Our "No Return Necessary"
Money-Back Guarantee
If you don’t like something of ours, guess what happens next?
No, we don’t request you deliver it to a PO box in the Gobi Desert by carrier pigeon. Nor do we ask you to fill a cursed inkwell with orc’s blood and demon saliva and then use it to complete reams of return forms written in ancient Cyrillic script.
We just . . . wait for it . . . give you your money back. Holy moo cows. And that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Do you sometimes lack the energy and motivation to get into the gym?
Do you sometimes want to hit the snooze button instead of the squat rack?
Are you sometimes just not able to give 100% in your workouts?
If so, then the Pre-Workout Performance Stack is for you.
It’s two 100% natural supplements that together boost energy, mood, and focus ; enhance strength, power, and endurance ; and reduce stress and fatigue :
- Pulse. Pulse is a 100% natural pre-workout supplement that increases energy levels, improves mood, sharpens mental focus, boosts strength and endurance, and reduces fatigue.
- Stim-Free Pulse. Stim-Free Pulse is a 100% natural stimulant-free pre-workout supplement that boosts strength, power, and endurance, and reduces fatigue.
- Performance Surge. Performance Surge is a 100% natural performance supplement that boosts power, strength, and stamina, and reduces stress and anxiety.
The reason this stack is so effective is simple:
Every ingredient is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research and is included at clinically effective levels .
The Pre-Workout Performance Stack is also naturally sweetened and flavored and contains no artificial food dyes or other chemical junk.
So, if you want some help getting fired up, zeroed in, and ready to crush your workouts . . . you want to try the Pre-Workout Performance Stack today.
You won’t be disappointed.
In fact, if you don’t absolutely love the Pre-Workout Performance Stack, just let us know and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot . No form or return necessary.
You really can’t lose, so order now, and try the Pre-Workout Performance Stack risk free, and see if it’s for you.
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
Reviews
The #1 brand of all-natural sports supplements.
Over 5+ million bottles sold to over 1+ million customers who have left us over 45,000 5-star reviews.
Natural Ingredients
The Pre-Workout Performance Stack doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients”—every ingredient is naturally sourced. We don’t use artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.
Clinically Effective Ingredients & Doses
Every ingredient and dose (important!) in the Pre-Workout Performance Stack is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits.
Naturally Sweetened & Flavored
The Pre-Workout Performance Stack is naturally sweetened and flavored with healthy, plant-based sweeteners and flavors.
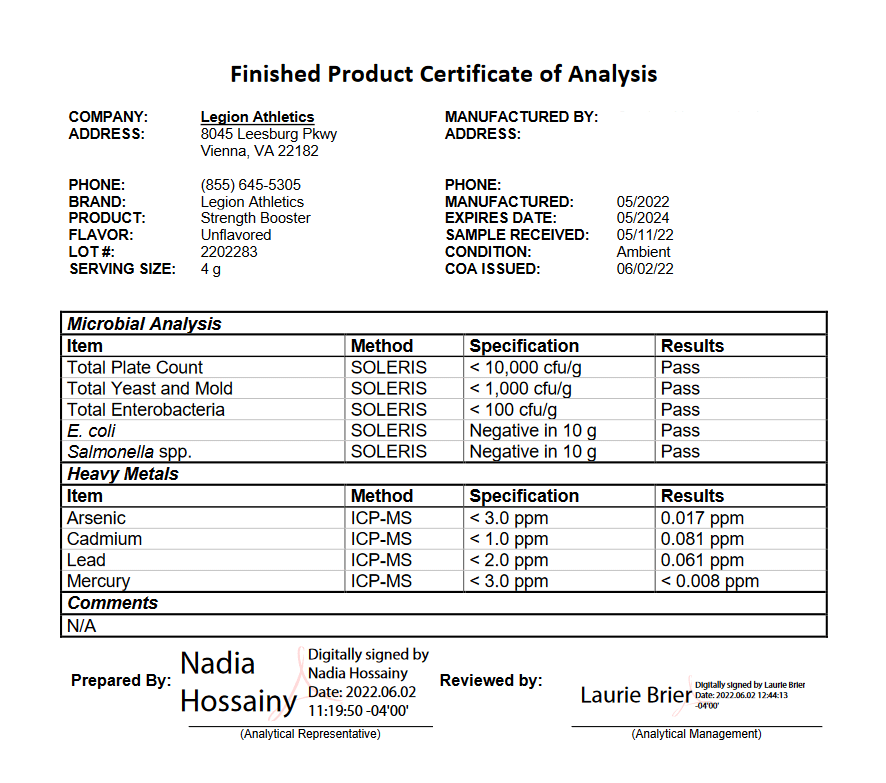
Third-Party Lab Tested
The Pre-Workout Performance Stack is tested by third-party labs for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure it meets FDA purity standards.
Made in the USA
The Pre-Workout Performance Stack is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
"No Return Necessary"
Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love the Pre-Workout Performance Stack, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Ingredients (16.4 grams per serving)
Pulse Pre-Workout
Caffeine (350 milligrams per serving)
Many of us can’t shake the cobwebs without our morning cup of coffee, but this powerful compound is a lot more than a mere pick-me-up.
Caffeine also boosts metabolism, improves strength, promotes muscle endurance, and enhances anaerobic performance.[1][2][3]
The clinically effective dose of caffeine for enhancing performance is between 3 and 6 milligrams per kilogram of body weight.[4]

