Our "No Return Necessary"
Money-Back Guarantee
If you don’t like something of ours, guess what happens next?
No, we don’t request you deliver it to a PO box in the Gobi Desert by carrier pigeon. Nor do we ask you to fill a cursed inkwell with orc’s blood and demon saliva and then use it to complete reams of return forms written in ancient Cyrillic script.
We just . . . wait for it . . . give you your money back. Holy moo cows. And that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Will The Muscle Growth Stack help you pack on brain-shrinking amounts of muscle in 30 days flat?
No.
Will it add another plate or two to the bar?
Absolutely not.
But will it help you train harder, recover faster, and gain more muscle and strength?
Yes. Or your money back.
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[8]
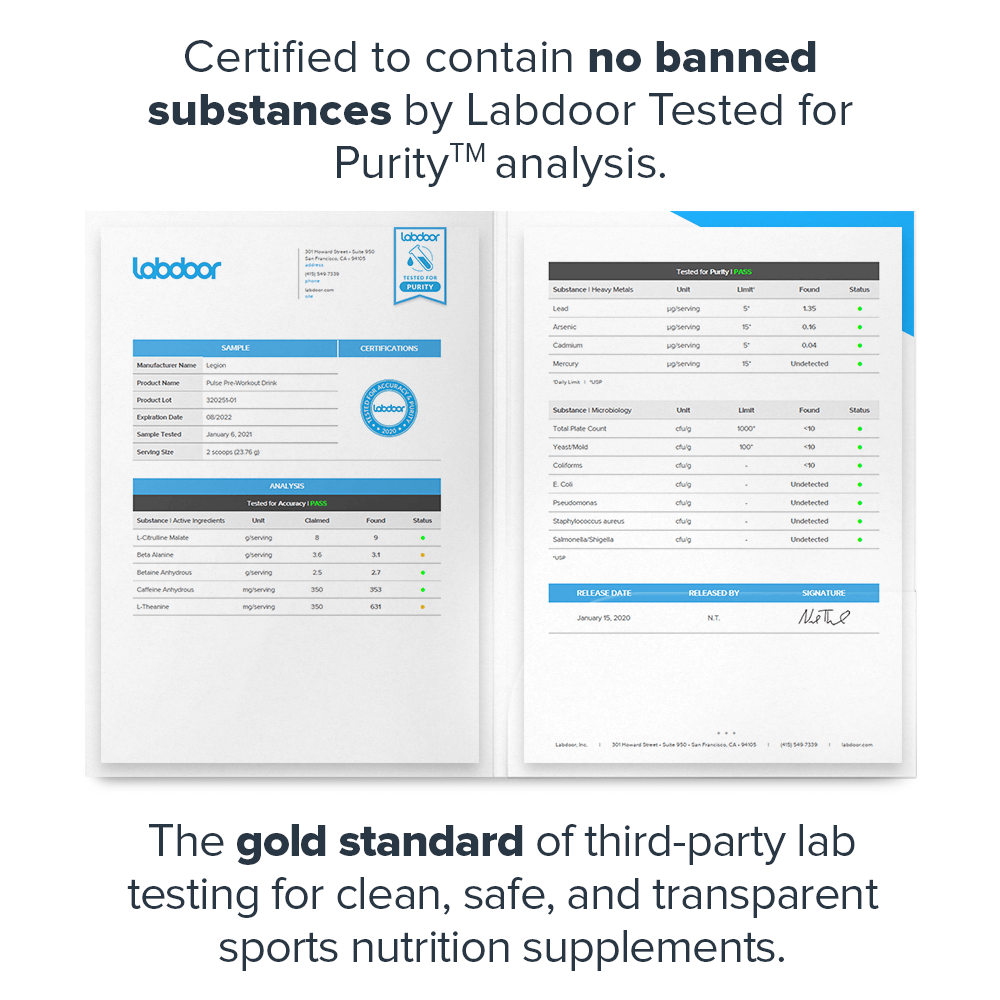
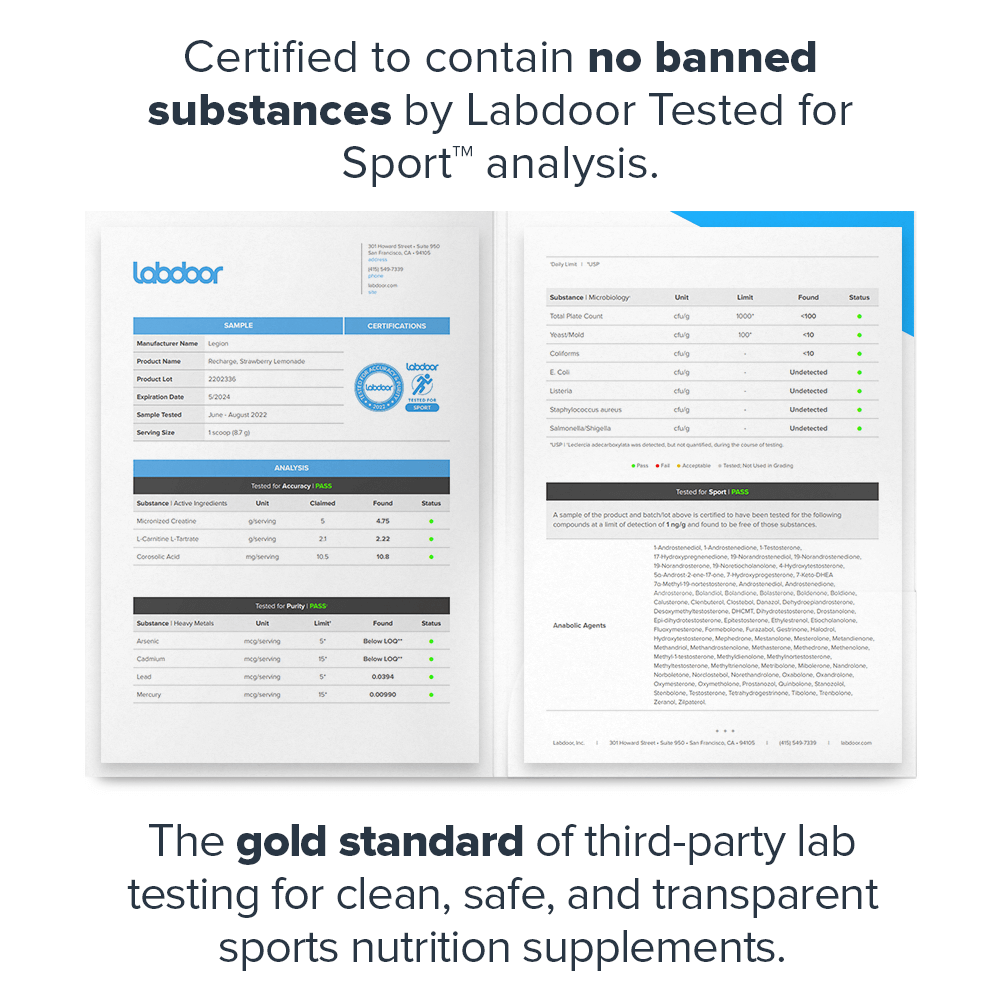
- Certified to contain no banned substances by Labdoor™, the gold standard of third-party lab testing[9]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
The Muscle Growth Stack is also backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this:
If you don’t absolutely love The Muscle Growth Stack, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try The Muscle Growth Stack risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect mix of all-natural muscle building supplements (that have sold over 2,000,000 bottles and counting!).
Will The Muscle Growth Stack help you pack on brain-shrinking amounts of muscle in 30 days flat?
No.
Will it add another plate or two to the bar?
Absolutely not.
But will it help you train harder, recover faster, and gain more muscle and strength?
Yes. Or your money back.
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[8]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
- Backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this: If you don’t absolutely love The Muscle Growth Stack, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try The Muscle Growth Stack risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect mix of all-natural muscle building supplements (that have sold over 2,000,000 bottles and counting!).
Will The Muscle Growth Stack help you pack on brain-shrinking amounts of muscle in 30 days flat?
No.
Will it add another plate or two to the bar?
Absolutely not.
But will it help you train harder, recover faster, and gain more muscle and strength?
Yes. Or your money back.
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[8]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
- Backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this: If you don’t absolutely love The Muscle Growth Stack, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try The Muscle Growth Stack risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect mix of all-natural muscle building supplements (that have sold over 2,000,000 bottles and counting!).
Will The Muscle Growth Stack help you pack on brain-shrinking amounts of muscle in 30 days flat?
No.
Will it add another plate or two to the bar?
Absolutely not.
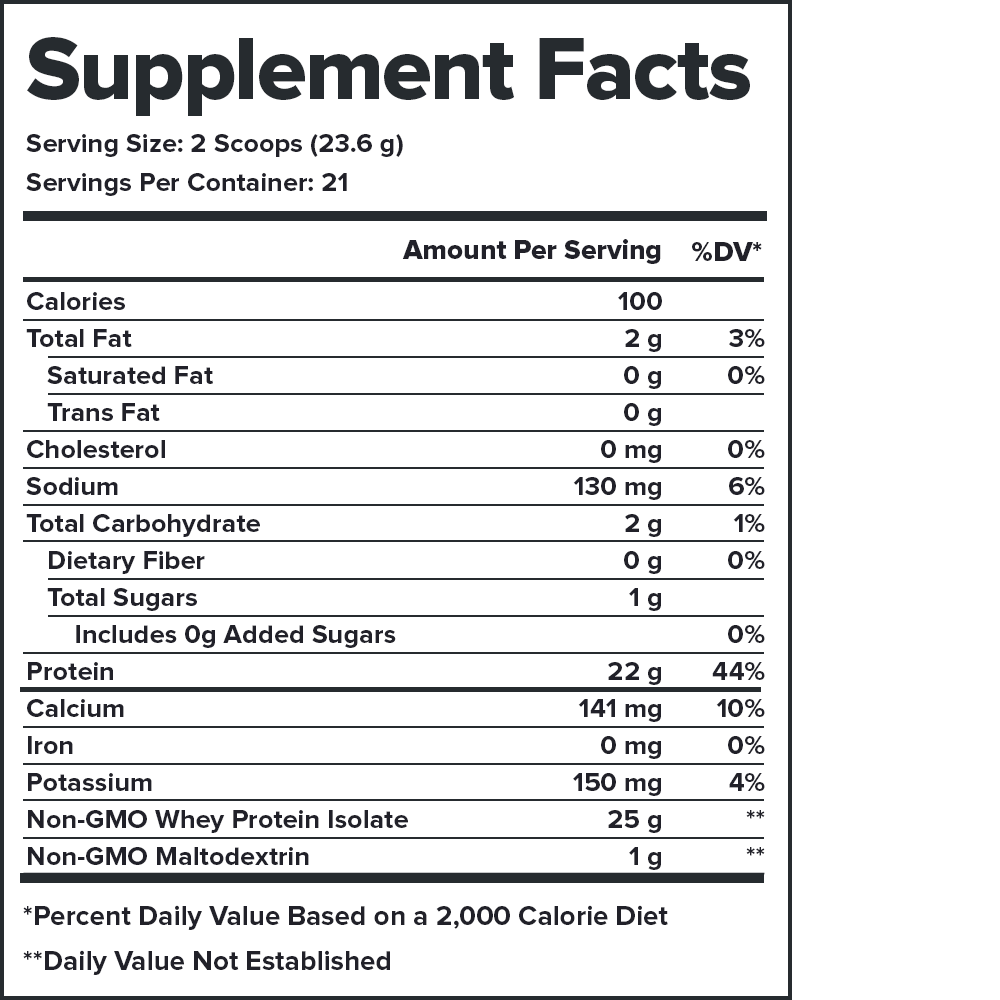
But is the Muscle Growth Stack the only[1] natural[2] sports supplement stack with clinically effective doses[3] of ten ingredients scientifically shown[4] to improve energy levels, focus, strength, endurance, and recovery and reduce fatigue and muscle soreness?
