If you don’t like something of ours, guess what happens next?
No, we don’t request you deliver it to a PO box in the Gobi Desert by carrier pigeon. Nor do we ask you to fill a cursed inkwell with orc’s blood and demon saliva and then use it to complete reams of return forms written in ancient Cyrillic script.
We just . . . wait for it . . . give you every penny of your money back. Holy moo cows. And that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Can Liposomal Vitamin C bulletproof your immune system and detoxify your body?
No.
Can it supercharge your energy levels, collagen production, and post-workout recovery?
Absolutely not.
But can it support your immune function, antioxidant protection, and metabolic health?
And without the upset stomachs or loose bowels?
Yes. Or your money back.
And how can Liposomal Vitamin C do these things?
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in numerous bodily processes, including neurotransmitter production, collagen formation, antioxidant activity, immune function, wound healing, and iron absorption.
Despite the importance of vitamin C, however, research shows that nearly half of Americans aren’t getting enough to meet even the Estimated Average Requirement, which is the amount required to meet the needs of only half the healthy individuals (with the other half requiring even more).[7]
Additionally, studies show that people who are overweight may need significantly more vitamin C than people at a healthy body weight.[8] Thus, with nearly 74% of Americans being overweight or obese, vitamin C insufficiency may be far more prevalent and severe than experts realize.[9]
These “subclinical deficiencies” are serious, too—they’re associated with an increased risk of numerous health problems.[10][11][12][13][14]
What’s more, while it’s easy to get enough vitamin C through your diet to meet the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of between 75 and 90 milligrams per day and prevent a deficiency, research suggests that this may not produce optimal health and longevity, especially for active people, which should be the ultimate goal.[15]
Therefore, if you want to maintain an intake of at least several hundred milligrams of vitamin C per day, this can be difficult to do through diet alone because . . .
- It requires eating several servings per day of foods that many people don’t eat, including citrus fruits, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, broccoli, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, and cantaloupe.
- Fruit and vegetables often contain less vitamin C than they did in the past.[16]
- Processing can remove up to 50% of the vitamin C from foods.[17]
This is why many health-conscious people who eat a nutritious diet also choose to supplement with vitamin C, and many choose liposomal vitamin C in particular for its superior absorption.
So order now, try Liposomal Vitamin C risk-free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect vitamin C supplement.
Can Liposomal Vitamin C bulletproof your immune system and detoxify your body?
No.
Can it supercharge your energy levels, collagen production, and post-workout recovery?
Absolutely not.
But can it support your immune function, antioxidant protection, and metabolic health?
And without the upset stomachs or loose bowels?
Yes. Or your money back.
And how can Liposomal Vitamin C do these things?
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in numerous bodily processes, including neurotransmitter production, collagen formation, antioxidant activity, immune function, wound healing, and iron absorption.
Despite the importance of vitamin C, however, research shows that nearly half of Americans aren’t getting enough to meet even the Estimated Average Requirement, which is the amount required to meet the needs of only half the healthy individuals (with the other half requiring even more).[1]
Additionally, studies show that people who are overweight may need significantly more vitamin C than people at a healthy body weight.[2] Thus, with nearly 74% of Americans being overweight or obese, vitamin C insufficiency may be far more prevalent and severe than experts realize.[3]
These “subclinical deficiencies” are serious, too—they’re associated with an increased risk of numerous health problems.[4][5][6][7][8]
What’s more, while it’s easy to get enough vitamin C through your diet to meet the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of between 75 and 90 milligrams per day and prevent a deficiency, research suggests that this may not produce optimal health and longevity, especially for active people, which should be the ultimate goal.[9]
Therefore, if you want to maintain an intake of at least several hundred milligrams of vitamin C per day, this can be difficult to do through diet alone because . . .
- It requires eating several servings per day of foods that many people don’t eat, including citrus fruits, potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, broccoli, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, and cantaloupe.
- Fruit and vegetables often contain less vitamin C than they did in the past.[10]
- Processing can remove up to 50% of the vitamin C from foods.[11]
This is why many health-conscious people who eat a nutritious diet also choose to supplement with vitamin C, and many choose liposomal vitamin C in particular for its superior absorption.
- 20 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Liposomal Vitamin C’s form and dose[12]
- Contains no artificial fillers, food dyes, or other chemical junk[13]
- Tested for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[14]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[15]
- Made in the USA in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
Liposomal Vitamin C is also backed by our 100% Money-Back Guarantee that works like this:
If you don’t absolutely love Liposomal Vitamin C, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try Liposomal Vitamin C risk-free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect vitamin C supplement.
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
Legion Liposomal Vitamin C Ingredient (500 milligrams per serving)
Liposomal PureWay-C® Vitamin C (500 milligrams per serving)
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that helps support the immune system, promotes healthy skin, and aids in the repair of body tissues. It's also an antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
Liposomal PureWay-C® vitamin C is a patented form of vitamin C that has been encased in liposomes, which are microscopic spheres made of phospholipids (molecules that consist primarily of glycerol and fatty acids).