L-Theanine (350 milligrams per serving)
L-theanine is an amino acid found primarily in tea that’s responsible for some of its health benefits.
It helps balance the levels of two chemicals in the brain known as glutamate and GABA, which transmit nerve impulses.
That’s why research shows that supplementation with L-theanine . . .
- Reduces the effects of mental stress[5]
- Increases the production of nitric oxide, which improves blood flow[6]
- When paired with caffeine, improves mood, memory performance, and attention[7][8][9][10]
The clinically effective dose of L-theanine when combined with caffeine is between a ratio of 1:1 and 2:1 theanine to caffeine, but as 2:1 may produce a calming effect, 1:1 is optimal for working out.

Citrulline Malate (8 grams per serving)
Citrulline malate is the amino acid L-citrulline bound with malic acid, a natural substance found in many fruits that is involved in the creation of cellular energy.
L-citrulline turns into another amino acid in the body known as L-arginine, which increases the production of a gas known as nitric oxide that widens blood vessels and improves blood flow.[11][12]
This is why research shows that supplementation with citrulline malate . . .
- Improves muscle endurance[13][14][15]
- Relieves muscle soreness[16]
- Improves aerobic performance[17][18]
The clinically effective dose of citrulline malate is between 4 and 10 grams.

CarnoSyn® Beta-Alanine (3.6 grams per serving)
Beta-alanine is a naturally occurring amino acid that regulates the amount of the molecule carnosine that can be stored in the muscles.[19]
Carnosine reduces muscle acidity, which increases the amount of work that muscles can do before they become fatigued.[20]
This is why research shows that supplementation with beta-alanine . . .
- Reduces exercise-induced fatigue[21][22][23][24]
- Improves anaerobic exercise capacity[25][26][27][28][29]
- Increases potential workload, which can lead to an increase in lean mass[30][31]
- Reduces feelings of fatigue during exercise[32][33][34]
The clinically effective dose of beta-alanine is between 2.6 and 6.4 grams.
We chose to include 3.6 grams of CarnoSyn® beta-alanine per serving because it provides significant performance benefits while also minimizing the common and harmless side effect of a mild prickling, itching, or tingling of the skin.[35]