And will it help you train harder, recover faster, and gain more muscle and strength?
Yes. Or your money back.
- 837483748677 peer-reviewed scientific studies support The Muscle Growth Stack’s combination of ingredients and doses[5]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[6]
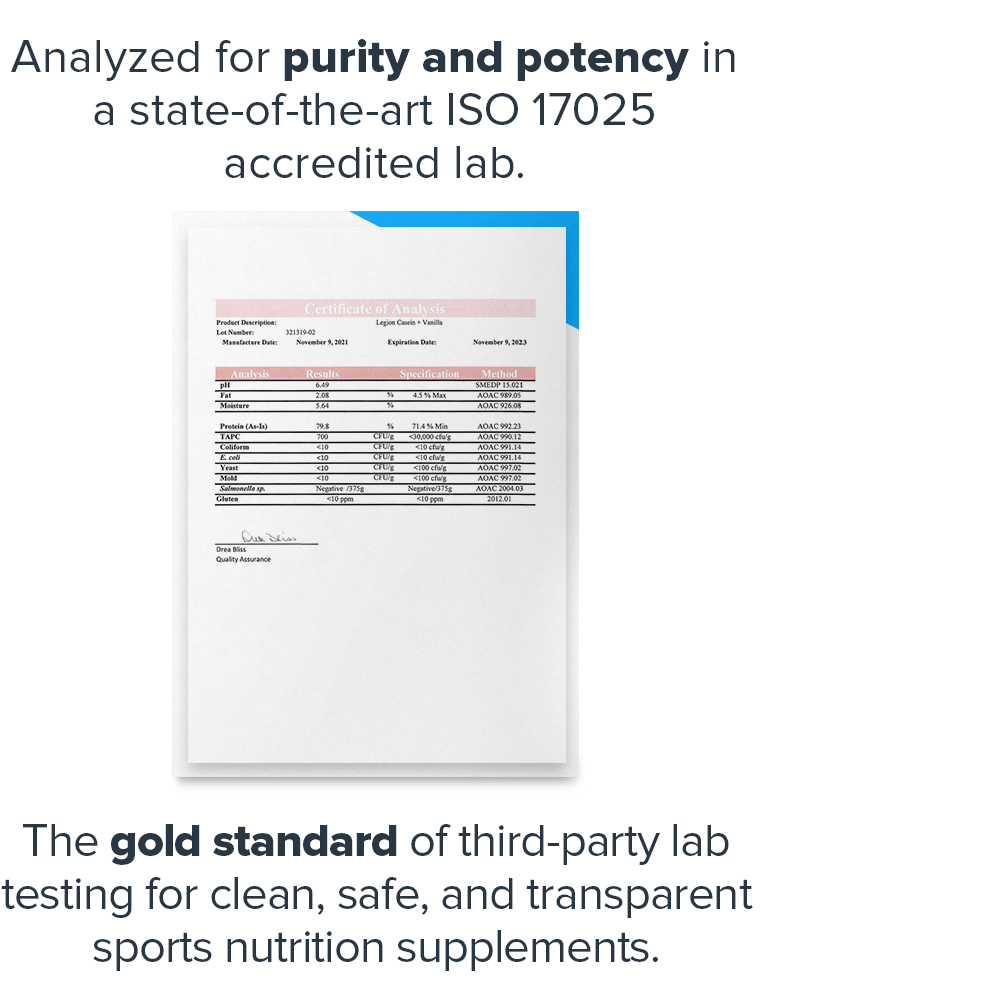
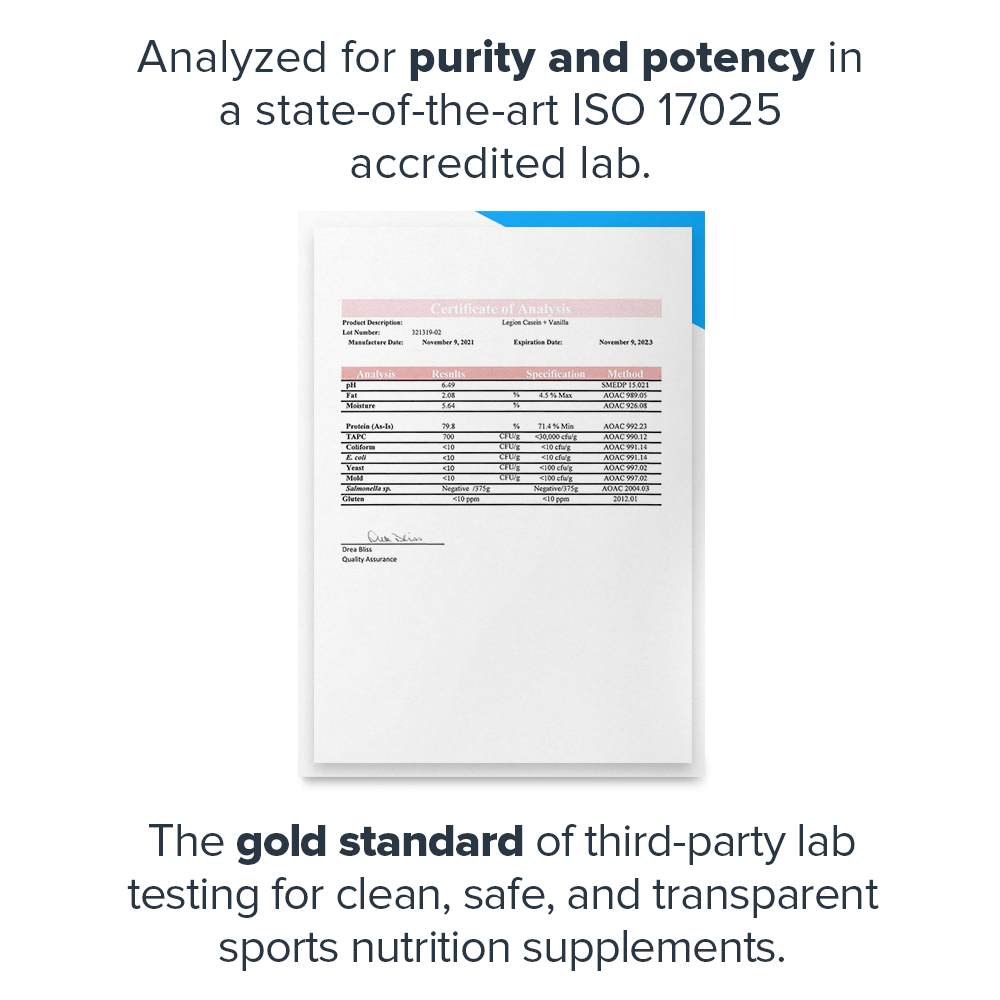
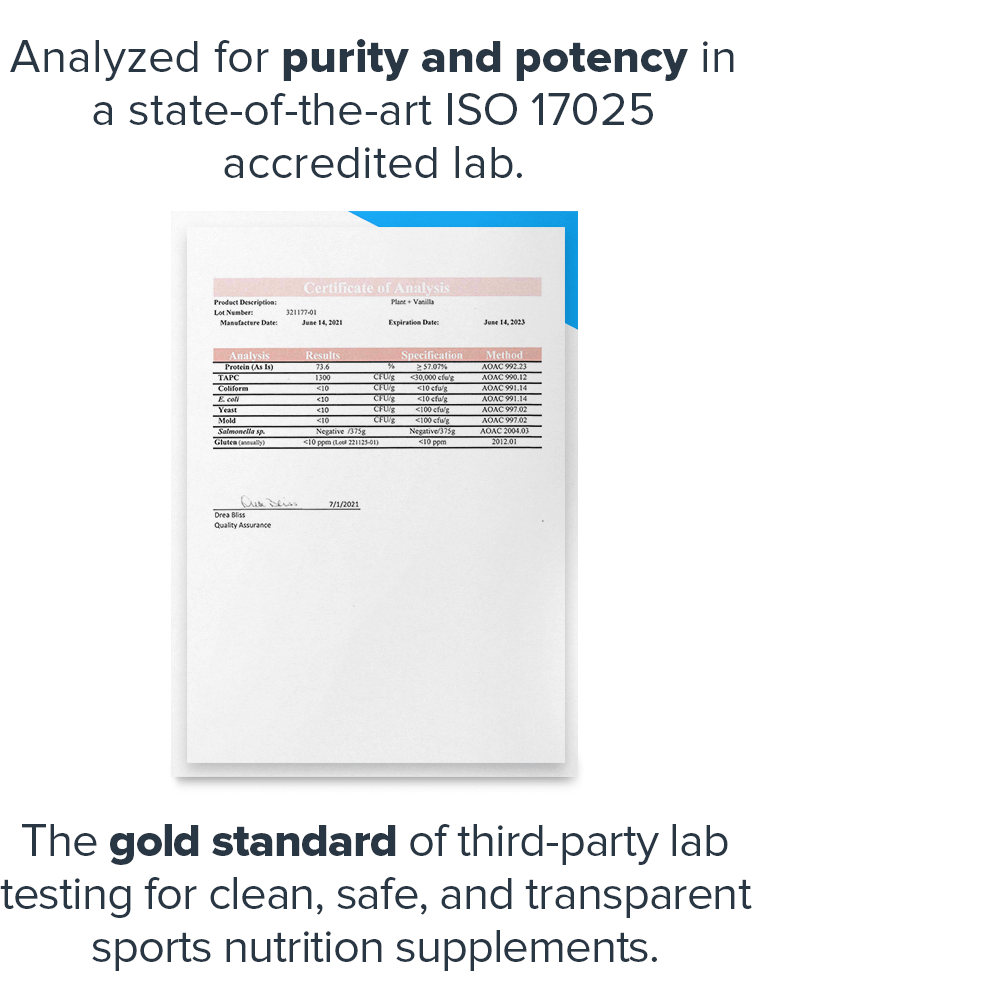
- Analyzed for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[7]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[8]
- Certified to contain no banned substances by Labdoor™, the gold standard of third-party lab testing[9]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
The Muscle Growth Stack is also backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this:
If you don’t absolutely love The Muscle Growth Stack, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try The Muscle Growth Stack risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect mix of all-natural muscle building supplements (that have sold over 2,000,000 bottles and counting!).