Encasing the vitamin C in liposomes greatly increases its bioavailability, which is why Liposomal PureWay-C® vitamin C is better absorbed by the body than other common forms on the market like ascorbic acid, buffered vitamin C, and even “natural” sources like acerola cherry extract or rosehip powder.[15][16][17][18][19][20]
This is also why you can get greater benefits with smaller doses of PureWay-C® vitamin C, which helps prevent the gastrointestinal problems associated with taking larger amounts of other forms of vitamin C.
Research shows that supplementation with Liposomal PureWay-C® vitamin C . . .
- Supports immune function[21]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[22]
- Supports metabolic health[23][24][25]
- Increases iron absorption[26][27]
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is 90 milligrams per day for adult men and 75 milligrams per day for women who aren’t pregnant or breastfeeding. That said, research suggests that this may not produce optimal health and longevity, especially for active people, which should be the ultimate goal.[28]
No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
Artificial food dyes and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, but studies show they can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[29][30][31][32][33]
That’s why we use natural coloring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for enhancing shelf life and facilitating the manufacturing process.

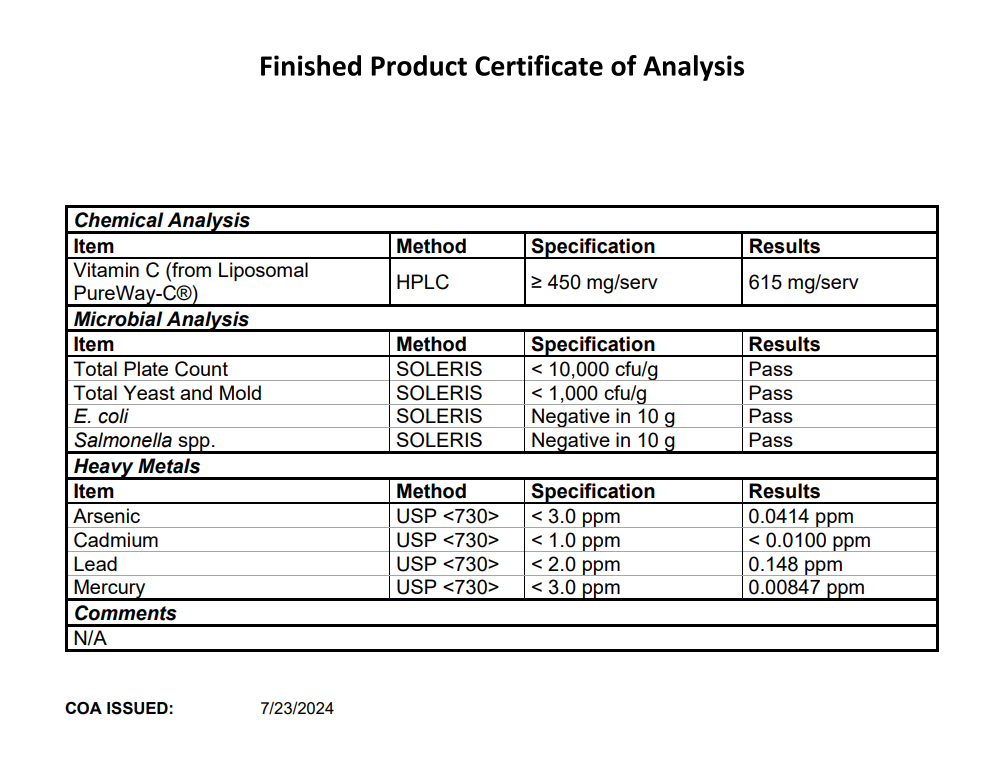
Third-Party Lab Tested for Potency & Purity
Liposomal Vitamin C is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
See how Legion Liposomal Vitamin C compares to the rest.
