Not happy with your purchase?
Simply let us know, and you'll get a full refund, no questions asked. And you don't even need to return anything.
So that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
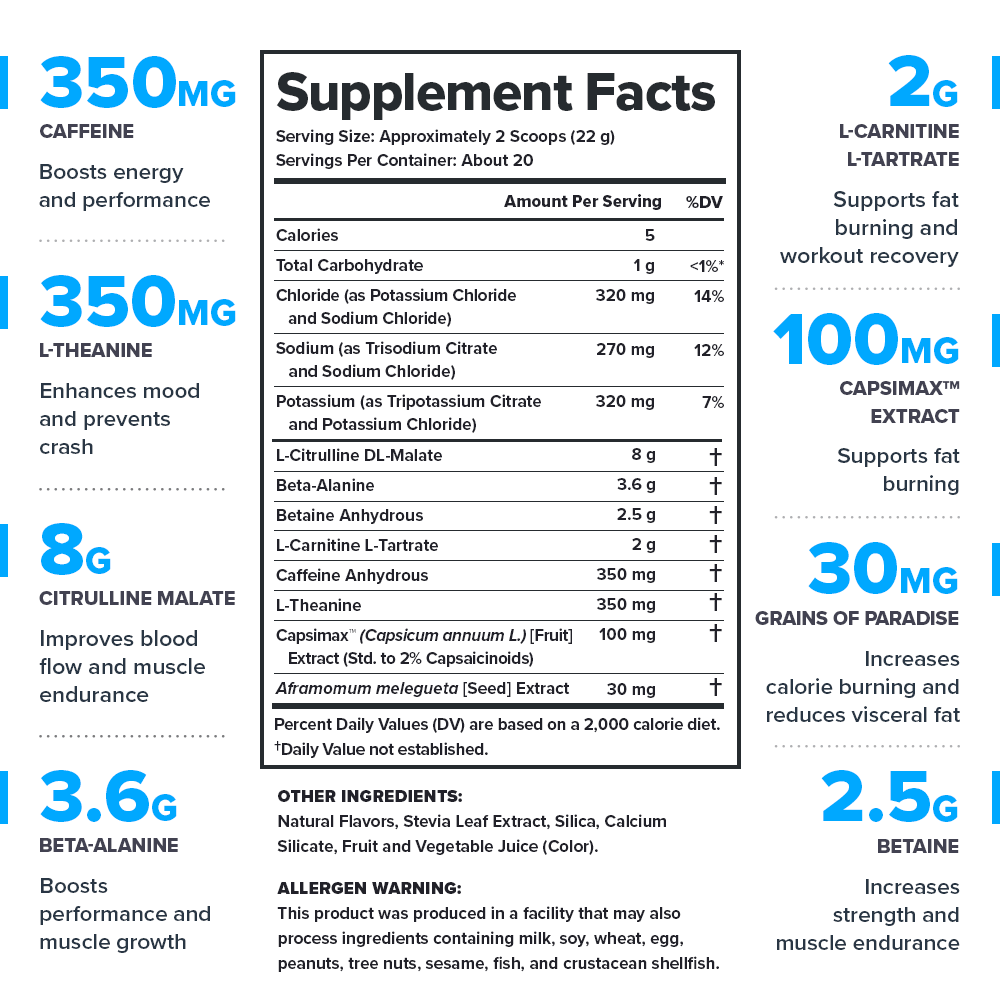
Legion Pulse+ Burn Ingredients (16.93 grams per serving)
Caffeine (350 milligrams per serving)
Caffeine is a naturally occurring substance found in many plants native to Africa, East Asia, and South America, including various kinds of tea, cocoa, and coffee.
Caffeine’s primary effects in the body are to stimulate the central nervous system and block the activity of another chemical—adenosine—that causes tiredness.
Research shows that supplementation with caffeine . . .
- Boosts mood and energy levels[9]
- Improves focus, drive, and wakefulness[10][11][12]
- Increases metabolic rate[13][14][15]
- Enhances strength and power[16][17][18][19][20][21][22]
- Boosts endurance[23][24][25][26][27]
- Improves anaerobic performance[28][29][30][31][32]
- Preserves power output during fatiguing workouts[33]
The clinically effective dose of caffeine for enhancing energy, focus, and performance is between 1 and 6 milligrams per kilogram of body weight.[34][35][36]