AlphaSize® Alpha-GPC (300 milligrams per serving)
Alpha-glycerophosphocholine (also known as alpha-GPC and glycerophosphocholine) is a compound that contains two molecules known as choline and glycerophosphate.
Choline is a nutrient that’s vital for brain health and function, and glycerophosphate is a substance that helps transport choline to the brain.
When ingested, alpha-GPC increases the activity of a chemical in the brain known as acetylcholine, which is used by nerves to communicate with each other, and provides the brain with glycerophosphate, which can improve its health and function.
This is why research shows that supplementation with alpha-GPC . . .
- Increases power output[36]
- Mitigates cognitive decline as we age[37]
- Increases growth hormone levels[38]
The clinically effective dose of alpha-GPC is between 150 and 1,200 milligrams, with 250 to 500 milligrams sufficient for cognitive benefits and higher doses required for affecting dementia.[39]
We chose to include 300 milligrams of AlphaSize® alpha-GPC (50%) per serving because it’s enough to provide some benefit without eating up too much budget that we’d rather spend on other ingredients.
Furthermore, this dose reduces the likelihood of headaches in people who are using Pulse and Forge together, and especially in people who are using Pulse, Forge, and Ascend together.
Betaine (2.5 grams per serving)
Betaine (also known as trimethylglycine) is an amino acid found in various foods like beets (hence the name), spinach, and quinoa.
Betaine’s rich in a special molecule known as a methyl group, which is a vital component of many physiological functions, including DNA production, fat metabolism, cellular energy production, and more.
Betaine’s also an osmolyte, which is a substance that helps balance fluid levels inside and outside cells.
These two properties are beneficial during times of physical stress, and this is why studies show that betaine boosts muscle endurance and increases strength.[40][41]
The clinically effective dose of betaine is between 1.25 and 2.5 grams.

Performance Surge Performance Supplement
KSM-66 Ashwagandha Extract (600 milligrams per serving)
Ashwagandha root extract is a substance derived from a plant root commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. It’s known as an adaptogen, which is a compound that causes an imperceivable level of stress in the body that trains it to better handle future stresses.
Research shows that supplementation with ashwagandha root extract . . .
- Increases power and strength[42]
- Reduces cortisol levels from stress[43][44]
- Lowers feelings of stress and anxiety[45][46][47]
- Helps restore lost fertility in men[48]
- Improves immune system function[49]
- Increases cardiovascular endurance[50]
- Protects against pigments that accumulate during Alzheimer’s disease and is thought to have a therapeutic effect in those with the disease[51][52]
The clinically effective dose of ashwagandha root extract is between 50 and 500 milligrams of the patented KSM-66® brand, with a few instances of over 5,000 milligrams of raw powder being used acutely.

PeakATP® (450 milligrams per serving)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most basic form of cellular energy in the body. It’s obtained through the conversion of carbohydrates and fat, and it fuels the myriad functions and processes that sustain life and activity, including metabolism and muscle contraction.
PeakATP® is a form of ATP obtained from the glucose in corn that’s chemically identical to what our body produces and thus is available for immediate use.
Research shows that supplementation with PeakATP® . . .
- Improves blood flow to muscles during exercise[53]
- Increases muscular endurance[54][55]
- Reduces perceived exertion[56]
The clinically effective dose of PeakATP® is 400 milligrams.

Alpha-GPC 50% (300 milligrams per serving)
Alpha-glycerophosphocholine (also known as alpha-GPC and glycerophosphocholine) is a compound that contains two molecules known as choline and glycerophosphate.
Choline is a nutrient that’s vital for brain health and function, and glycerophosphate is a substance that helps transport choline to the brain.
When ingested, alpha-GPC increases the activity of a chemical in the brain known as acetylcholine, which is used by nerves to communicate with each other, and provides the brain with glycerophosphate, which can improve its health and function.
Research shows supplementation with alpha-GPC . . .
- Increases power output[57]
- Mitigates cognitive decline as we age[58]
- Increases growth hormone levels[59]
The clinically effective dose of alpha-GPC is between 150 and 1,200 milligrams, with 250-to-600 milligrams sufficient for performance and cognitive benefits and higher doses required for affecting dementia.[60]

Ingredients (15.7 grams per serving)
Stim-Free Pulse Pre-Workout
Citrulline Malate (8 grams per serving)
Citrulline malate is the amino acid L-citrulline bound with malic acid, a natural substance found in many fruits that is involved in the creation of cellular energy.
L-citrulline turns into another amino acid in the body known as L-arginine, which increases the production of a gas known as nitric oxide that widens blood vessels and improves blood flow.[1][2]
This is why research shows that supplementation with citrulline malate . . .
The clinically effective dose of citrulline malate is between 4 and 10 grams.

