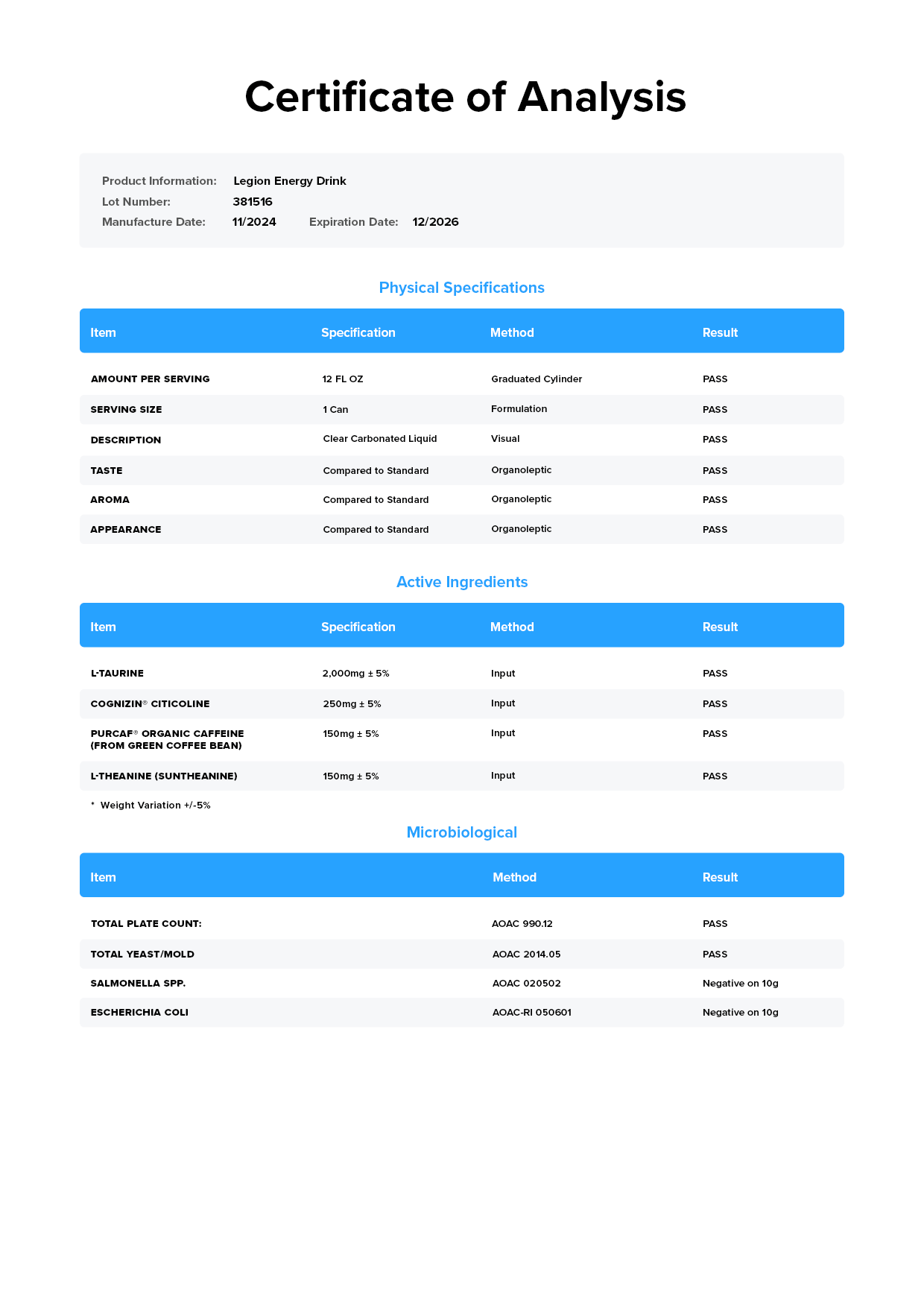
See how Legion energy drinks compare to the rest.