L-Theanine (350 milligrams per serving)
L-theanine is an amino acid mainly found in green tea. It supports relaxation and focus by interacting with neurotransmitters like glutamate, GABA, serotonin, and dopamine to lower excitatory brain signals and boost calming ones.
Research shows that supplementation with L-theanine . . .
- Reduces the effects of mental stress[37]
- Promotes relaxation[38]
- Improves mood, memory performance, and attention (when paired with caffeine)[39][40][41][42]
The clinically effective dose of L-theanine when combined with caffeine is between a ratio of 1:1 and 2:1 theanine to caffeine.

L-Carnitine L-Tartrate (2 grams per serving)
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid mainly found in meat and dairy. It’s “conditionally essential,” meaning your body can only make it if you’re eating enough lysine and methionine, two amino acids it can’t produce on its own.
L-tartrate is a salt that improves the absorption of other nutrients.
L-carnitine helps your body burn fat more efficiently by shuttling long-chain fatty acids into your cells’ mitochondria, where they’re broken down for energy via a process called β-oxidation.
It also enhances the function of CPT1—the enzyme that controls this process—which may help you burn more fat during exercise, preserve glycogen, and train harder for longer.
Research shows that supplementation with L-carnitine . . .
- Supports fat burning[43][44][45]
- Reduces exercise-induced muscle damage and soreness[46][47][48][49][50]
- May improve strength endurance and power[51]
- May enhance antioxidant protection[52][53][54][55]
- May increase nitric oxide production[56]
The clinically effective dose of L-carnitine L-tartrate is 500–2000 milligrams per day.

Capsimax™ Capsaicinoid Extract (100 milligrams per serving)
Capsaicinoids are the group of naturally occurring compounds in chili peppers that give the fruit its signature spicy heat.
Capsimax™ is a patented capsaicinoid extract with a controlled-release coating that delivers an effective dose without the digestive discomfort often associated with capsaicin supplements.
Capsaicinoids support fat burning by decreasing the activity of genes that promote fat storage like PPAR-γ and SCD, while activating ones that boost energy expenditure like PGC1α and PRDM16.
Additionally, capsaicinoids activate TRPV1, a protein that responds to heat and supports fat burning and appetite control.
Research shows that supplementation with capsaicinoids . . .
- Supports fat burning[57]
- Supports appetite control[58]
- Increases strength and strength endurance[59][60][61]
- Reduces perceived effort during exercise[62][63][64]
- May enhance cognitive function[65]
The clinically effective dose of capsaicinoids is 2–10 milligrams per day.
Pulse+ Burn contains 100 milligrams of Capsimax™, which provides 2 milligrams of active capsaicinoids.

Grains of Paradise (30 milligrams per serving)
Grains of Paradise is the common name for the plant Aframomum melegueta, which is an herb in the ginger family that’s commonly used as a spice.
It contains compounds like 6-gingerol and 6-paradol that influence receptors on fat cells involved in energy regulation and temperature perception.
That’s why research shows that supplementation with Grains of Paradise increases energy expenditure and supports visceral fat burning.[66][67][68][69]
The clinically effective dose of Grains of Paradise is around 30 milligrams of an extract providing 3–4 milligrams of 6-paradol.

Citrulline Malate (8 grams per serving)
Citrulline malate is a compound consisting of L-citrulline—an amino acid found in foods like watermelon, pumpkin, and cucumber—and malic acid, a naturally occurring component of many fruits and vegetables that supports energy production.
The body converts L-citrulline into the amino acid L-arginine, which increases the production of nitric oxide—a gas that widens blood vessels and improves circulation.[70][71]
Research shows that supplementation with citrulline malate . . .
- Improves muscle endurance[72][73][74][75]
- Boosts strength and power[76]
- Relieves muscle soreness[77][78]
- Reduces perceived effort during exercise[79]
The clinically effective dose of citrulline malate is between 6 and 8 grams.