CarnoSyn® Beta-Alanine (3.6 grams per serving)
Beta-alanine is a naturally occurring amino acid that regulates the amount of the molecule carnosine that can be stored in the muscles.[9]
Carnosine reduces muscle acidity, which increases the amount of work that muscles can do before they become fatigued.[10]
This is why research shows that supplementation with beta-alanine . . .
- Reduces exercise-induced fatigue[11][12][13][14]
- Improves anaerobic exercise capacity[15][16][17][18][19]
- Increases potential workload, which can lead to an increase in lean mass[20][21]
- Reduces feelings of fatigue during exercise[22][23][24]
The clinically effective dose of beta-alanine is between 2.6 and 6.4 grams.
We chose to include 3.6 grams of CarnoSyn® beta-alanine per serving because it provides significant performance benefits while also minimizing the common and harmless side effect of a mild prickling, itching, or tingling of the skin.[25]

AlphaSize® Alpha-GPC (300 milligrams per serving)
Alpha-glycerophosphocholine (also known as alpha-GPC and glycerophosphocholine) is a compound that contains two molecules known as choline and glycerophosphate.
Choline is a nutrient that’s vital for brain health and function, and glycerophosphate is a substance that helps transport choline to the brain.
When ingested, alpha-GPC increases the activity of a chemical in the brain known as acetylcholine, which is used by nerves to communicate with each other, and provides the brain with glycerophosphate, which can improve its health and function.
This is why research shows that supplementation with alpha-GPC . . .
- Increases power output[26]
- Mitigates cognitive decline as we age[27]
- Increases growth hormone levels[28]
The clinically effective dose of alpha-GPC is between 150 and 1,200 milligrams, with 250 to 500 milligrams sufficient for cognitive benefits and higher doses required for affecting dementia.[29]
We chose to include 300 milligrams of AlphaSize® alpha-GPC (50%) per serving because it’s enough to provide some benefit without eating up too much budget that we’d rather spend on other ingredients.
Furthermore, this dose reduces the likelihood of headaches in people who are using stim-free Pulse and Forge together, and especially in people who are using stim-free Pulse, Forge, and Ascend together.

Betaine (2.5 grams per serving)
Betaine (also known as trimethylglycine) is an amino acid found in various foods like beets (hence the name), spinach, and quinoa.
Betaine’s rich in a special molecule known as a methyl group, which is a vital component of many physiological functions, including DNA production, fat metabolism, cellular energy production, and more.
Betaine’s also an osmolyte, which is a substance that helps balance fluid levels inside and outside cells.
These two properties are beneficial during times of physical stress, and this is why studies show that betaine boosts muscle endurance and increases strength.[30][31]
The clinically effective dose of betaine is between 1.25 and 2.5 grams.

Performance Surge Performance Supplement
KSM-66 Ashwagandha Extract (600 milligrams per serving)
Ashwagandha root extract is a substance derived from a plant root commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. It’s known as an adaptogen, which is a compound that causes an imperceivable level of stress in the body that trains it to better handle future stresses.
Research shows that supplementation with ashwagandha root extract . . .
- Increases power and strength[32]
- Reduces cortisol levels from stress[33][34]
- Lowers feelings of stress and anxiety[35][36][37]
- Helps restore lost fertility in men[38]
- Improves immune system function[39]
- Increases cardiovascular endurance[40]
- Protects against pigments that accumulate during Alzheimer’s disease and is thought to have a therapeutic effect in those with the disease[41][42]
The clinically effective dose of ashwagandha root extract is between 50 and 500 milligrams of the patented KSM-66® brand, with a few instances of over 5,000 milligrams of raw powder being used acutely.

