If you don’t like something of ours, guess what happens next?
No, we don’t request you deliver it to a PO box in the Gobi Desert by carrier pigeon. Nor do we ask you to fill a cursed inkwell with orc’s blood and demon saliva and then use it to complete reams of return forms written in ancient Cyrillic script.
We just . . . wait for it . . . give you every penny of your money back. Holy moo cows. And that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
Ingredients & Directions
Directions
Take 4 capsules, two times daily, with meals. For optimal results, take every day.
Warning
Check with a qualified healthcare professional before using this product if you are under 18 years of age or if you have any known or suspected medical condition(s) and/or are taking any prescription or OTC medication(s).
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. STORE IN A COOL, DRY PLACE. DO NOT USE IF SAFETY SEAL IS BROKEN OR MISSING.
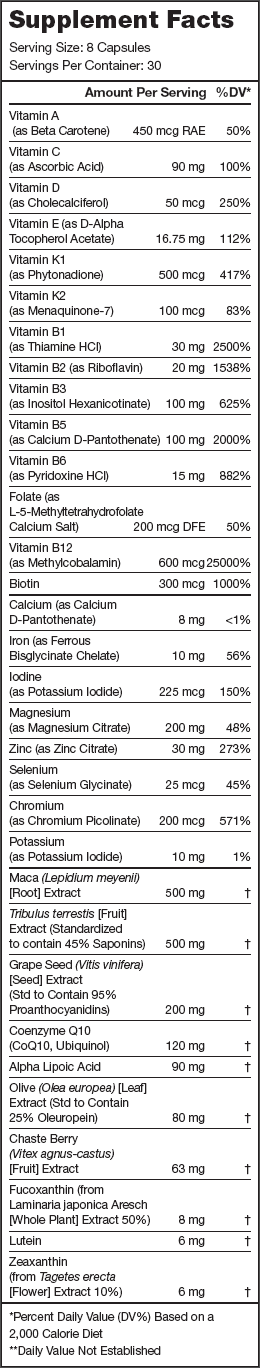
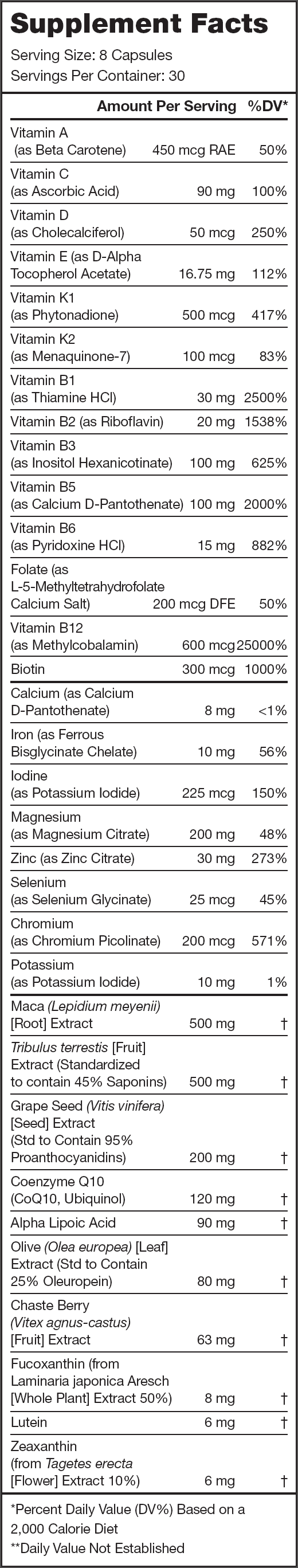
Legion Triumph Ingredients (2,196 milligrams per serving)
22 Essential Vitamins and Minerals (623 milligrams per serving)
Triumph contains clinically effective doses of twenty-two vitamins and minerals that are vital for health, performance, and wellbeing, including those often overlooked or under-dosed in other multivitamins like vitamin K1, K2, and D, and zinc, magnesium, iodine, and chromium.

Alpha-Lipoic Acid (90 milligrams per serving)
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) is a molecule produced by the body and found in several foods, including yeast, liver, kidney, spinach, broccoli, and potatoes.
It acts as an antioxidant and can increase the activity of other antioxidants by influencing a protein known as Nrf2.[7]
Research shows that supplementation with alpha-lipoic acid supports levels of an antioxidant known as glutathione in the body, which occurs in all cells and is a primary defense against oxidative damage.[8][9]
It also supports your body’s energy production by increasing the activity of enzymes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase, which help turn food into usable energy in your cells.[10][11]
We chose to include 90 milligrams of ALA per serving because this dose provides meaningful health benefits and enhances the effects of CoQ10, another key ingredient in Triumph.