Beta-Alanine (3.6 grams per serving)
Beta-alanine is a naturally occurring amino acid that regulates the amount of the molecule carnosine that can be stored in the muscles.[80]
Carnosine reduces muscle acidity, which increases the amount of work that muscles can do before they become fatigued.[81]
Research shows that supplementation with beta-alanine . . .
- Improves muscle endurance, particularly during bouts of exercise lasting 1–4 minutes (like circuits or supersets)[82][83][84][85][86]
- Improves anaerobic exercise capacity[87][88][89][90][91][92][93]
- Reduces feelings of fatigue during exercise[94][95][96]
The clinically effective dose of beta-alanine is between 2.6 and 6.4 grams.
We chose to include 3.6 grams per serving because it provides significant performance benefits while also minimizing the common and harmless side effect of a mild prickling, itching, or tingling of the skin.[97]

Betaine (2.5 grams per serving)
Betaine (or trimethylglycine) is a compound derived from the amino acid glycine and found in foods like beets, spinach, and quinoa.
Betaine has three methyl groups—small chemical units containing one carbon and three hydrogen atoms that your body uses in essential processes like building DNA, breaking down fats, and producing energy.
Betaine's also an osmolyte, which is a substance that helps balance fluid levels inside and outside cells.
These two properties are beneficial during times of physical stress, which is why studies show that supplementation with betaine . . .
The clinically effective dose of betaine is between 2 and 4 grams, with most studies using 2.5 grams.[100][101]

Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.[102][103][104][105][106][107]
That’s why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, allulose, and monk fruit instead. Research shows that these ingredients are not only safe but can also confer several health benefits, such as supporting weight management, antioxidant activity, digestive health, and more.[108][109][110][111]

No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
As with artificial sweeteners, studies show that artificial food dyes and fillers can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[112][113][114][115][116]
That’s why we use natural coloring and flavoring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for improving texture, enhancing shelf life, and facilitating the manufacturing process.

Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Pulse+ Burn is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA safety guidelines.[117]
Made in the USA with Globally Sourced Ingredients
If you want to ensure the supplements you’re swallowing every day are safe and effective, you want to buy from a company that:
- Sources ingredients from premium suppliers around the world
- Tests all products for purity and accuracy in accredited laboratories
- Manufactures in America, which has some of the strictest regulations in the world
And that’s exactly what we do here at Legion.
See how Legion Pulse+ Burn compares to the rest.
- Active Ingredients
- Clinically Effective Ingredients & Doses
- Caffeine
- L-Carnitine L-Tartrate
- Capsimax™ Extract
- Grains of Paradise
- Citrulline Malate
- Beta-Alanine
- Betaine
- L-Theanine
- Naturally Sweetened & Flavored
- Lab-Tested for Purity & Accuracy
- Labdoor™ Certified Brand
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion Pulse+ Burn

- 16,930 mg
per serving - 350 mg
per serving - 2,000 mg
per serving - 100 mg
per serving - 30 mg
per serving - 8,000 mg
per serving - 3,600 mg
per serving - 2,500 mg
per serving - 350 mg
per serving
-
C4 Ultimate Shred

- 12,426 mg
per serving - 300 mg
per serving - 40 mg
per serving - 3,000 mg
per serving - 3,200 mg
per serving - 1,250 mg
per serving - $2.75
-
PEScience Alphamine

- 4,580 mg
per serving - 300 mg
per serving - 2,000 mg
per serving - 30 mg
per serving - 200 mg
per serving - $1.33
-
Kaged Clean Burn