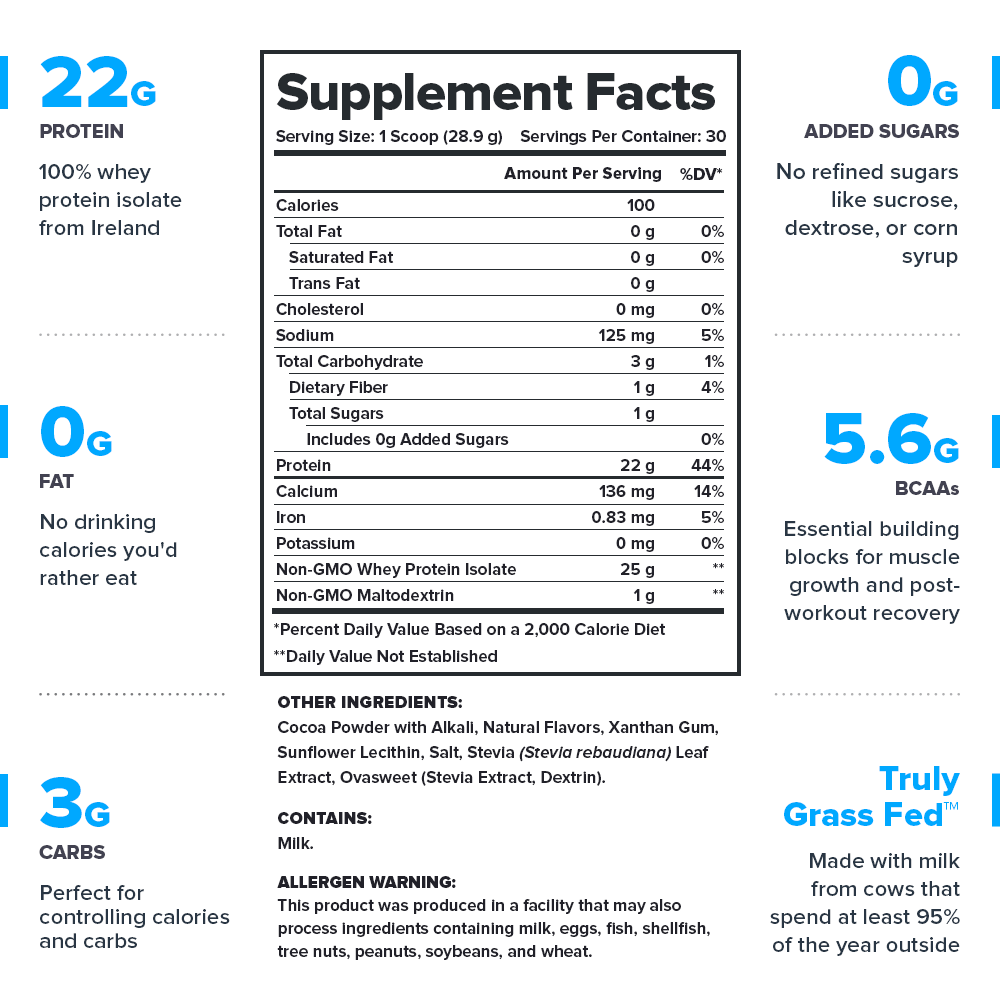
Get the only[10] 100% natural[11] whey protein isolate powder[12] made with Truly Grass Fed™ milk[13] from small dairy farms in Ireland renowned for their superior and sustainable farming practices.[14]
- 15 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Whey+’s ingredients[15]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[16]
- Analyzed for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[17]
- Made with pure Truly Grass Fed™ milk from hormone- and antibiotic-free cows that live the way nature intended—outside, roaming and grazing on grass[18]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[19]
- Certified to contain no banned substances by Labdoor™, the gold standard of third-party lab testing[20]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
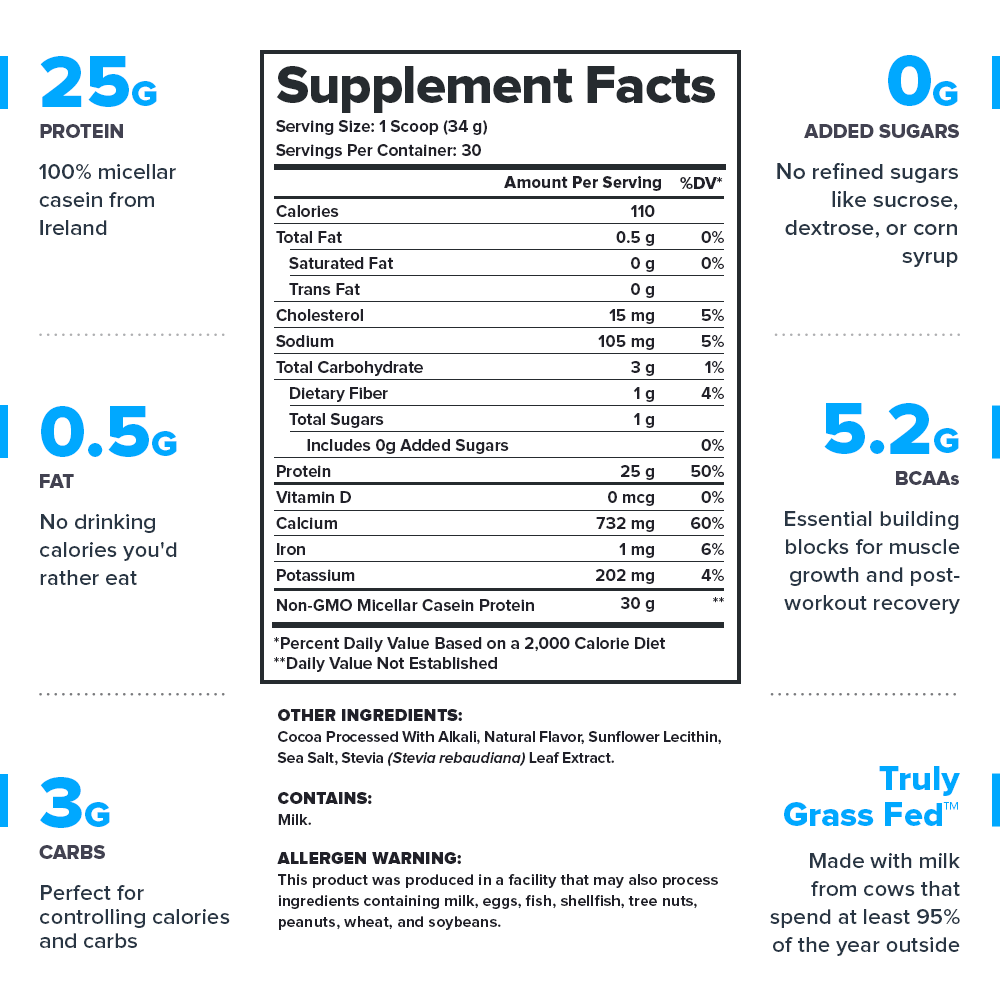
Get the only[null] 100% natural[null] micellar casein powder[null] made with Truly Grass Fed™[null] milk from small dairy farms in Ireland renowned for their healthy and sustainable farming practices.[null]
- 15 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Casein+’s ingredients[null]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[null]
- Analyzed for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[null]
- Made with pure Truly Grass Fed™ milk from hormone- and antibiotic-free cows that live the way nature intended—outside, roaming and grazing on grass[null]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[null]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
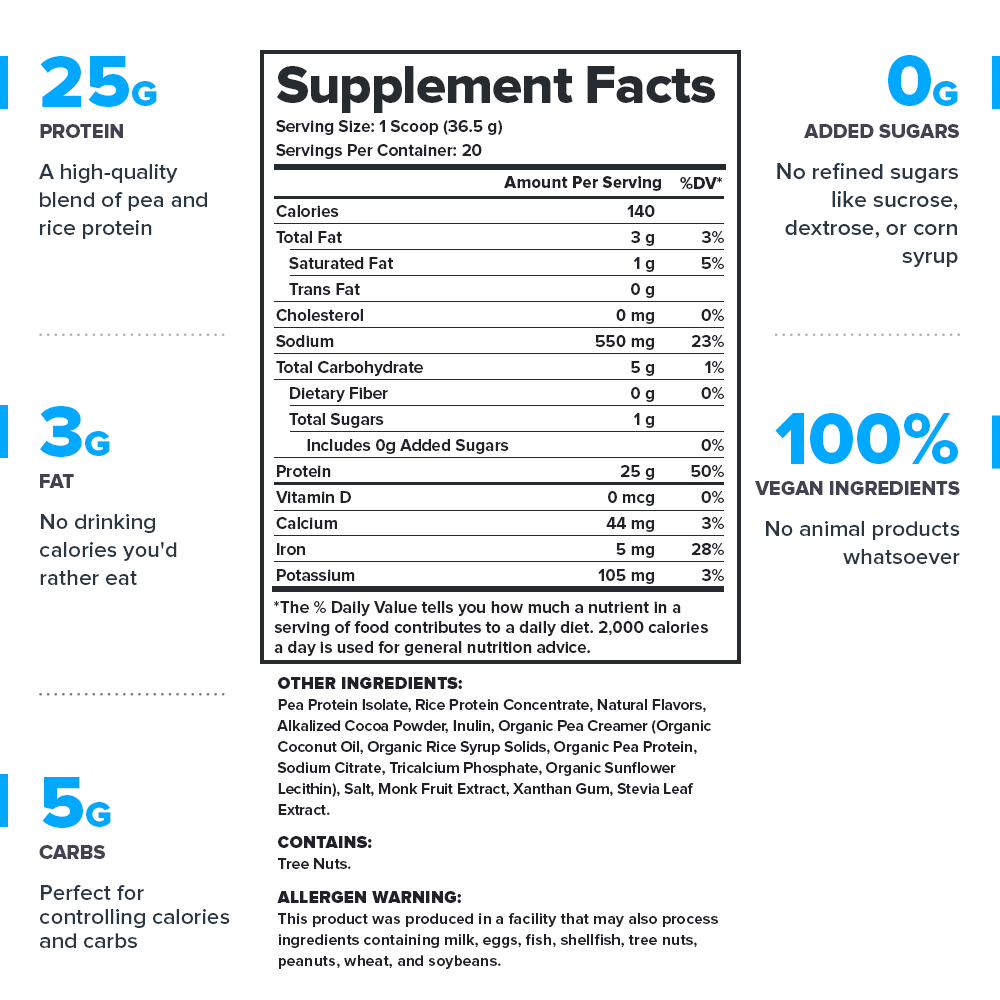
Get our 100% natural[null] and vegan-friendly plant-based protein powder with a premium blend of rice and pea protein[null] and no animal-derived ingredients or added sugars.
- 18 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Plant+’s ingredients[null]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[null]
- Analyzed for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[null]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[null]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
- Backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this: If you don’t absolutely love Plant+, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
Pulse Pre-Workout
Pulse Stim-Free Pre-Workout
Recharge Post-Workout
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
See how Legion compares to the rest.