Grape Seed Extract (200 milligrams per serving)
Grape seed extract is a substance derived from the ground-up seeds of red wine grapes.
It has long been used in European medicine because it contains a powerful antioxidant known as procyanidin B2.
Research shows that supplementation with grape seed extract . . .
- Increases nitric oxide production (which improves blood flow and endurance)[12][13]
- Enhances blood flow to the extremities, which can reduce the appearance of varicose veins[14]
- May protect eye health[15]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[16]
The clinically effective dose of grape seed extract is between 75 and 300 milligrams.

Maca (500 milligrams per serving)
Maca is a plant native to Peru that has been cultivated for thousands of years for its root, which was an integral part of the diet and commerce of the ancient Incan civilization.
It contains several types of molecules known as alkaloids, which cause a number of positive effects in the body and are responsible for maca’s beneficial effects.
Research shows that supplementation with maca . . .
- Improves subjective sense of well-being[17]
- Improves sexual function in men and women[18]
- Improves libido in men and women[19][20]
- Helps preserve joint health[21]
The clinically effective dose of maca extract is between 1 and 3 grams.
We chose to include 500 milligrams per serving because it’s enough to support sexual health and well-being but not so much as to produce an aphrodisiac effect, which, alongside tribulus terrestris, could be quite significant.

Tribulus Terrestris (500 milligrams per serving)
Tribulus terrestris is an herb that has long been used in Ayurvedic medicine to promote male sexual wellness, health, and virility.
It contains molecules known as saponins, which can mimic the effect of various steroid hormones in the body.
Studies show that tribulus terrestris doesn’t improve testosterone levels in men, as is often claimed, but interestingly, does support female sexual health and well-being.[22][23]
That’s why research shows that supplementation with tribulus terrestris benefits women experiencing diminished sex drive, including those experiencing menopause.[24][25]
The clinically effective dose of tribulus terrestris is between 500 and 750 milligrams, depending on saponin content.

Vitex Agnus-Castus (63 milligrams per serving)
Vitex agnus-castus (also known as chasteberry) is a shrub native to the Mediterranean and Central Asia.
Research shows that supplementation with vitex agnus-castus alleviates and can even help reduce side effects of menstruation including cramping, breast tenderness, headaches, and irritability.[26][27][28][29][30]
The clinically effective dose of vitex agnus-castus is between 150 and 250 milligrams of dry fruit.
Triumph contains 63 milligrams of vitex agnus-castus extract (providing the equivalent of 250 milligrams of dry fruit) per serving.

Olive Leaf Extract (80 milligrams per serving)
Olive leaf extract comes from the leaves of the olive plant, which has been used in European and Middle Eastern medicine for many centuries.
It contains an antioxidant called oleuropein, which can get into your cells’ energy centers—known as mitochondria—and help protect them from damage.
Research shows that supplementation with olive leaf extract helps protect against aging and damage caused by oxidative stress.[31][32][33]
The clinically effective dose of olive leaf extract is between 10 and 1,000 milligrams.

Coenzyme Q10 (120 milligrams per serving)
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance found in a wide variety of foods, but it’s particularly abundant in organ meats such as heart, liver, and kidney.
It’s also in every cell of the body and functions as an antioxidant and helps with the production of cellular energy.
Research shows that supplementation with CoQ10 . . .
- Supports cardiovascular function[34][35][36]
- Protects sperm structure and function[37]
- Supports antioxidant protection[38]
- Supports mitochondrial function[39][40][41]
The clinically effective dose of CoQ10 is between 50 and 200 milligrams, with the majority of benefits seen at 90 milligrams.
Fucoxanthin (8 milligrams per serving)
Fucoxanthin is a carotenoid, a vitamin A-like molecule found primarily in brown seaweed and microalgae.
It enters cells and increases levels of PGC1-α, a protein in mitochondria that controls how cells produce energy. This process helps your body use energy more efficiently, which is why research shows that supplementation with fucoxanthin improves aerobic performance.[42]
It’s also an antioxidant that crosses the blood-brain barrier and reduces reactive oxygen species—unstable molecules that damage neurons. In doing so, it supports memory, focus, and concentration.[43]
The clinically effective dose of fucoxanthin is between 2.4 and 8 milligrams.