- Active Ingredient
Per Serving - Clinically Effective Ingredient
& Dose - Liposomal
PureWay-C® Vitamin C - Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Brand
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion
Liposomal Vitamin C
- 500 mg
per serving - 500 mg
per serving - $
-
GNC
Vitamin C
- 1000 mg
per serving - $0.11
-
NOW Foods
Vitamin C
- 500 mg
per serving - $0.09
-
Nature Made
Vitamin C
- 1000 mg
per serving - $0.16
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredient and Dose
The active ingredient, form, and dose in Liposomal Vitamin C is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
No Unnecessary Junk
Liposomal Vitamin C contains no artificial food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in Liposomal Vitamin C on the label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Third-Party Lab Tested for Purity and Potency
Liposomal Vitamin C is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
Made in the USA
Liposomal Vitamin C is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love Liposomal Vitamin C, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Brauchla M, Dekker MJ, Rehm CD. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):420. Published 2021 Jan 28. doi:10.3390/nu13020420. ↑
Carr AC, Block G, Lykkesfeldt J. Nutrients. 2022;14(7):1460. Published 2022 Mar 31. doi:10.3390/nu14071460.↑
Ogden CL, Fryar CD, Martin CB, et al. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2021;324(12):1208-1210. doi:10.1001/JAMA.2020.14590.↑
Bechara N, Flood VM, Gunton JE. 2022;11(8):1605. Published 2022 Aug 19. doi:10.3390/antiox11081605. ↑
Loria CM, Klag MJ, Caulfield LE, Whelton PK. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(1):139-145. doi:10.1093/AJCN/72.1.139.↑
Carr AC, Frei B. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69(6):1086-1107. doi:10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1086. ↑
Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G. Nutr Clin Care. 2002;5(2):66-74. doi:10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x.↑
Knekt P, Ritz J, Pereira MA, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(6):1508-1520. doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1508. ↑
Hemilä H, Chalker E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(1):CD000980. Published 2013 Jan 31. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4. ↑
Davis DR, Epp MD, Riordan HD. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004;23(6):669-682. doi:10.1080/07315724.2004.10719409. ↑
Mieszczakowska-Frąc M, Celejewska K, Płocharski W. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(1):54. Published 2021 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/antiox10010054. ↑
That’s 315 pages of scientific research that shows Liposomal Vitamin C works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Liposomal Vitamin C.↑
Every bottle of Liposomal Vitamin C is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Liposomal Vitamin C—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Liposomal Vitamin C is naturally sourced from plants and animals and contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
Every serving of Liposomal Vitamin C contains 500 milligrams of vitamin C that has been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
The active ingredient in Liposomal Vitamin C is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
That’s 315 pages of scientific research that shows Liposomal Vitamin C works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Liposomal Vitamin C. ↑
Every bottle of Liposomal Vitamin C is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
Brauchla M, Dekker MJ, Rehm CD. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):420. Published 2021 Jan 28. doi:10.3390/nu13020420. ↑
Carr AC, Block G, Lykkesfeldt J. Nutrients. 2022;14(7):1460. Published 2022 Mar 31. doi:10.3390/nu14071460.↑
Ogden CL, Fryar CD, Martin CB, et al. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2021;324(12):1208-1210. doi:10.1001/JAMA.2020.14590.↑
Bechara N, Flood VM, Gunton JE. 2022;11(8):1605. Published 2022 Aug 19. doi:10.3390/antiox11081605. ↑
Loria CM, Klag MJ, Caulfield LE, Whelton PK. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(1):139-145. doi:10.1093/AJCN/72.1.139.↑
Carr AC, Frei B. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69(6):1086-1107. doi:10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1086. ↑
Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G. Nutr Clin Care. 2002;5(2):66-74. doi:10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x.↑
Knekt P, Ritz J, Pereira MA, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(6):1508-1520. doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1508. ↑
Hemilä H, Chalker E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(1):CD000980. Published 2013 Jan 31. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4. ↑
Davis DR, Epp MD, Riordan HD. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004;23(6):669-682. doi:10.1080/07315724.2004.10719409. ↑
Mieszczakowska-Frąc M, Celejewska K, Płocharski W. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(1):54. Published 2021 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/antiox10010054. ↑
Tinsley GM, Harty PS, Stratton MT, Siedler MR, Rodriguez C. Nutrients. 2022;14(16):3321. Published 2022 Aug 13. doi:10.3390/nu14163321.↑
Wen CJ, Chiang CF, Lee CS, Lin YH, Tsai JS. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2022;18(3):922-927. doi:10.1166/jbn.2022.3274.↑
Ko J, Yoo C, Xing D, et al. Nutrients. 2023;15(13):3073. Published 2023 Jul 7. doi:10.3390/nu15133073.↑
Davis JL, Paris HL, Beals JW, et al. Nutr Metab Insights. 2016;9:25-30. Published 2016 Jun 20. doi:10.4137/NMI.S39764.↑
Łukawski M, Dałek P, Borowik T, et al. J Liposome Res. 2020;30(3):227-234. doi:10.1080/08982104.2019.1630642.↑
Gopi S, Balakrishnan P. J Liposome Res. 2021;31(4):356-364. doi:10.1080/08982104.2020.1820521.↑
National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. 2023. Accessed March 16, 2024.↑
Weeks BS, Lee S, Perez PP, Brown K, Chauhan H, Tsaava T. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14(12):BR279-BR285.↑
National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. 2023. Accessed March 16, 2024.↑
Carr AC, Frei B. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69(6):1086-1107. doi:10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1086. ↑
Jacob RA, Sotoudeh G. Nutr Clin Care. 2002;5(2):66-74. doi:10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x.↑
National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. 2023. Accessed March 16, 2024.↑
Lynch SR, Cook JD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;355:32-44. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21325.x.↑
Hemilä H, Chalker E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(1):CD000980. Published 2013 Jan 31. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4.↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8.↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7.↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9.↑
