- Protein Per Serving
- Calories Per Serving
- 100% Whey Protein Isolate
- Certified Truly
Grass-Fed™ - No Added Sugars
- Natural Ingredients
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Ranking
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion Whey+
Protein Powder
- 21–23 g
- 100–130
- A
- $1.601.60
-
Gold Standard
100% Whey - 24 g
- 110–130
- C
- $1.21
-
Pro JYM
Protein Blend - 24 g
- 140–170
- $1.40
-
PEScience
Select Protein - 23–24 g
- 120
- $1.30
- Protein Per Serving
- Calories Per Serving
- 100% Micellar Casein Protein
- Certified Truly
Grass-Fed™ - No Added Sugars
- Natural Ingredients
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor
Certified Brand - Price Per Serving
-
Legion Casein+
Protein Powder
- 25–26 g
- 110–140
- $1.601.60
-
Gold Standard
100% Casein
- 24 g
- 120
- $1.44
-
Pro JYM
Protein Blend
- 24 g
- 140–170
- $1.40
-
PEScience
Select Protein
- 23–24 g
- 120
- $1.30
- Protein Per Serving
- Calories Per Serving
- Pea & Rice Protein
- No Added Sugars
- Natural Ingredients
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Brand
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion
Plant+
- 24–25 g
- 130–140
- $2.002.00
-
Vega
Protein
- 15 g
- 100
- $1.20
-
Plant
Jym
- 24 g
- 140
- $1.67
-
PEScience Select
Plant Protein
- 20 g
- 100–130
-
- $1.48
The #1 brand of all-natural sports supplements.
Over 4,000,000 bottles sold to over 800,000 customers who have left us over 45,000 5-star reviews.
Natural Ingredients
The Muscle Growth Stack doesn't just “contain natural ingredients”—every ingredient is naturally sourced. We don’t use artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.
Clinically Effective Ingredients & Doses
Every ingredient and dose (important!) in The Muscle Growth Stack is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits.
Naturally Sweetened & Flavored
The Muscle Growth Stack is naturally sweetened and flavored with healthy, plant-based sweeteners and flavors.
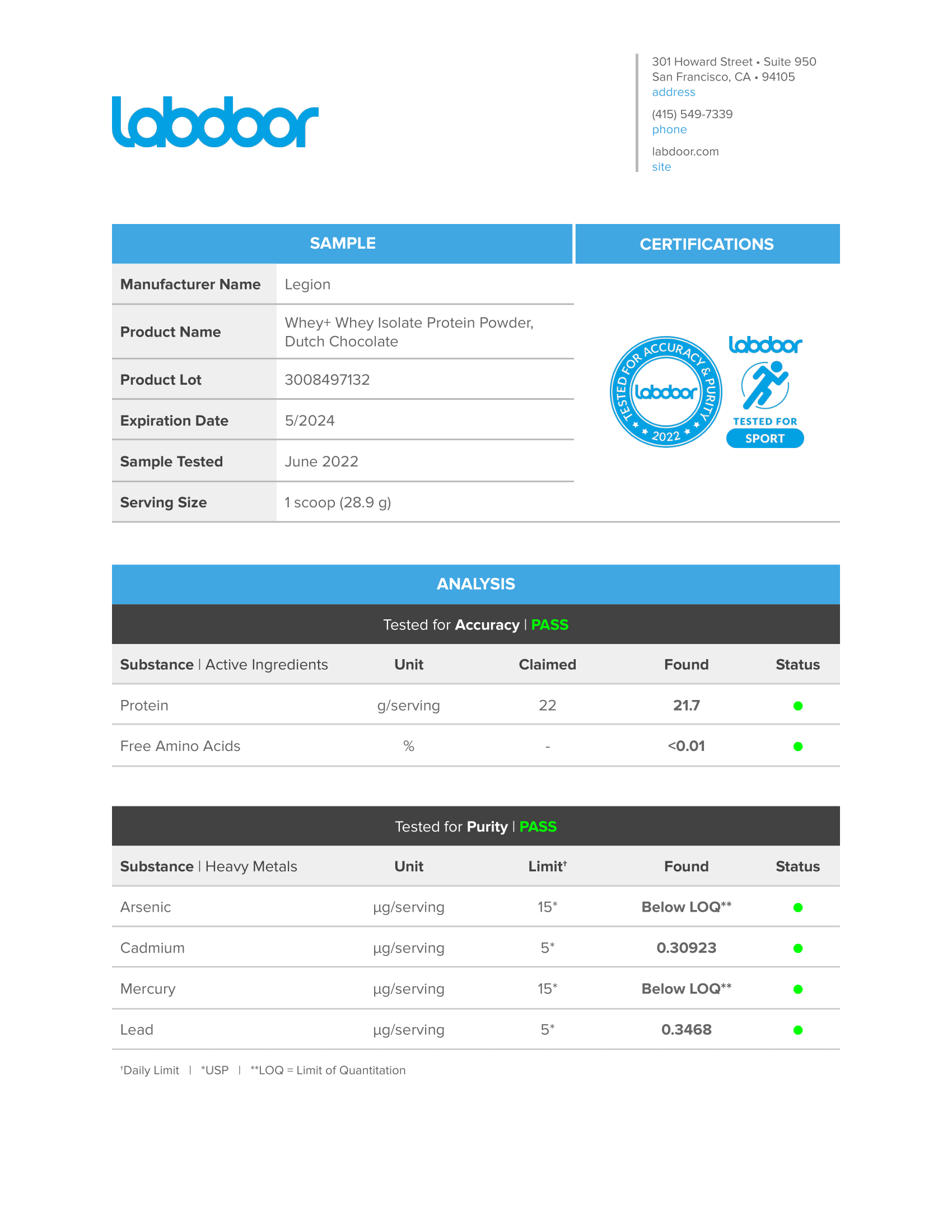
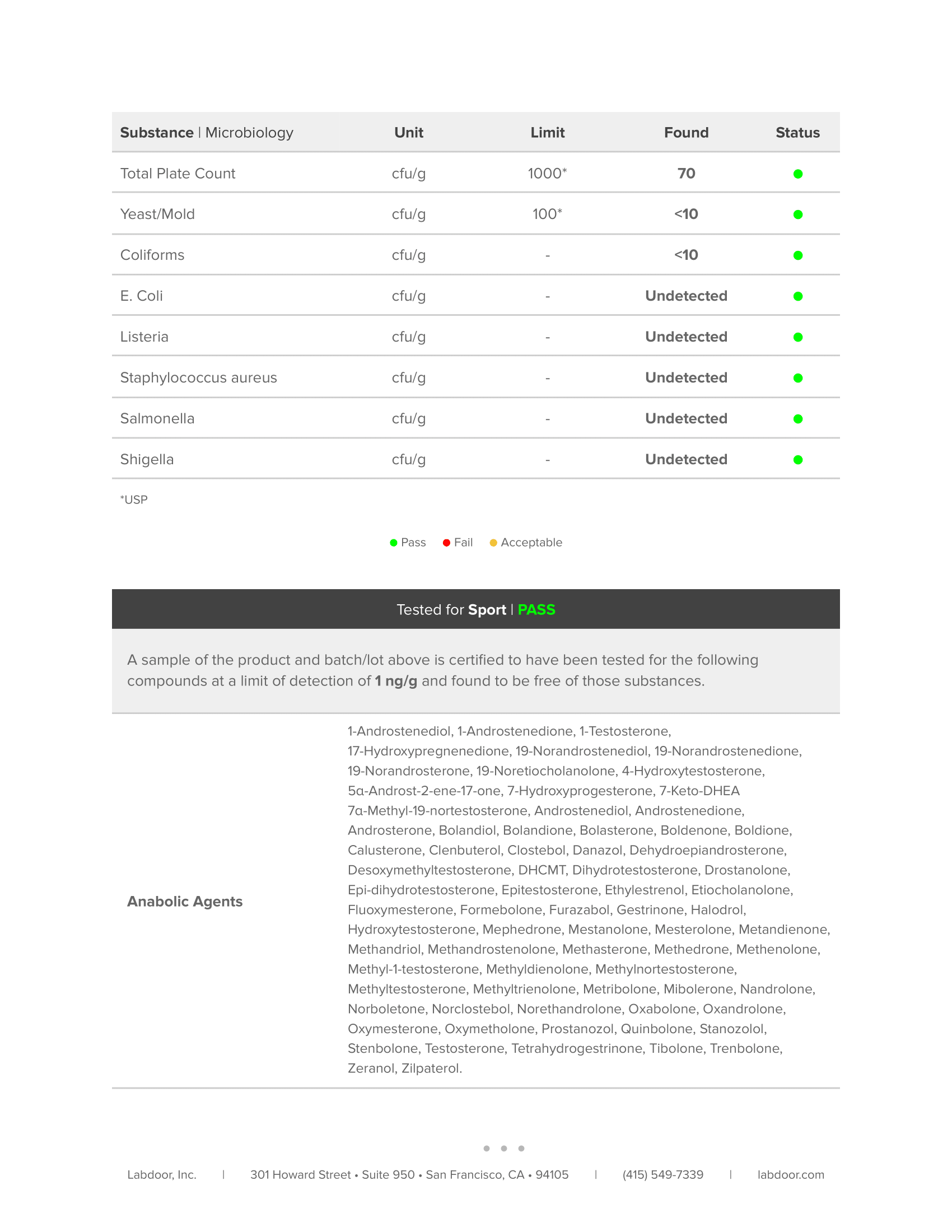
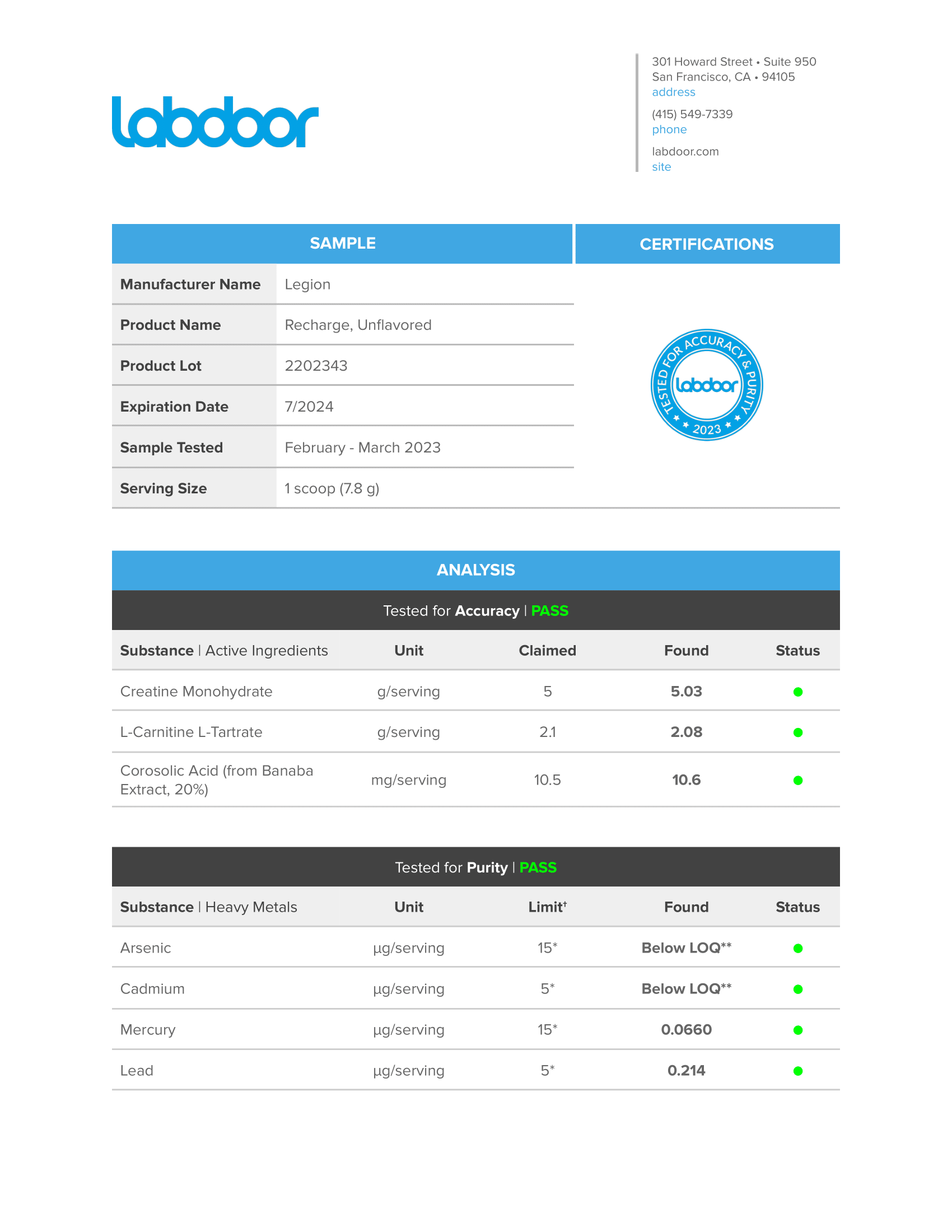
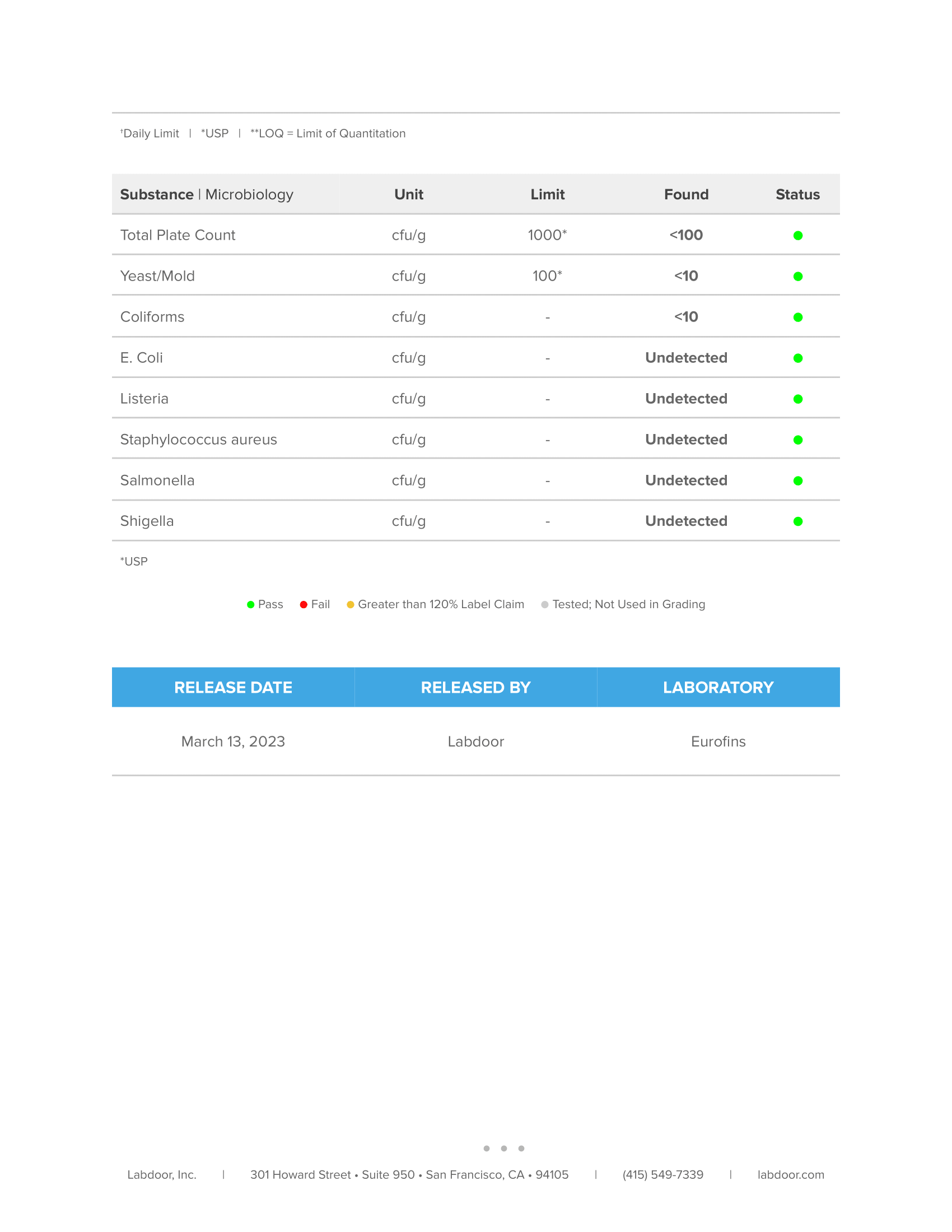
Third-Party Lab Tested
The Muscle Growth Stack is tested by third-party labs for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure it meets FDA purity standards.
Made in USA with Globally Sourced Ingredients
The Muscle Growth Stack is proudly made in America in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected facilities in accordance with the Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations.
"No Return Necessary"
Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love The Muscle Growth Stack, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Some popular performance supplements are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only The Muscle Growth Stack checks each of these boxes.↑
The Muscle Growth Stack doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. The Muscle Growth Stack contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
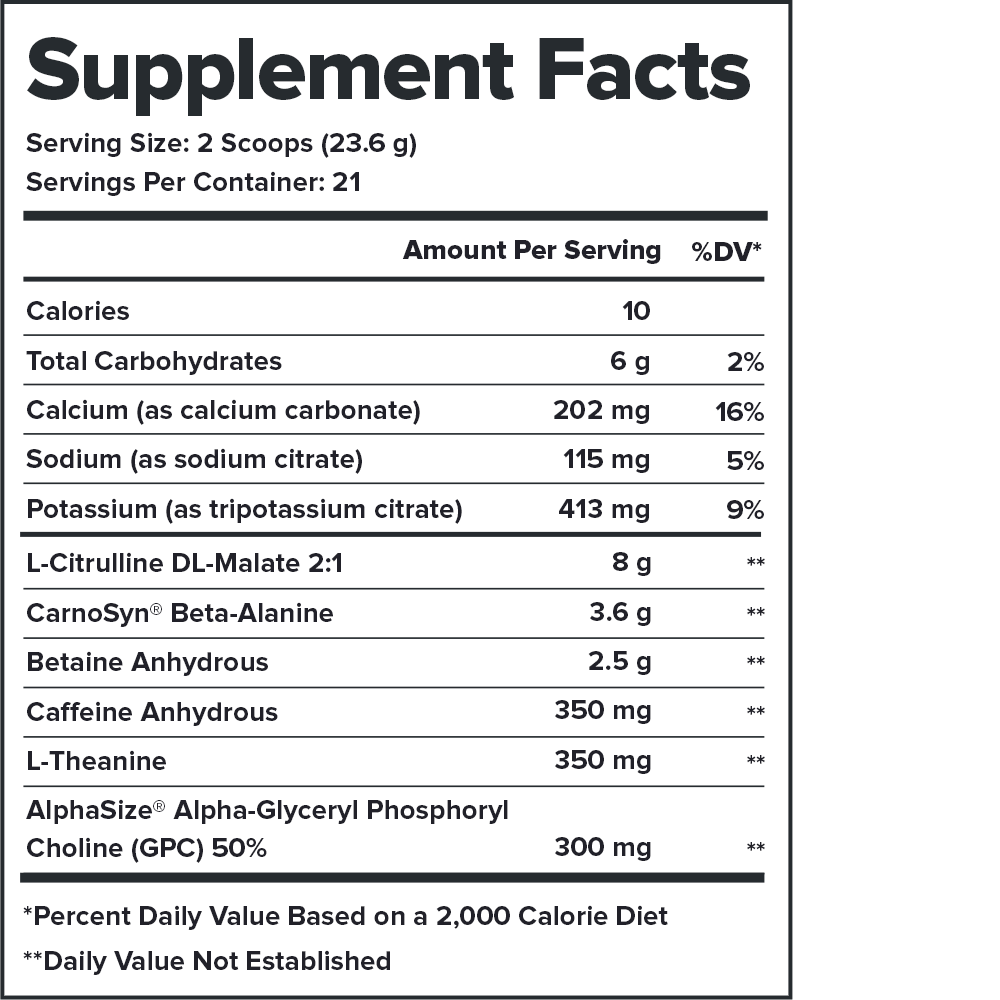
Every serving of The Muscle Growth Stack contains 44.243.548.247.546.245.5 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Each active ingredient in The Muscle Growth Stack is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
That’s 807735807735831759 pages of scientific research that shows The Muscle Growth Stack works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in The Muscle Growth Stack.↑
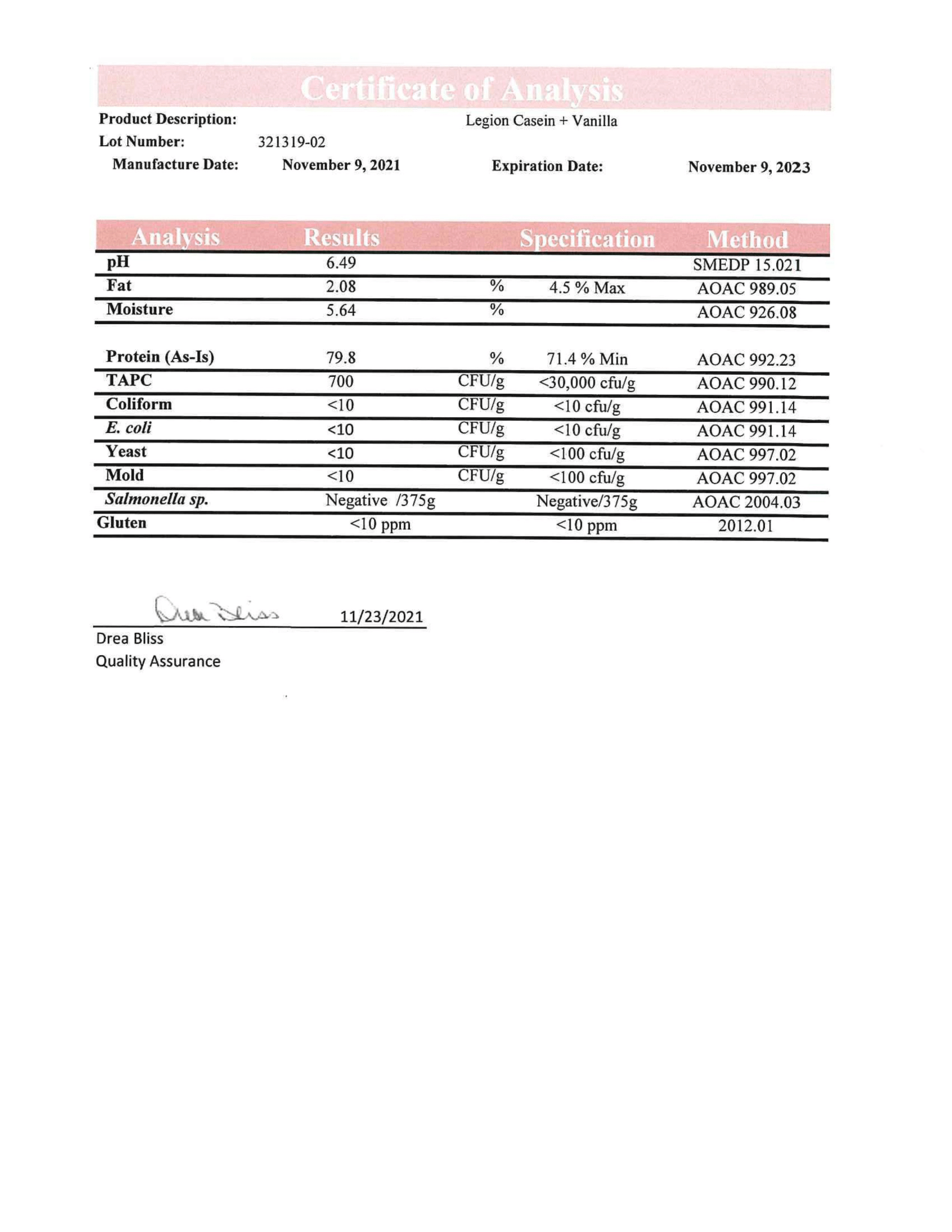
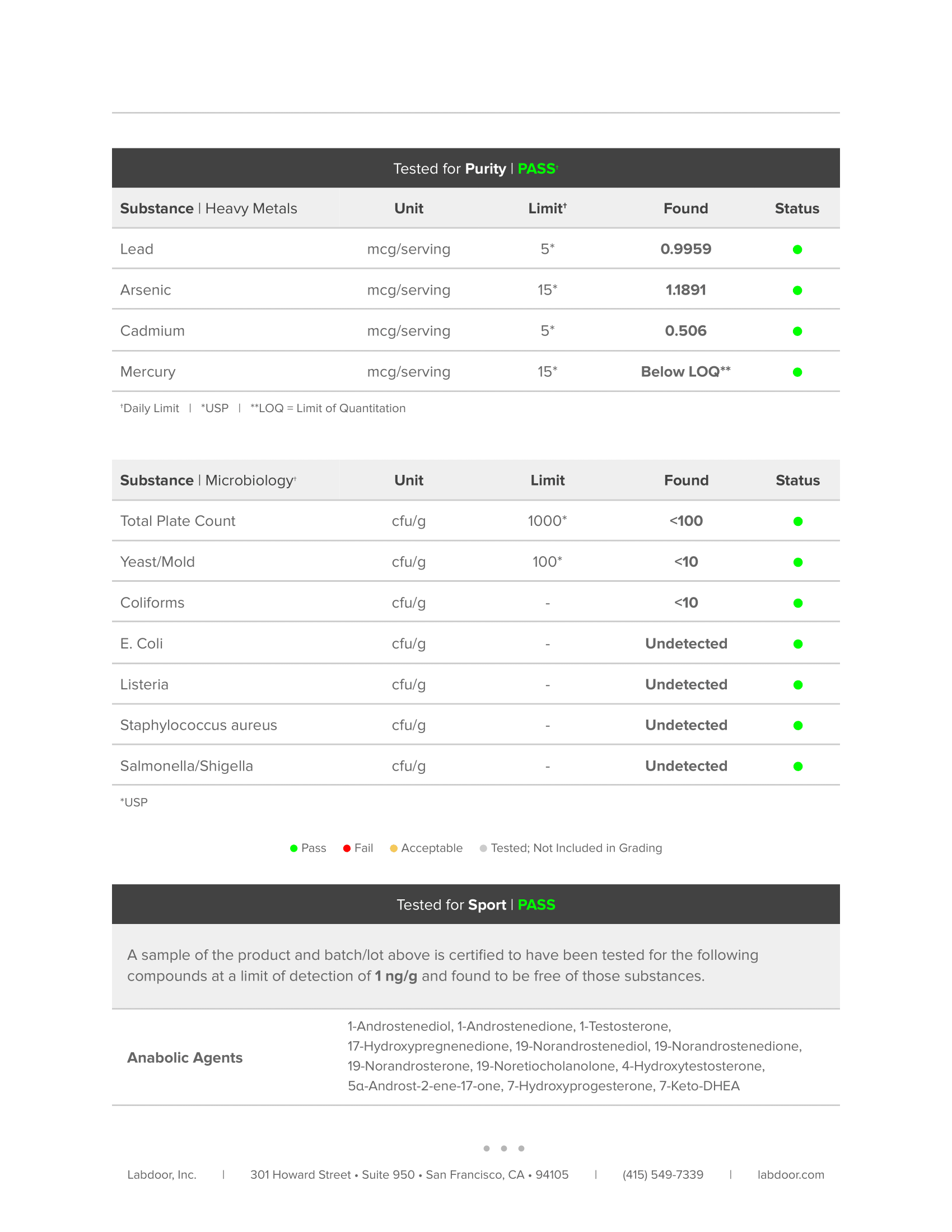