Zeaxanthin (6 milligrams per serving)
Zeaxanthin is a vitamin A-like molecule known as a carotenoid, and it’s found in egg yolks as well as a wide variety of plants and fruits.
Like all carotenoids, it’s an antioxidant but is unique in that it can access areas of the body that others can’t, including the brain and eyes.
Research shows that supplementation with zeaxanthin . . .
- Supports eye function and health[44][45][46][47]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[48]
- May support cognitive function[49][50]
The clinically effective dose of zeaxanthin is between 4 and 8 milligrams.
Lutein (6 milligrams per serving)
Lutein is a vitamin A-like molecule known as a carotenoid, and it’s found in a number of foods including broccoli, grapes, and squash.
Like zeaxanthin, it’s unique in that it can access areas of the body that other antioxidants can’t, including the brain and eyes.
Research shows that supplementation with lutein . . .
- Supports eye function and health[51][52][53][54][55]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[56]
- May support cognitive function[57][58]
The clinically effective dose of lutein is between 4 and 8 milligrams.

No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
Artificial food dyes and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, but studies show they can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[59][60][61][62][63]
That’s why we use natural coloring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for enhancing shelf life and facilitating the manufacturing process.

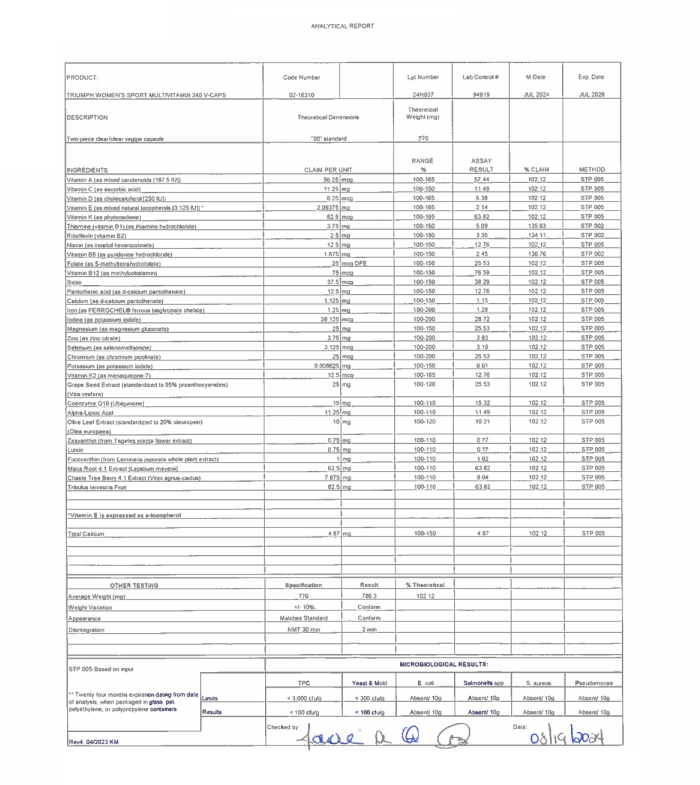
Third-Party Lab Tested for Purity and Potency
Triumph is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
See how Legion Triumph compares to the rest.
- Active Ingredients
- Vitamins K1 and K2
- Folate as 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate
- Vitamin B12 as Methylcobalamin
- Vitex Agnus-Castus (Chasteberry)
- CoQ10
- Maca Extract
- Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Product
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion
Triumph
- 2,196 mg
per serving - 600 mcg
per serving - 200 mcg
per serving - 600 mcg
per serving - 63 mg
per serving - 120 mg
per serving - 500 mg
per serving - $
-
Vita
JYM
- 1,157 mg
per serving - 120 mcg
per serving - $0.83
-
PEScience
TruMulti
- 1,325 mg
per serving - 120 mcg
per serving - 2.4 mcg
per serving - $0.83
-
Optimum Nutrition
Opti-Women
- 1,017 mg
per serving - 80 mcg
per serving - 50 mg
per serving - $0.42
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in Triumph is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
No Unnecessary Junk
Triumph contains no artificial food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in Triumph on the label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Third-Party Lab Tested for Purity and Potency
Triumph is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
Made in the USA
Triumph is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love Triumph, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Some popular sport multivitamins contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. Some don’t have any unnecessary junk. But only Triumph checks each of these boxes. ↑
Every serving of Triumph contains 2,196 milligrams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research. ↑
Each active ingredient in Triumph is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans. ↑
That’s 437 pages of scientific research that shows Triumph works exactly like we say it does. ↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Triumph. ↑
Every bottle of Triumph is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants. ↑
Suh JH, Shenvi SV, Dixon BM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(10):3381-3386. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400282101 ↑
Bast A, Haenen GR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988;963(3):558-561. doi:10.1016/0005-2760(88)90326-8 ↑
Suh JH, Shenvi SV, Dixon BM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(10):3381-3386. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400282101 ↑
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8409329. Published 2019 Nov 30. doi:10.1155/2019/8409329 ↑
Rodriguez MC, MacDonald JR, Mahoney DJ, Parise G, Beal MF, Tarnopolsky MA. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35(2):235-242. doi:10.1002/mus.20688 ↑