- Active Ingredients
- Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
- Caffeine
- L-Theanine
- Citicoline
- Taurine
- Vitamin B Complex
- Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
- Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Brand
- Price Per Can
-
Legion
Energy Drink
- 3,577 mg
per serving - 150 mg
per serving - 150 mg
per serving - 250 mg
per serving - 2,000 mg
per serving - 27.4 mg
per serving
-
Ghost
Energy
- 2,492 mg
per serving - 200 mg
per serving - 1,000 mg
per serving - 17.7 mg
per serving - $2.50
-
Cellucor C4
Energy Drink
(proprietary blend)- 200 mg
per serving - 36 mg
per serving - $2.33
-
Red Bull
Sugar Free
(proprietary blend)- 114 mg
per serving
(proprietary blend)- 31.85 mg
per serving - $2.13
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in our energy drink is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
Our energy drink is naturally sweetened with stevia and erythritol and naturally flavored with extracts from fruit, vegetables, plants, and other foods.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in our energy drink on the label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Our energy drink is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA and WADA safety guidelines.
Made in the USA
Our energy drink is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love our energy drink, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That's why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, allulose, and monk fruit instead, which are scientifically shown to be safe and can confer several health benefits, including weight management, antioxidant activity, digestive health, and more.↑
404 peer-reviewed scientific studies support our energy drink’s ingredients and doses. That’s 3,232 pages of scientific research that shows our energy drink works the way we say it does.↑
Our energy drink contains the exact ingredients, forms, and doses used in peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.↑
View Supplement Facts↑
View Supplement Facts↑
Our energy drink contains an equal amount of PurCaf® organic caffeine and Suntheanine® L-theanine (150 milligrams of each).
This 1:1 ratio provides a focused, balanced boost in energy, mood, and performance without the negative side effects associated with high-caffeine energy drinks.↑
Our energy drink contains an equal amount of PurCaf® organic caffeine and Suntheanine® L-theanine (150 milligrams of each).
This 1:1 ratio provides a focused, balanced boost in energy, mood, and performance without the negative side effects associated with high-caffeine energy drinks.↑
While artificial sweeteners, food dyes, and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That’s why we use naturally derived alternatives instead like stevia, allulose, monk fruit, and fruit extracts.↑
That’s 3,232 pages of scientific research that shows our energy drink works the way we say it does.↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
Many supplement ingredients lack scientific validation in humans—we aren't large rodents, after all.
And even when ingredients have proven benefits, they're often used in doses too small to be effective.
That's why we exclusively use ingredients and doses shown to work in peer-reviewed scientific studies on healthy men and women.↑
While artificial sweeteners, food dyes, and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That’s why we use naturally derived alternatives instead like stevia, allulose, monk fruit, and fruit extracts.↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
Spriet LL. Sports Med. 2014;44 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S175-S184. doi:10.1007/s40279-014-0257-8.↑
McLellan TM, Caldwell JA, Lieberman HR. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;71:294-312. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.09.001.↑
Crawford C, Teo L, Lafferty L, et al. Nutr Rev. 2017;75(suppl_2):17-35. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nux007.↑
Kamimori GH, McLellan TM, Tate CM, Voss DM, Niro P, Lieberman HR. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015;232(12):2031-2042. doi:10.1007/s00213-014-3834-5.↑
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51(5):759-767. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.5.759.↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1.↑
Warren GL, Park ND, Maresca RD, McKibans KI, Millard-Stafford ML. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(7):1375-1387. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cabbd8.↑
Grgic J, Pickering C. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(3):353-360. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2018.08.016.↑
Grgic J, Trexler ET, Lazinica B, Pedisic Z. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018;15:11. Published 2018 Mar 5. doi:10.1186/s12970-018-0216-0.↑