Every bottle is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
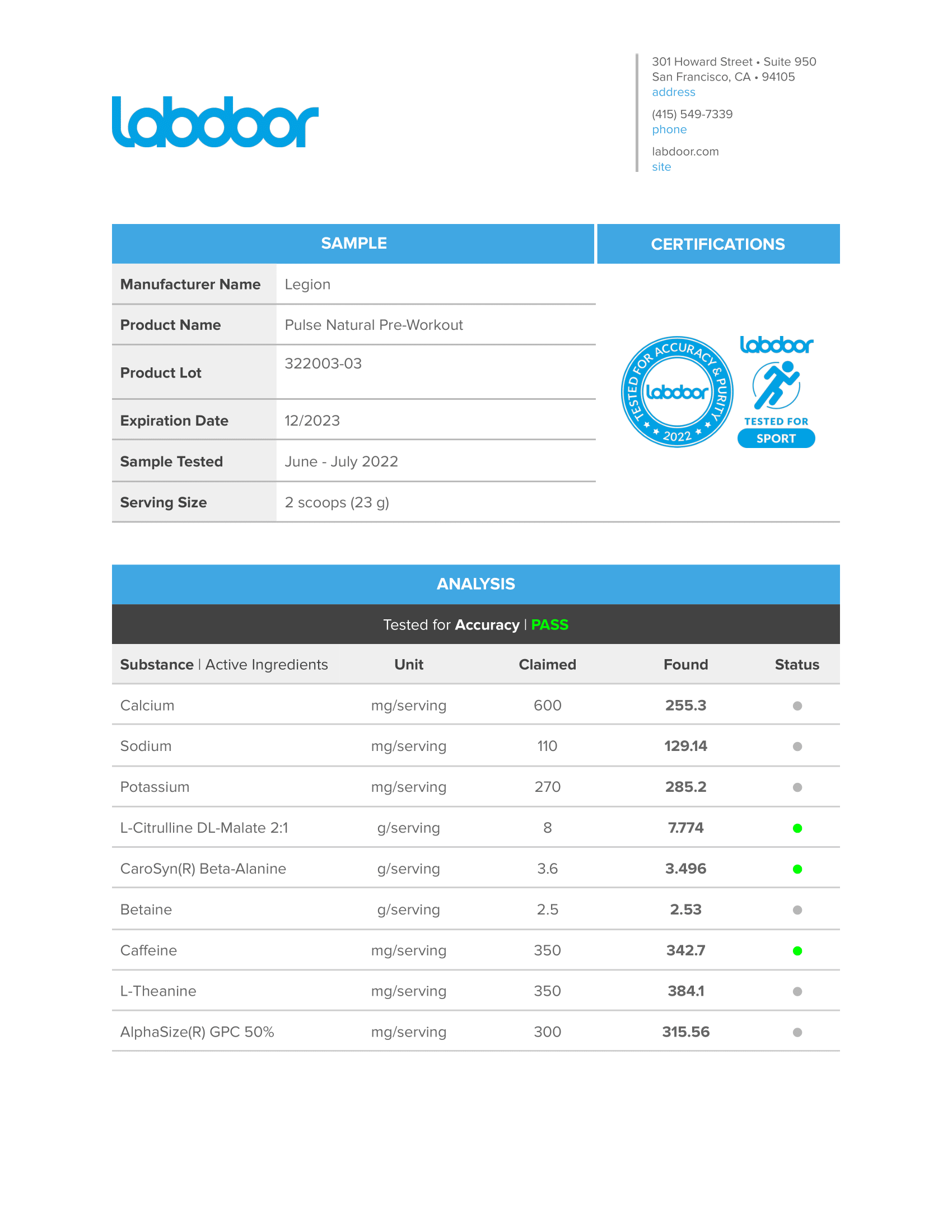
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of The Muscle Growth Stack—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Some popular whey protein powders are all-natural. Some contain 100% whey protein isolate. Some are made with Truly Grass Fed™ milk. But only Whey+ checks each of these boxes.↑
Whey+ doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Whey+ contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
Whey protein isolate is the highest quality whey protein you can buy because it has been processed to remove fat and lactose, making it at least 90% protein by weight (which means it contains minimal calories, carbs, and fat).↑
Truly Grass Fed™ milk comes from hormone- and antibiotic-free cows that live how nature intended—outside, roaming and grazing on grass.↑
Ireland produces some of the healthiest, cleanest milk in the world, and Whey+ comes from farms certified by Ireland’s Sustainable Dairy Assurance Scheme, which ensures the farmers adhere to best practices in animal welfare, sustainability, product quality, traceability, and soil and grass management.↑
That’s 187 pages of scientific research that shows Whey+ works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Whey+.↑
Every bottle of Whey+ is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
Studies show that the more grass cows eat (instead of other types of feed such as grains or soybeans), the more nutritious their milk and beef is.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Whey+—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511.↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Some popular casein protein powders are all-natural. Some contain 100% micellar casein. Some are made with Truly Grass Fed™ milk. But only Casein+ checks each of these boxes. ↑
Casein+ doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Casein+ contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
Micellar casein is the highest quality form of casein protein you can buy because it has been produced in a way that maximally preserves its slow-digesting properties.↑
Truly Grass Fed™ milk comes from hormone- and antibiotic-free cows that live how nature intended—outside, roaming and grazing on grass.↑
Ireland produces some of the healthiest, cleanest milk in the world, and Casein+ comes from farms certified by Ireland’s Sustainable Dairy Assurance Scheme, which ensures the farmers adhere to best practices in animal welfare, sustainability, product quality, traceability, and soil and grass management.↑
That’s 187 pages of scientific research that shows Casein+ works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Casein+.↑
Every bottle of Casein+ is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
Studies show that the more grass cows eat (instead of other types of feed such as grains or soybeans), the more nutritious their milk and beef is.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Casein+—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019. ↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Plant+ doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Plant+ contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
When combined, rice and pea protein are often called the “vegan’s whey” because their robust amino acid profile is similar to whey protein.↑
That’s 211 pages of scientific research that shows Plant+ works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Plant+.↑