Nho H, Kim KA. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):14223. Published 2022 Oct 31. doi:10.3390/ijerph192114223. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9658680/ ↑
Kim JK, Stebbins CL. Res Inves Sports Med. 2018;2(2):113-114. doi:10.31031/RISM.2018.02.000531. https://crimsonpublishers.com/rism/pdf/RISM.000531.pdf ↑
Sano A, Tokutake S, Seo A.. J Sci Food Agric. 2013;93(3):457-462. doi:10.1002/jsfa.5773. ↑
Yang H, Lee BK, Kook KH, Jung YS, Ahn J. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37(4):339-344. doi:10.3109/02713683.2011.645106. ↑
Gupta M, Dey S, Marbaniang D, Pal P, Ray S, Mazumder B. J Food Sci Technol. 2020;57(4):1205-1215. doi:10.1007/s13197-019-04113-w. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7054588/ ↑
G. Cicero, Linda Valmorri, Melissa Mercuriali, and Eduard Bercovich, Andrologia 41, no. 2 (2009): 95–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2008.00892.x. ↑
Brooks, Gisela Wilcox, Karen Z. Walker, John F. Ashton, Marc B. Cox, and Lily Stojanovska, Menopause 15, no. 6 (2008): 1157–62. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3181732953. ↑
Gonzales, Amanda Córdova, Karla Vega, Arturo Chung, Arturo Villena, Carmen Góñez, and Sonia Castillo, Andrologia 34, no. 6 (2002): 367–72. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0272.2002.00519.x; ↑
meyenii) for the Management of SSRI-Induced Sexual Dysfunction,” Christina M. Dording, Lauren Fisher, George Papakostas, Amy Farabaugh, Shamsah Sonawalla, Maurizio Fava, and David Mischoulon, CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 14, no. 3 (2008): 182–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00052.x. ↑
S. Miller, Salahuddin Ahmed, Paul Bobrowski, and Tariq M. Haqqi, BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 6 (2006): 13. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-6-13. ↑
Qureshi A, Naughton DP, Petroczi A. J Diet Suppl. 2014;11(1):64-79. doi:10.3109/19390211.2014.887602 ↑
Akhtari E, Raisi F, Keshavarz M, et al. Daru. 2014;22(1):40. Published 2014 Apr 28. doi:10.1186/2008-2231-22-40 ↑
Akhtari E, Raisi F, Keshavarz M, et al. Daru. 2014;22(1):40. Published 2014 Apr 28. doi:10.1186/2008-2231-22-40 ↑
Postigo S, Lima SM, Yamada SS, dos Reis BF, da Silva GM, Aoki T. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2016;38(3):140-146. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1571472 ↑
Momoeda M, Sasaki H, Tagashira E, Ogishima M, Takano Y, Ochiai K. Adv Ther. 2014;31(3):362-373. doi:10.1007/s12325-014-0106-z ↑
Schellenberg R, Zimmermann C, Drewe J, Hoexter G, Zahner C.. Phytomedicine. 2012;19(14):1325-1331. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2012.08.006 ↑
Zamani M, Neghab N, Torabian S.. Acta Med Iran. 2012;50(2):101-106. ↑
Ma L, Lin S, Chen R, Wang X.. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2010;26(8):612-616. doi:10.3109/09513591003632126 ↑
He Z, Chen R, Zhou Y, et al. Treatment for premenstrual syndrome with Vitex agnus castus:. Maturitas. 2009;63(1):99-103. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.01.006 ↑
Covas MI, de la Torre K, Farré-Albaladejo M, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40(4):608-616. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.09.027 ↑
Raederstorff D. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2009;79(3):152-165. doi:10.1024/0300-9831.79.3.152 ↑
García-Villalba R, Larrosa M, Possemiers S, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(4):1015-1027. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0604-9 ↑
Watts GF, Playford DA, Croft KD, Ward NC, Mori TA, Burke V.. Diabetologia. 2002;45(3):420-426. doi:10.1007/s00125-001-0760-y ↑
Hamilton SJ, Chew GT, Watts GF. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(5):810-812. doi:10.2337/dc08-1736 ↑
Ahmadvand H, Mabuchi H, Nohara A, Kobayahi J, Kawashiri MA. Acta Med Iran. 2013;51(1):12-18. ↑
Talevi R, Barbato V, Fiorentino I, Braun S, Longobardi S, Gualtieri R. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:81. Published 2013 Aug 16. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-11-81 ↑
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH, Lin PT. Nutr J. 2013;12(1):142. Published 2013 Nov 6. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-12-142 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24192015 ↑
Drobnic F, Lizarraga MA, Caballero-García A, Cordova A. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1811. Published 2022 Apr 26. doi:10.3390/nu14091811 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9104583/ ↑