PeakATP® (450 milligrams per serving)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most basic form of cellular energy in the body. It’s obtained through the conversion of carbohydrates and fat, and it fuels the myriad functions and processes that sustain life and activity, including metabolism and muscle contraction.
PeakATP® is a form of ATP obtained from the glucose in corn that’s chemically identical to what our body produces and thus is available for immediate use.
Research shows that supplementation with PeakATP® . . .
- Improves blood flow to muscles during exercise[43]
- Increases muscular endurance[44][45]
- Reduces perceived exertion[46]
The clinically effective dose of PeakATP® is 400 milligrams.

Alpha-GPC 50% (300 milligrams per serving)
Alpha-glycerophosphocholine (also known as alpha-GPC and glycerophosphocholine) is a compound that contains two molecules known as choline and glycerophosphate.
Choline is a nutrient that’s vital for brain health and function, and glycerophosphate is a substance that helps transport choline to the brain.
When ingested, alpha-GPC increases the activity of a chemical in the brain known as acetylcholine, which is used by nerves to communicate with each other, and provides the brain with glycerophosphate, which can improve its health and function.
Research shows supplementation with alpha-GPC . . .
- Increases power output[47]
- Mitigates cognitive decline as we age[48]
- Increases growth hormone levels[49]
The clinically effective dose of alpha-GPC is between 150 and 1,200 milligrams, with 250-to-600 milligrams sufficient for performance and cognitive benefits and higher doses required for affecting dementia.[50]

No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
As with artificial sweeteners, artificial food dyes aren’t a hazard per se, but studies show they can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[61][62][63][64][65][51][52][53][54][55]
That’s why we use natural coloring derived from fruits and other foods, as well as natural flavoring.
No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk

Third-Party Lab Tested for Potency & Purity
Third-Party Lab Tested for Potency & Purity
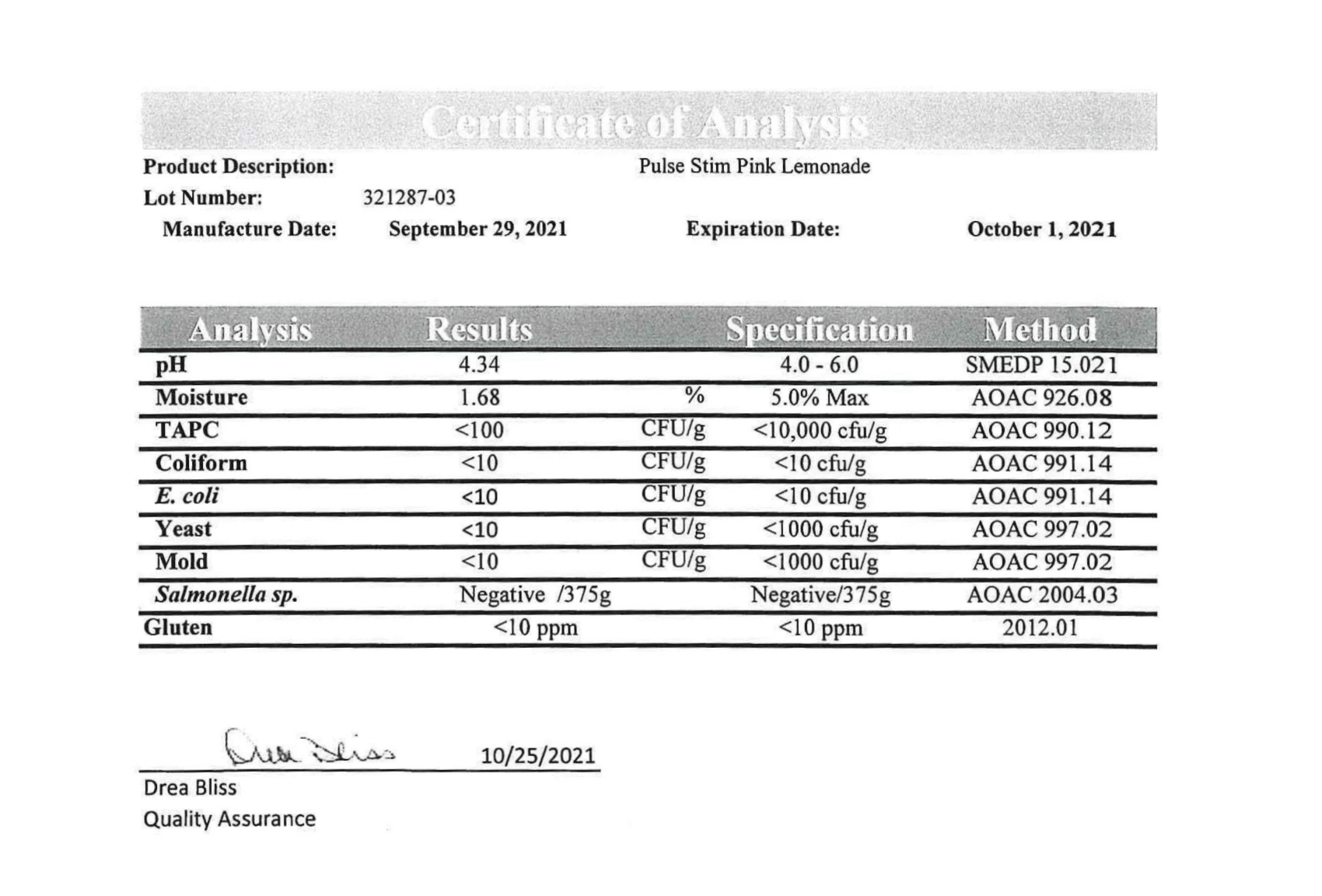
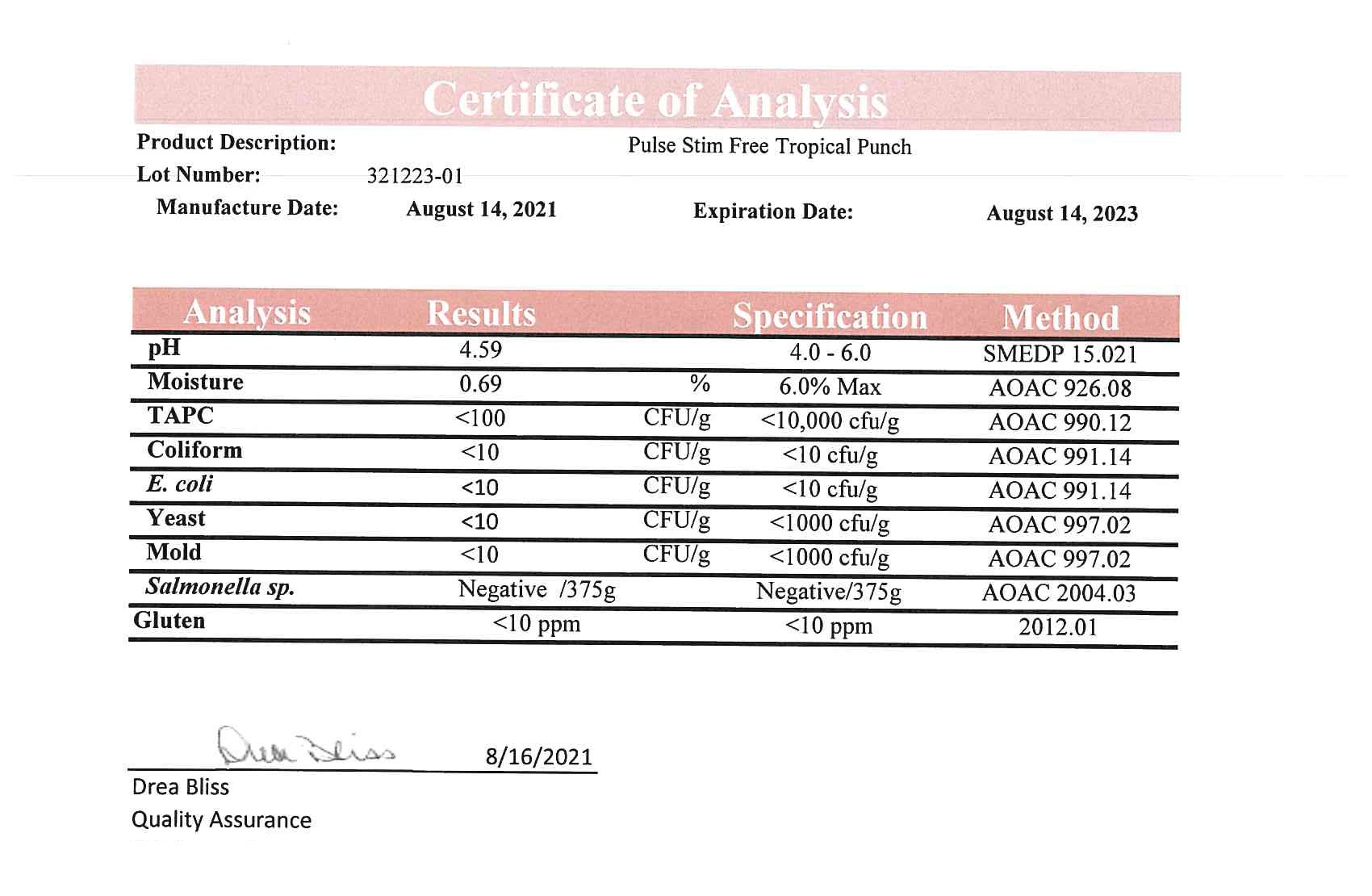
Every bottle of PulseStim-Free Pulse and Performance Surge is analyzed in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab to verify what is and isn’t in it. That way, you know exactly what you’re getting and putting into your body.
How to Use the Pre-Workout Performance Stack
If this is your first time using Pulse, assess your individual tolerance by mixing 1 scoop with 10-12 ounces of water and drinking it 15-30 minutes prior to exercise. If you experience any unwanted effects, stop and consult your doctor.
If 1 scoop is well tolerated and you want the full clinically effective dose of Pulse, including 350 milligrams of caffeine, mix 2 scoops into 10-12 ounces of water, and drink it 15-30 minutes prior to exercise.
As for Performance Surge, mix 1 serving (1 scoop) into 10-12 ounces of water containing ½-to-1 serving of Pulse (1-to-2 scoops), and drink it 15-30 minutes prior to exercise.
Mix 1 serving of Performance Surge (1 scoop) into 10-12 ounces of water containing 1 serving of Stim-Free Pulse (2 scoops), and drink it 15-30 minutes prior to exercise.
Frequently Asked Questions
+Scientific References
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51(5):759-767. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.5.759. ↑
Astorino TA, Rohmann RL, Firth K. Department of Kinesiology, CSU - San Marcos, San Marcos, CA. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008 Jan;102(2):127-32. ↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Coburn JW, Malek MH. Department of Nutrition and Health Sciences, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Nebraska-Lincoln. J Strength Cond Res. 2006 Aug;20(3):506-10. ↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. Department of Kinesiology, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Jan;23(1):315-24. ↑
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H. Nagoya University Department of Psychology, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8601, Japan. Biol Psychol. 2007 Jan;74(1):39-45. ↑
Siamwala JH, Dias PM, Majumder S, Joshi MK, Sinkar VP, Banerjee G, Chatterjee S. Vascular Biology Lab, AU-KBC Research Centre, Anna University, MIT Campus, Chennai, India. J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Mar;24(3):595-605. ↑
Bryan J. School of Psychology, University of South Australia, Adelaide, 5001, South Australia, Australia. Nutr Rev. 2008 Feb;66(2):82-90. ↑