Every bottle of Plant+ is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Plant+—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Joy JM, Lowery RP, Wilson JM, Purpura M, De Souza EO, Wilson SM, Kalman DS, Dudeck JE, Jäger R. Nutr J. 2013 Jun 20;12:86. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-86. ↑
Kalman DS. Foods. 2014 Jun 30;3(3):394-402. doi: 10.3390/foods3030394. ↑
Mariotti F, Pueyo ME, Tomé D, Bérot S, Benamouzig R, Mahé S. J Nutr. 2001 Jun;131(6):1706-13. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.6.1706. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Some popular pre-workouts are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Pulse checks each of these boxes.↑
Pulse doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Pulse contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
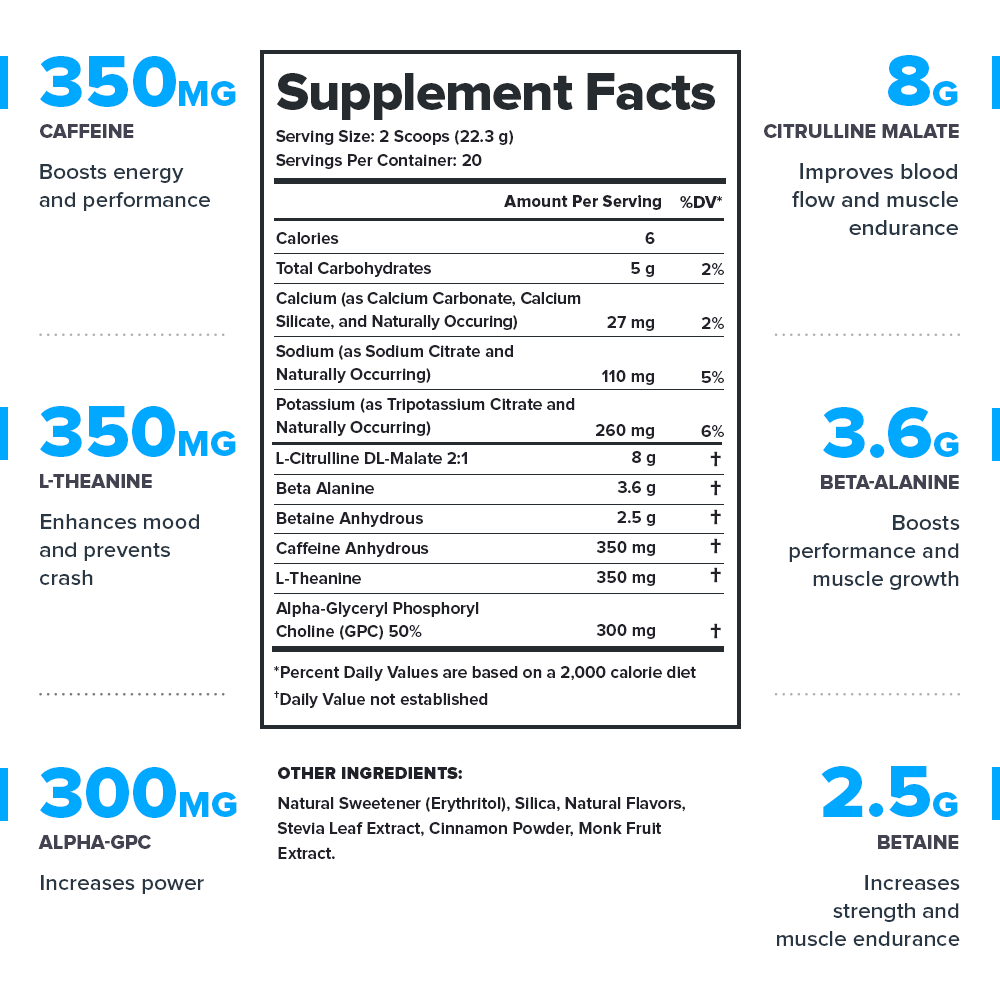
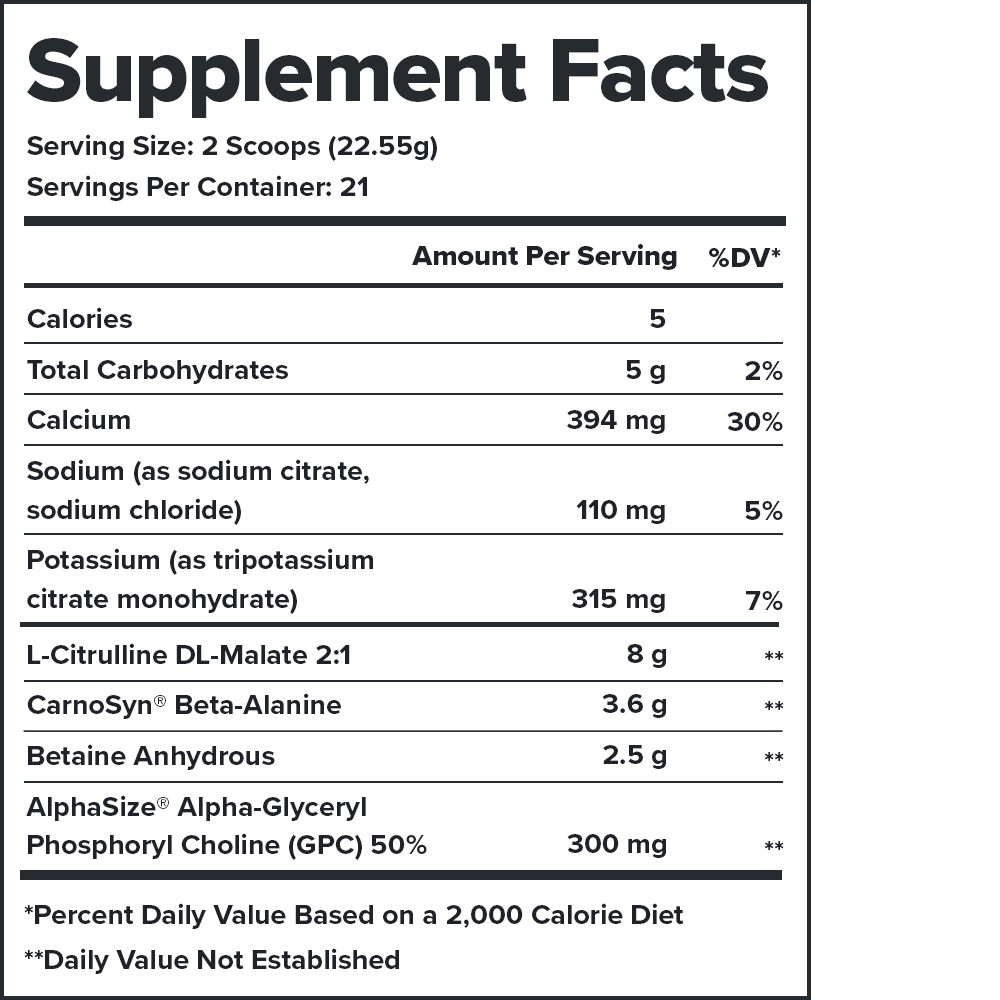
Every serving of Pulse contains 15.1 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Every active ingredient in Pulse is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Pulse contains no harsh stimulants that wind you up and burn you out. Instead, it contains a 1:1 ratio of caffeine and L-theanine, which produces a smooth energy rush and comfortable comedown.↑
That’s 508 pages of scientific research that shows Pulse works the way we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Pulse.↑
Every bottle of Pulse is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Pulse—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51(5):759-767. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.5.759.↑
Astorino TA, Rohmann RL, Firth K. Department of Kinesiology, CSU - San Marcos, San Marcos, CA. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008 Jan;102(2):127-32. ↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Coburn JW, Malek MH. Department of Nutrition and Health Sciences, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Nebraska-Lincoln. J Strength Cond Res. 2006 Aug;20(3):506-10. ↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. Department of Kinesiology, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Jan;23(1):315-24. ↑
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H. Nagoya University Department of Psychology, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8601, Japan. Biol Psychol. 2007 Jan;74(1):39-45. ↑
Siamwala JH, Dias PM, Majumder S, Joshi MK, Sinkar VP, Banerjee G, Chatterjee S. Vascular Biology Lab, AU-KBC Research Centre, Anna University, MIT Campus, Chennai, India. J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Mar;24(3):595-605. ↑
Bryan J. School of Psychology, University of South Australia, Adelaide, 5001, South Australia, Australia. Nutr Rev. 2008 Feb;66(2):82-90. ↑
Einöther SJ, Martens VE, Rycroft JA, De Bruin EA. Sensation, Perception & Behaviour, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen, Vlaardingen, The Netherlands. Appetite. 2010 Apr;54(2):406-9. ↑
Gomez-Ramirez M, Kelly SP, Montesi JL, Foxe JJ. Program in Cognitive Neuroscience and Schizophrenia, The Cognitive Neurophysiology Laboratory, Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, Orangeburg, NY, USA. Brain Topogr. 2009 Jun;22(1):44-51. ↑
Kahathuduwa CN, Dhanasekara CS, Chin S-H, et al. Nutr Res. 2018;49:67-78. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2017.11.002.↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Some stim-free pre-workouts are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Pulse checks each of these boxes.↑