Metabolic Targets of Coenzyme Q10 in Mitochondria. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(4):520. Published 2021 Mar 26. doi:10.3390/antiox10040520 ↑
Quinzii CM, Hirano M. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2010;16(2):183-188. doi:10.1002/ddrr.108 ↑
Dickerson B, Maury J, Jenkins V, et al. Nutrients. 2024;16(7):990. Published 2024 Mar 28. doi:10.3390/nu16070990 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11013338/ ↑
Yoo C, Maury J, Gonzalez DE, et al. Nutrients. 2024;16(17):2999. Published 2024 Sep 5. doi:10.3390/nu16172999 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11397347/ ↑
Dawczynski J, Jentsch S, Schweitzer D, Hammer M, Lang GE, Strobel J.. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(12):2711-2723. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2376-6 ↑
3. Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2) Research Group, Chew EY, Clemons TE, et al. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(2):142-149. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.7376 ↑
Ma L, Hao ZX, Liu RR, Yu RB, Shi Q, Pan JP.. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252(1):63-70. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2492-3 ↑
Karppi J, Laukkanen JA, Kurl S. Br J Nutr. 2012;108(1):148-154. doi:10.1017/S0007114511005332 ↑
Murillo AG, Hu S, Fernandez ML. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(9):390. Published 2019 Sep 11. doi:10.3390/antiox8090390 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6770730/ ↑
Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Drummond PD. Front Nutr. 2022;9:843512. Published 2022 Feb 17. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.843512https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8891800/ ↑
Renzi-Hammond LM, Bovier ER, Fletcher LM, et al. Nutrients. 2017;9(11):1246. Published 2017 Nov 14. doi:10.3390/nu9111246https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29135938/ ↑
Improvement of retinal function in early age-related macular degeneration after lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation: a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;154(4):625-634.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2012.04.014 ↑
Ma L, Yan SF, Huang YM, et al.. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(11):2290-2297. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.06.014 ↑
Berrow EJ, Bartlett HE, Eperjesi F, Gibson JM.. Br J Nutr. 2013;109(11):2008-2014. doi:10.1017/S0007114512004187 ↑
Nidhi B, Mamatha BS, Padmaprabhu CA, Pallavi P, Vallikannan B. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2013;61(12):722-727. doi:10.4103/0301-4738.120218 ↑
Ma L, Hao ZX, Liu RR, Yu RB, Shi Q, Pan JP. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252(1):63-70. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2492-3http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24150707 ↑
Lutein as a Modulator of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(9):1448. Published 2021 Sep 13. doi:10.3390/antiox10091448 ↑
Dietary Lutein and Cognitive Function in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Molecules. 2021;26(19):5794. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3390/molecules26195794 ↑
Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Drummond PD. Front Nutr. 2022;9:843512. Published 2022 Feb 17. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.843512 ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H.. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4(2):568-586. Published 2012 Jan 1. doi:10.2741/e400http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22201895 ↑
Kanarek RB. Nutr Rev. 2011;69(7):385-391. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00385.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21729092 ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(1):86-97.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.10.015 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22176942 ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, et al. [published correction appears in Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1542]. Lancet. 2007;370(9598):1560-1567. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17825405 ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. J Food Sci. 2011;76(6):T125-T129. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02267.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22417523 ↑
