- 3,211 mg
per serving - 166 mg
per serving - 1,500 mg
per serving - 50 mg
per serving - 20 mg
per serving - $1.33
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in Pulse+ Burn is backed by peer-reviewed research in healthy humans.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient on our Pulse+ Burn label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Pulse+ Burn is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA safety guidelines.
Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
Pulse+ Burn is naturally sweetened with stevia and naturally flavored with extracts from fruit, vegetables, plants and other foods.
Made in the USA
Pulse+ Burn is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don’t absolutely love Pulse+ Burn, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That’s why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, allulose, and monk fruit instead, which are scientifically shown to be safe and can confer several health benefits, including weight management, antioxidant activity, digestive health, and more. ↑
Pulse+ Burn contains the exact ingredients, forms, and doses used in peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans. ↑
View Supplement Facts↑
Pulse+ Burn contains an equal amount of caffeine and L-theanine (350 milligrams of each).
This 1:1 ratio provides a focused, balanced boost in energy, mood, and performance without overwhelming stimulant effects or the negative side effects associated with high-caffeine/high-stim pre-workouts. ↑
That’s 3,971 pages of scientific research that shows Pulse+ Burn works the way we say it does. ↑
Many supplement ingredients lack scientific validation in humans—we aren't large rodents, after all.
And even when ingredients have proven benefits, they're often used in doses too small to be effective.
That's why we exclusively use ingredients and doses shown to work in peer-reviewed scientific studies on healthy men and women. ↑
While artificial sweeteners, food dyes, and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That’s why we use naturally derived alternatives instead like stevia, allulose, monk fruit, and fruit extracts. ↑
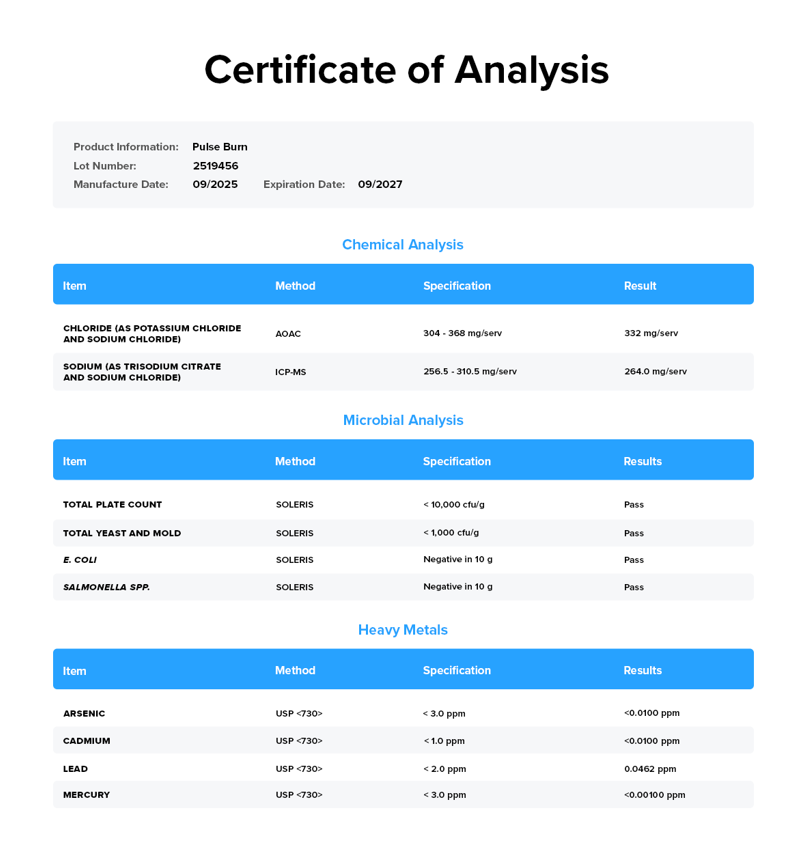
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
View Latest Certificate of Analysis ↑
Pulse+ Burn contains the precise ingredients, forms, and doses used in peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.↑
View Supplement Facts↑
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health.
That’s why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, allulose, and monk fruit instead, which are scientifically shown to be safe and can confer several health benefits, including weight management, antioxidant activity, digestive health, and more.↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
View Latest Certificate of Analysis↑
Spriet LL. Sports Med. 2014;44 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S175-S184. doi:10.1007/s40279-014-0257-8. ↑
McLellan TM, Caldwell JA, Lieberman HR. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;71:294-312. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.09.001. ↑
Crawford C, Teo L, Lafferty L, et al. Nutr Rev. 2017;75(suppl_2):17-35. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nux007. ↑
Kamimori GH, McLellan TM, Tate CM, Voss DM, Niro P, Lieberman HR. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015;232(12):2031-2042. doi:10.1007/s00213-014-3834-5. ↑
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51(5):759-767. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.5.759. ↑
Conger SA, Tuthill LM, Millard-Stafford ML. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2022;33(2):112-120. Published 2022 Dec 10. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2022-0131 ↑
Fernández-Sánchez J, Trujillo-Colmena D, Rodríguez-Castaño A, et al. Nutrients. 2024;16(2):207. Published 2024 Jan 8. doi:10.3390/nu16020207 ↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1. ↑
Warren GL, Park ND, Maresca RD, McKibans KI, Millard-Stafford ML.. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(7):1375-1387. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cabbd8. ↑
Grgic J, Pickering C. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(3):353-360. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2018.08.016. ↑
Grgic J, Trexler ET, Lazinica B, Pedisic Z. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018;15:11. Published 2018 Mar 5. doi:10.1186/s12970-018-0216-0. ↑
Grgic J. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018;18(2):219-225. doi:10.1080/17461391.2017.1394371. ↑
Grgic J, Mikulic P.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2022;32(4):644-653. doi:10.1111/sms.14109 ↑