Pulse doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Pulse contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
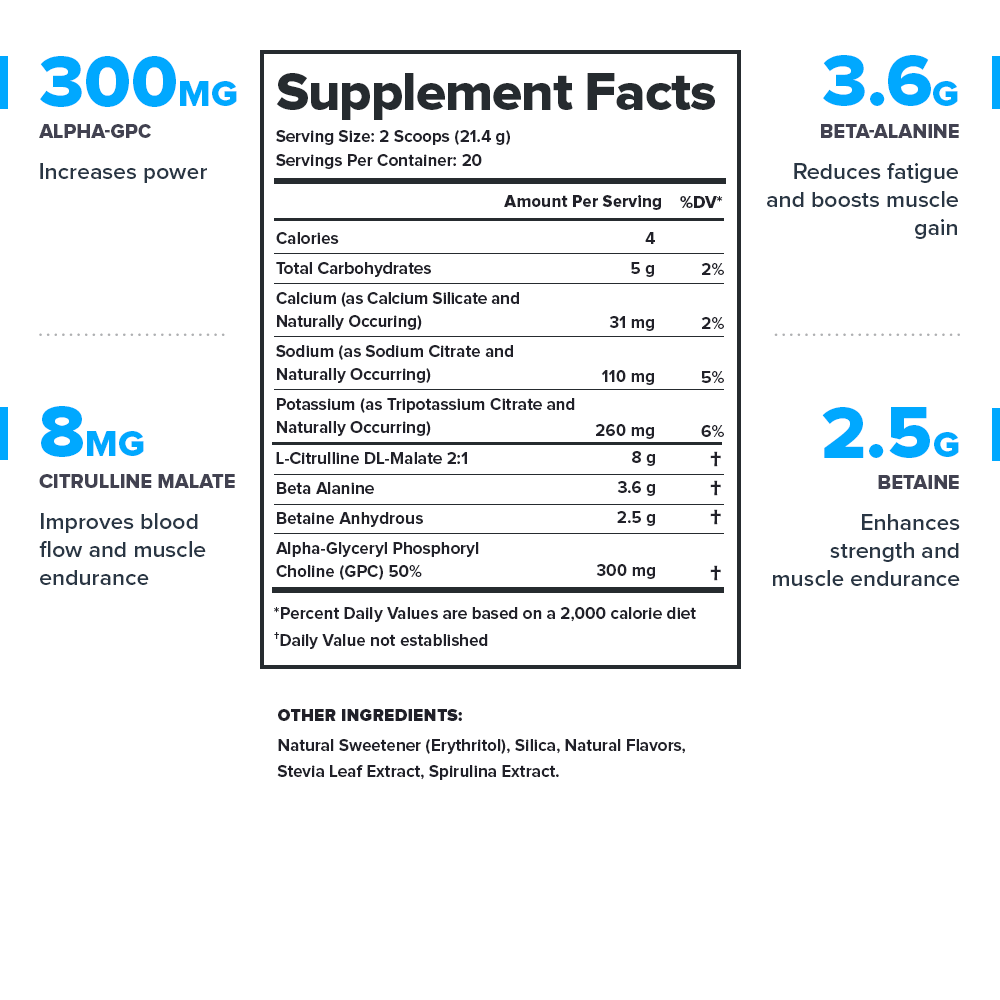
Every serving of Pulse contains 14.4 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Every active ingredient in Pulse is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Stim-free Pulse contains no stimulants of any kind, so it won’t wind you up and burn you out.↑
That’s 436 pages of scientific research that shows Pulse works the way we say it does.↑
While these chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why we don’t put any of them into our products.↑
Every bottle of Pulse is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Pulse—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Recharge doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Recharge contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
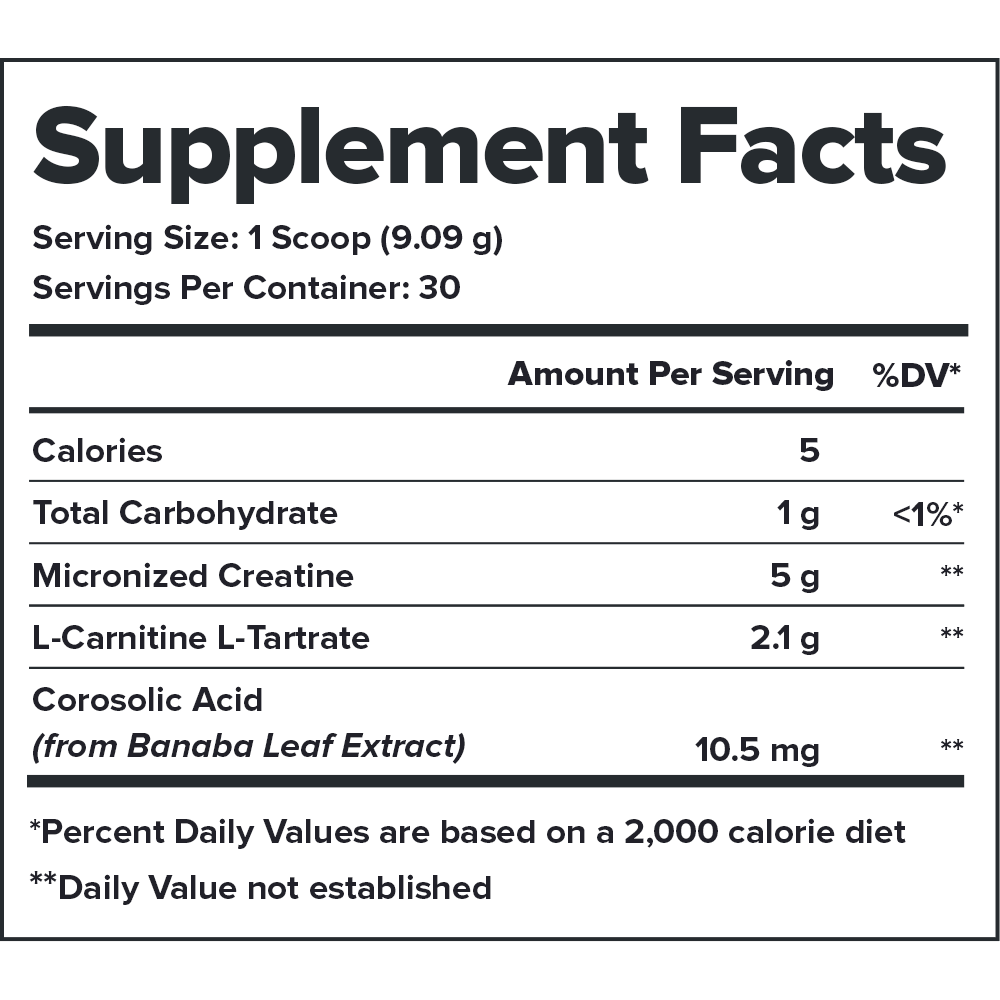
Every serving of Recharge contains 7.1 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.
Each active ingredient in Recharge is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
That’s 486 pages of scientific research that shows Recharge works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Recharge.↑
Every bottle of Recharge is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Recharge—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Branch JD. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2003 Jun;13(2):198-226. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.13.2.198. ↑
Hoffman J, Ratamess N, Kang J, Mangine G, Faigenbaum A, Stout J. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2006 Aug;16(4):430-46. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.16.4.430. ↑
Law YL, Ong WS, GillianYap TL, Lim SC, Von Chia E. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 May;23(3):906-14. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a06c59. ↑
Rawson ES, Volek JS. J Strength Cond Res. 2003 Nov;17(4):822-31. doi: 10.1519/1533-4287(2003)017<0822:eocsar>2.0.co;2. ↑
Eckerson JM, Stout JR, Moore GA, Stone NJ, Iwan KA, Gebauer AN, Ginsberg R. J Strength Cond Res. 2005 Nov;19(4):756-63. doi: 10.1519/R-16924.1. ↑
Mero AA, Keskinen KL, Malvela MT, Sallinen JM. J Strength Cond Res. 2004 May;18(2):306-10. doi: 10.1519/R-12912.1. ↑
Eckerson JM, Stout JR, Moore GA, Stone NJ, Nishimura K, Tamura K. J Strength Cond Res. 2004 Feb;18(1):168-73. doi: 10.1519/1533-4287(2004)018<0168:eotafd>2.0.co;2. ↑
Koçak S, Karli U. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2003 Dec;43(4):488-92. ↑
Kendall KL, Smith AE, Graef JL, Fukuda DH, Moon JR, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Sep;23(6):1663-9. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b1fd1f. ↑
Fukuda DH, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Dwyer TR, Kerksick CM, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Jul;24(7):1826-33. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181e06d0e. ↑
Bassit RA, Pinheiro CH, Vitzel KF, Sproesser AJ, Silveira LR, Curi R. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Mar;108(5):945-55. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1305-1. Epub 2009 Dec 3. ↑
Santos RV, Bassit RA, Caperuto EC, Costa Rosa LF. Life Sci. 2004 Sep 3;75(16):1917-24. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.11.036. ↑
Nelson AG, Arnall DA, Kokkonen J, Day R, Evans J. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001 Jul;33(7):1096-100. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200107000-00005. ↑