Grgic J. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018;18(2):219-225. doi:10.1080/17461391.2017.1394371.↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1.↑
Warren GL, Park ND, Maresca RD, McKibans KI, Millard-Stafford ML. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(7):1375-1387. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cabbd8.↑
Polito MD, Souza DB, Casonatto J, Farinatti P. Sci Sports. 2016;31(3):119-128. doi:10.1016/J.SCISPO.2016.01.006.↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1.↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(1):315-324↑
Shen JG, Brooks MB, Cincotta J, Manjourides JD. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(2):232-238. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2018.07.022.↑
Southward K, Rutherfurd-Markwick KJ, Ali A. Sports Med. 2018;48(8):1913-1928. doi:10.1007/s40279-018-0939-8.↑
Desbrow B, Biddulph C, Devlin B, Grant GD, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, Leveritt MD. J Sports Sci. 2012;30(2):115-120. doi:10.1080/02640414.2011.632431.↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(1):315-324. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31818b979a.↑
McLellan TM, Caldwell JA, Lieberman HR. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;71:294-312. doi:10.1016/J.NEUBIOREV.2016.09.001.↑
Guest NS, VanDusseldorp TA, Nelson MT, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1). doi:10.1186/S12970-020-00383-4.↑
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H. Biol Psychol. 2007;74(1):39-45. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.06.006.↑
Rao TP, Ozeki M, Juneja LR. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(5):436-447. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.926153.↑
Bryan J. Nutr Rev. 2008;66(2):82-90. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.00011.x.↑
Einöther SJ, Martens VE, Rycroft JA, De Bruin EA. Appetite. 2010;54(2):406-409. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2010.01.003.↑
Gomez-Ramirez M, Kelly SP, Montesi JL, Foxe JJ. Brain Topogr. 2009;22(1):44-51.↑
Kahathuduwa CN, Dhanasekara CS, Chin SH, et al. Nutr Res. 2018;49:67-78. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2017.11.002.↑
Siamwala JH, Dias PM, Majumder S, et al. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24(3):595-605.↑
McGlade E, Locatelli A, Hardy J, et al. Food Nutr Sci. 2012;3(6):769-773. doi:10.4236/FNS.2012.36103.↑
Alvarez XA, Laredo M, Corzo D, et al. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1997;19(3):201-210.↑
McGlade E, Agoston AM, DiMuzio J, et al. J Atten Disord. 2019;23(2):121-134. doi:10.1177/1087054715593633↑
Spiers PA, Myers D, Hochanadel GS, Lieberman HR, Wurtman RJ. Arch Neurol. 1996;53(5):441-448. doi:10.1001/archneur.1996.00550050071026.↑
Brown ES, Gorman AR, Hynan LS. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2007;27(5):498-502. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e31814db4c4.↑
Alvarez XA, Laredo M, Corzo D, et al. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1997;19(3):201-210.↑
Warburton DM, Bersellini E, Sweeney E. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001;158(3):322-328. doi:10.1007/s002130100884.↑
Seidl R, Peyrl A, Nicham R, Hauser E. Amino Acids. 2000;19(3-4):635-642. doi:10.1007/s007260070013.↑
Schaffer S, Kim HW. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2018;26(3):225-241. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2017.251.↑
Tsuchiya Y, Kawamata K. 2015:164. doi:10.11428/KASEI.67.0_164.↑
Tsuchiya Y, Kawamata K. Anim Sci J. 2017;88(11):1763-1767. doi:10.1111/asj.12829.↑
Stough C, Scholey A, Lloyd J, Spong J, Myers S, Downey LA. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011;26(7):470-476. doi:10.1002/hup.1229.↑
Benton D, Griffiths R, Haller J. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1997;129(1):66-71. doi:10.1007/s002130050163.↑
Walker JG, Batterham PJ, Mackinnon AJ, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(1):194-203. doi:10.3945/ajcn.110.007799.↑
Deijen JB, van der Beek EJ, Orlebeke JF, van den Berg H. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1992;109(4):489-496. doi:10.1007/BF02247729.↑
Skarupski KA, Tangney C, Li H, Ouyang B, Evans DA, Morris MC. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92(2):330-335. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2010.29413.↑
Syed EU, Wasay M, Awan S. Open Neurol J. 2013;7:44-48. Published 2013 Nov 15. doi:10.2174/1874205X01307010044.↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019. ↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every ingredient in a third-party lab for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants, ensuring they meet the strict purity standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and World Anti Doping Agency (WADA).↑