Grgic J, Varovic D.Nutrients. 2022;14(19):4155. Published 2022 Oct 6. doi:10.3390/nu14194155 ↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1. ↑
Warren GL, Park ND, Maresca RD, McKibans KI, Millard-Stafford ML. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(7):1375-1387. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181cabbd8. ↑
Polito MD, Souza DB, Casonatto J, Farinatti P. Sci Sports. 2016;31(3):119-128. doi:10.1016/J.SCISPO.2016.01.006. ↑
Wang Z, Qiu B, Gao J, Del Coso J. Nutrients. 2022;15(1):148. Published 2022 Dec 28. doi:10.3390/nu15010148 ↑
Chen B, Ding L, Qin Q, Lei TH, Girard O, Cao Y. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024 Dec;21(1):2363789. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2363789. Epub 2024 Jun 5. PMID: 38836626; PMCID: PMC11155427.↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, et al.. J Strength Cond Res. 2006;20(3):506-510. doi:10.1519/18285.1. ↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(1):315-324. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31818b979a. ↑
Shen JG, Brooks MB, Cincotta J, Manjourides JD. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(2):232-238. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2018.07.022. ↑
Southward K, Rutherfurd-Markwick KJ, Ali A. [published correction appears in Sports Med. 2018 Aug 9;:]. Sports Med. 2018;48(8):1913-1928. doi:10.1007/s40279-018-0939-8. ↑
Desbrow B, Biddulph C, Devlin B, Grant GD, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, Leveritt MD.. J Sports Sci. 2012;30(2):115-120. doi:10.1080/02640414.2011.632431. ↑
Sun R, Sun J, Li J, Li S.. Brain Behav. 2022;12(4):e2529. doi:10.1002/brb3.2529. ↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(1):315-324. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31818b979a. ↑
McLellan TM, Caldwell JA, Lieberman HR. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;71:294-312. doi:10.1016/J.NEUBIOREV.2016.09.001. ↑
Guest NS, VanDusseldorp TA, Nelson MT, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18(1). doi:10.1186/S12970-020-00383-4. ↑
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H. Biol Psychol. 2007;74(1):39-45. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2006.06.006. ↑
Rao TP, Ozeki M, Juneja LR. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(5):436-447. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.926153. ↑
Bryan J. Nutr Rev. 2008;66(2):82-90. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.00011.x. ↑
Einöther SJ, Martens VE, Rycroft JA, De Bruin EA. Appetite. 2010;54(2):406-409. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2010.01.003. ↑
Gomez-Ramirez M, Kelly SP, Montesi JL, Foxe JJ. Brain Topogr. 2009;22(1):44-51. doi:10.1007/s10548-008-0068-z. ↑
Kahathuduwa CN, Dhanasekara CS, Chin SH, et al. Nutr Res. 2018;49:67-78. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2017.11.002. ↑
Askarpour M, Hadi A, Miraghajani M, Symonds ME, Sheikhi A, Ghaedi E. Pharmacol Res. 2020;151:104554. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104554 ↑
Pooyandjoo M, Nouhi M, Shab-Bidar S, Djafarian K, Olyaeemanesh A. Obes Rev. 2016;17(10):970-976. doi:10.1111/obr.12436 ↑
Talenezhad N, Mohammadi M, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Salehi-Abargouei A.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020;37:9-23. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.03.008 ↑
Spiering BA, Kraemer WJ, Vingren JL, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2007;21(1):259-264. doi:10.1519/00124278-200702000-00046 ↑
Ho JY, Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, et al. Metabolism. 2010;59(8):1190-1199. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.11.012 ↑
Volek JS, Kraemer WJ, Rubin MR, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Gaynor P. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282(2):E474-E482. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00277.2001 ↑
Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, French DN, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2003;17(3):455-462. doi:10.1519/1533-4287(2003)017<0455:teolls>2.0.co;2 ↑
Yarizadh H, Shab-Bidar S, Zamani B, Vanani AN, Baharlooi H, Djafarian K. J Am Coll Nutr. 2020;39(5):457-468. doi:10.1080/07315724.2019.1661804 ↑
Koozehchian MS, Daneshfar A, Fallah E, et al. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2018;22(4):7-19. doi:10.20463/jenb.2018.0026 ↑
Volek JS, Kraemer WJ, Rubin MR, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Gaynor P. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282(2):E474-E482. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00277.2001 ↑
Koozehchian MS, Daneshfar A, Fallah E, et al. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2018;22(4):7-19. doi:10.20463/jenb.2018.0026 ↑