Rockwell JA, Rankin JW, Toderico B. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001 Jan;33(1):61-8. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200101000-00011. ↑
Poortmans JR, Francaux M. Sports Med. 2000 Sep;30(3):155-70. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200030030-00002. ↑
Terjung RL, Clarkson P, Eichner ER, Greenhaff PL, Hespel PJ, Israel RG, Kraemer WJ, Meyer RA, Spriet LL, Tarnopolsky MA, Wagenmakers AJ, Williams MH. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000 Mar;32(3):706-17. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200003000-00024. ↑
Yoshizumi WM, Tsourounis C. J Herb Pharmacother. 2004;4(1):1-7. ↑
Bizzarini E, De Angelis L. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2004 Dec;44(4):411-6. ↑
Groeneveld GJ, Beijer C, Veldink JH, Kalmijn S, Wokke JH, van den Berg LH. Int J Sports Med. 2005 May;26(4):307-13. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-817917. ↑
Bemben MG, Lamont HS. Sports Med. 2005;35(2):107-25. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200535020-00002. ↑
Pekala J, Patkowska-Sokoła B, Bodkowski R, Jamroz D, Nowakowski P, Lochyński S, Librowski T. Curr Drug Metab. 2011 Sep;12(7):667-78. doi: 10.2174/138920011796504536. ↑
Evans AM, Fornasini G. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(11):941-67. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200342110-00002. ↑
Wall BT, Stephens FB, Constantin-Teodosiu D, Marimuthu K, Macdonald IA, Greenhaff PL. J Physiol. 2011 Feb 15;589(Pt 4):963-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343. Epub 2011 Jan 4. ↑
Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, French DN, Rubin MR, Sharman MJ, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Newton RU, Jemiolo B, Craig BW, Häkkinen K. J Strength Cond Res. 2003 Aug;17(3):455-62. doi: 10.1519/1533-4287(2003)017<0455:teolls>2.0.co;2. ↑
Volek JS, Kraemer WJ, Rubin MR, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Gaynor P. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Feb;282(2):E474-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00277.2001. ↑
Ho JY, Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Fragala MS, Thomas GA, Dunn-Lewis C, Coday M, Häkkinen K, Maresh CM. Metabolism. 2010 Aug;59(8):1190-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.11.012. ↑
Ho JY, Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Fragala MS, Thomas GA, Dunn-Lewis C, Coday M, Häkkinen K, Maresh CM. Metabolism. 2010 Aug;59(8):1190-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.11.012. ↑
Galloway SD, Craig TP, Cleland SJ. Amino Acids. 2011 Jul;41(2):507-15. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0770-5. ↑
Spiering BA, Kraemer WJ, Vingren JL, Hatfield DL, Fragala MS, Ho JY, Maresh CM, Anderson JM, Volek JS. J Strength Cond Res. 2007 Feb;21(1):259-64. doi: 10.1519/00124278-200702000-00046. ↑
Fukushima M, Matsuyama F, Ueda N, Egawa K, Takemoto J, Kajimoto Y, Yonaha N, Miura T, Kaneko T, Nishi Y, Mitsui R, Fujita Y, Yamada Y, Seino Y. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006 Aug;73(2):174-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.01.010. ↑
Fukushima M, Matsuyama F, Ueda N, Egawa K, Takemoto J, Kajimoto Y, Yonaha N, Miura T, Kaneko T, Nishi Y, Mitsui R, Fujita Y, Yamada Y, Seino Y. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006 Aug;73(2):174-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2006.01.010. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019. ↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