Einöther SJ, Martens VE, Rycroft JA, De Bruin EA. Sensation, Perception & Behaviour, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen, Vlaardingen, The Netherlands. Appetite. 2010 Apr;54(2):406-9. ↑
Gomez-Ramirez M, Kelly SP, Montesi JL, Foxe JJ. Program in Cognitive Neuroscience and Schizophrenia, The Cognitive Neurophysiology Laboratory, Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, Orangeburg, NY, USA. Brain Topogr. 2009 Jun;22(1):44-51. ↑
Kahathuduwa CN, Dhanasekara CS, Chin S-H, et al. Nutr Res. 2018;49:67-78. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2017.11.002.↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, Sinha SR, Bhattacharyya S. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015;12:43. Published 2015 Nov 25. doi:10.1186/s12970-015-0104-9↑
Khan B, Ahmad SF, Bani S, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006;6(9):1394-1403. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2006.04.001↑
Auddy, Biswajit, Jayaram Hazra, and Achintya Mitra. (2008).↑
Andrade C, Aswath A, Chaturvedi SK, Srinivasa M, Raguram R. Indian J Psychiatry. 2000;42(3):295-301.↑
Cooley K, Szczurko O, Perri D, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6628. Published 2009 Aug 31. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006628.↑
Auddy, Biswajit, Jayaram Hazra, and Achintya Mitra. (2008).↑
Ambiye VR, Langade D, Dongre S, Aptikar P, Kulkarni M, Dongre A. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:571420. doi:10.1155/2013/571420.↑
Mikolai J, Erlandsen A, Murison A, et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2009;15(4):423-430. doi:10.1089/acm.2008.0215.↑
Shenoy S, Chaskar U, Sandhu JS, Paadhi MM. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2012;3(4):209-214. doi:10.4103/0975-9476.104444.↑
Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(9):3510-3515. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112209109.↑
Kurapati KRV, Atluri VSR, Samikkannu T, Nair MPN. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77624. doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0077624.↑
Jordan AN, Jurca R, Abraham EH, et al. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(6):983-990. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000128198.97260.8b. ↑
Freitas MC, Cholewa JM, Gerosa-Neto J, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(12):3345-3352. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002198.↑
Dos Santos Nunes de Moura HP, Jäger R, Purpura M, Rathmacher JA, Fuller JC Jr, Rossi FE. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:780459. Published 2021 Dec 8. doi:10.3389/fspor.2021.780459.↑