Gülçin I.. Life Sci. 2006;78(8):803-811. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.05.103 ↑
Atalay Guzel N, Erikoglu Orer G, Sezen Bircan F, Coskun Cevher S. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015;55(1-2):9-15. ↑
Atalay Guzel N, Erikoglu Orer G, Sezen Bircan F, Coskun Cevher S. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015;55(1-2):9-15. ↑
Bloomer RJ, Canale RE, Shastri S, Suvarnapathki S. Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Jul 15;9:72. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-72. PMID: 20633266; PMCID: PMC2912905. ↑
Urbina SL, Roberts MD, Kephart WC, Villa KB, Santos EN, Olivencia AM, Bennett HM, Lara MD, Foster CA, Purpura M, Jäger R, Taylor LW, Wilborn CD. Appetite. 2017 Jun 1;113:264-273. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.02.025. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Erratum in: Appetite. 2018 Dec 1;131:169. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2018.07.021. PMID: 28235621.↑
Grgic J, Memon AR, Chen S, et al. Nutrients. 2022;14(21):4531. Published 2022 Oct 28. doi:10.3390/nu14214531 ↑
de Freitas MC, Cholewa JM, Panissa VLG, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(1):130-134. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000003431 ↑
Conrado de Freitas M, Cholewa JM, Freire RV, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2018;32(8):2227-2232. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002109 ↑
de Freitas MC, Cholewa JM, Panissa VLG, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(1):130-134. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000003431. ↑
de Freitas MC, Cholewa JM, Panissa VLG, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(1):130-134. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000003431 ↑
Conrado de Freitas M, Cholewa JM, Freire RV, et al. J Strength Cond Res. 2018;32(8):2227-2232. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002109 ↑
Liu CH, Bu XL, Wang J, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;52(3):1081-1088. doi:10.3233/JAD-151079 ↑
Sugita J, Yoneshiro T, Sugishima Y, et al.. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2014;60(1):22-27. doi:10.3177/jnsv.60.22. ↑
Sugita J, Yoneshiro T, Hatano T, et al. Br J Nutr. 2013;110(4):733-738. doi:10.1017/S0007114512005715. ↑
Yoneshiro T, Matsushita M, Sugita J, et al. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2021;67(2):99-104. doi:10.3177/jnsv.67.99 ↑
Sudeep HV, Aman K, Jestin TV, Shyamprasad K. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:3777-3791. Published 2022 Oct 28. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S367350 ↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304 ↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SW. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002 ↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(5):1215-1222. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cb28e0 ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW Jr, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6 ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321 ↑
Vårvik FT, Bjørnsen T, Gonzalez AM. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2021;31(4):350-358. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2020-0295 ↑
Trexler ET, Persky AM, Ryan ED, Schwartz TA, Stoner L, Smith-Ryan AE.. Sports Med. 2019;49(5):707-718. doi:10.1007/s40279-019-01091-z ↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(5):1215-1222. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cb28e0 ↑
Rhim HC, Kim SJ, Park J, Jang KM.. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(6):553-561. doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2020.02.003 ↑
Rhim HC, Kim SJ, Park J, Jang KM. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(6):553-561. doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2020.02.003 ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2013;22(5):739-744. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2013;22(5):739-744. ↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, et al. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;103(5):1736-1743. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00397.2007 ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, et al. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-386. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0474-z ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5:21. Published 2008 Nov 7. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-21 ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, et al. Nutr Res. 2008;28(1):31-35. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2007.11.004 ↑
Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Stout JR, et al.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015;12:30. Published 2015 Jul 15. doi:10.1186/s12970-015-0090-y ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, et al. Amino Acids. 2007;32(2):225-233. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0364-4 ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(10):1972-1978. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182188501 ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(5):1199-1207. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181d82f8b ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009;6:5. Published 2009 Feb 11. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-6-5 ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Amino Acids. 2012;43(1):25-37. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-1200-z ↑
Georgiou GD, Antoniou K, Antoniou S, et al. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2024;34(6):397-412. Published 2024 Jul 19. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2024-0027 ↑
Saunders B, Elliott-Sale K, Artioli GG, et al.. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(8):658-669. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2016-096396 ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, et al. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-386. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0474-z ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5:21. Published 2008 Nov 7. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-21 ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, et al. Nutr Res. 2008;28(1):31-35. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2007.11.004 ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018;15(1):59. Published 2018 Dec 18. doi:10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3 ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. T J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(12):3461-3471. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e318217d48d ↑
Zawieja E, Machek S, Zanchi NE, Cholewa J, Woźniewicz M. J Sports Sci. 2024;42(22):2131-2144. doi:10.1080/02640414.2024.2423578 ↑
Zawieja E, Machek S, Zanchi NE, Cholewa J, Woźniewicz M. J Sports Sci. 2024;42(22):2131-2144. doi:10.1080/02640414.2024.2423578 ↑
Ashtary-Larky D, Bagheri R, Ghanavati M, et al. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(23):6516-6533. doi:10.1080/10408398.2021.1902938 ↑
Abou-Donia MB, El-Masry EM, Abdel-Rahman AA, McLendon RE, Schiffman SS. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2008;71(21):1415-1429. doi:10.1080/15287390802328630 ↑
Qin X. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011;25(9):511. doi:10.1155/2011/451036 ↑
Schernhammer ES, Bertrand KA, Birmann BM, Sampson L, Willett WC, Feskanich D. [published correction appears in Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 Aug;98(2):512]. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96(6):1419-1428. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.030833. ↑
Fowler SP, Williams K, Resendez RG, Hunt KJ, Hazuda HP, Stern MP. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16(8):1894-1900. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.284 ↑
Sylvetsky A, Rother KI, Brown R. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011;58(6):1467-xi. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2011.09.007. ↑
Yang Q. Neuroscience 2010. Yale J Biol Med. 2010;83(2):101-108. ↑
Peteliuk V, Rybchuk L, Bayliak M, Storey KB, Lushchak O. EXCLI J. 2021;20:1412-1430. Published 2021 Sep 22. doi:10.17179/excli2021-4211. ↑
Samuel P, Ayoob KT, Magnuson BA, et al. J Nutr. 2018;148(7):1186S-1205S. doi:10.1093/jn/nxy102. ↑
Ahmad J, Khan I, Blundell R, Azzopardi J, Mahomoodally MF. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2020;100:177-189. doi:10.1016/J.TIFS.2020.04.030. ↑
Kasti AN, Nikolaki MD, Synodinou KD, et al. Microorganisms. 2022;10(4):744. Published 2022 Mar 30. doi:10.3390/microorganisms10040744. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4(2):568-586. Published 2012 Jan 1. doi:10.2741/e400 ↑
Kanarek RB. Nutr Rev. 2011;69(7):385-391. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00385.x ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(1):86-97.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.10.015 ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, et al. [published correction appears in Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1542]. Lancet. 2007;370(9598):1560-1567. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3 ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H.. J Food Sci. 2011;76(6):T125-T129. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02267.x ↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
View Latest Certificate of Analysis ↑