Dos Santos Nunes de Moura HP, Jäger R, Purpura M, Rathmacher JA, Fuller JC Jr, Rossi FE. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:780459. Published 2021 Dec 8. doi:10.3389/fspor.2021.780459.↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, Sinha SR, Bhattacharyya S. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015;12:43. Published 2015 Nov 25. doi:10.1186/s12970-015-0104-9↑
Khan B, Ahmad SF, Bani S, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006;6(9):1394-1403. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2006.04.001↑
Auddy, Biswajit, Jayaram Hazra, and Achintya Mitra. (2008).↑
Andrade C, Aswath A, Chaturvedi SK, Srinivasa M, Raguram R. Indian J Psychiatry. 2000;42(3):295-301.↑
Cooley K, Szczurko O, Perri D, et al. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6628. Published 2009 Aug 31. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006628.↑
Auddy, Biswajit, Jayaram Hazra, and Achintya Mitra. (2008).↑
Ambiye VR, Langade D, Dongre S, Aptikar P, Kulkarni M, Dongre A. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:571420. doi:10.1155/2013/571420.↑
Mikolai J, Erlandsen A, Murison A, et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2009;15(4):423-430. doi:10.1089/acm.2008.0215.↑
Shenoy S, Chaskar U, Sandhu JS, Paadhi MM. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2012;3(4):209-214. doi:10.4103/0975-9476.104444.↑
Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(9):3510-3515. doi:10.1073/pnas.1112209109.↑
Kurapati KRV, Atluri VSR, Samikkannu T, Nair MPN. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77624. doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0077624.↑
Jordan AN, Jurca R, Abraham EH, et al. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(6):983-990. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000128198.97260.8b. ↑
Freitas MC, Cholewa JM, Gerosa-Neto J, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(12):3345-3352. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002198.↑
Dos Santos Nunes de Moura HP, Jäger R, Purpura M, Rathmacher JA, Fuller JC Jr, Rossi FE. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:780459. Published 2021 Dec 8. doi:10.3389/fspor.2021.780459.↑
Dos Santos Nunes de Moura HP, Jäger R, Purpura M, Rathmacher JA, Fuller JC Jr, Rossi FE. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:780459. Published 2021 Dec 8. doi:10.3389/fspor.2021.780459.↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑









