Not happy with your purchase?
Simply let us know, and you'll get a full refund, no questions asked. And you don't even need to return anything.
So that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
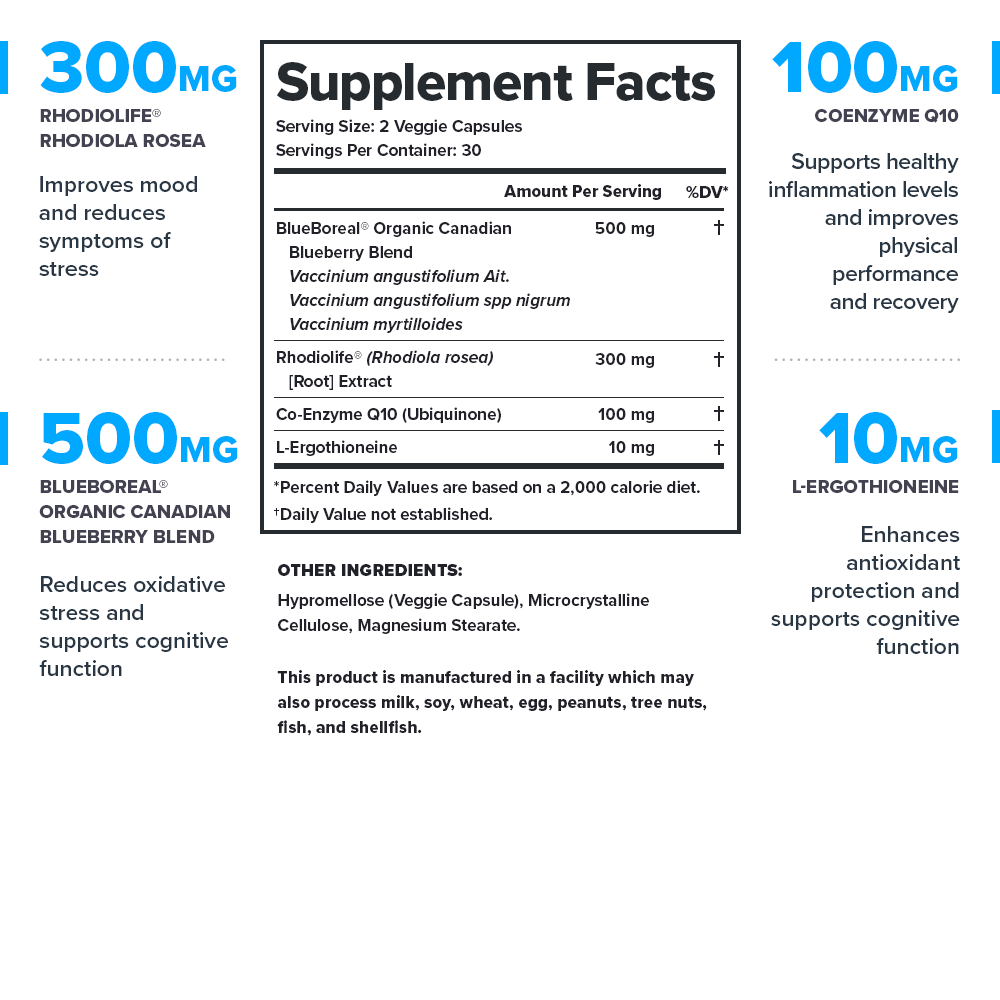
Legion Vitality Ingredients (910 milligrams per serving)
Rhodiolife® Rhodiola Rosea (300 milligrams per serving)
Rhodiola rosea (also known as Golden Root) is a plant that grows in cold parts of the world, including the Arctic regions of Europe, Asia, and North America.
Rhodiolife® is a patented and standardized form of Rhodiola rosea that has demonstrated superior effectiveness to other commonly available forms in clinical research.
Rhodiola rosea contains a number of bioactive molecules, including three in particular that have been extensively studied: salidroside, rosavin, and rosarin.
These are known as adaptogens, which are substances that support various systems in the body related to physical, environmental, and emotional resilience.
Research shows that supplementation with Rhodiolife® rhodiola rosea . . .
- Improves mood and reduces symptoms of stress[7][8][9]
- Reduces stress-related fatigue[10]
- Supports cognition during strenuous periods[11]
- Enhances post-workout recovery[12]
- Supports immune health[13]
- May boost physical performance[14]
The clinically effective dose of rhodiola rosea is 100-to-400 milligrams of an extract standardized to contain 3% rosavins and 1% salidroside (like the Rhodiolife® rhodiola rosea extract in Vitality).

BlueBoreal® Organic Canadian Blueberry Blend (500 milligrams per serving)
Blueberries are a rich source of health-promoting nutrients, phytochemicals, and antioxidants, including vitamin K, quercetin, resveratrol, and more.
They’re also one of the best natural sources of anthocyanins, which are pigments that give blueberries their color and possess powerful antioxidant properties.
Research shows that supplementation with blueberries . . .
- Supports cognitive function[15][16]
- Reduces oxidative stress[17][18][19][20][21]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[22][23][24][25][26]
- Supports fat burning during exercise[27]
The clinically effective dose of blueberries is 25 grams or its equivalent in a concentrated extract. And in the case of the BlueBoreal® Organic Canadian Blueberry Blend extract, 500 milligrams provides the equivalent of 27.5 grams of blueberries.

Coenzyme Q10 (100 milligrams per serving)
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance that helps enzymes perform bodily processes (hence “coenzyme”). It’s found in a variety of foods, especially organ meats such as heart, liver, and kidney.
It’s present in every cell of the body, particularly in the mitochondria (the “powerhouses” of the cells), and it plays a crucial role in the production of cellular energy and functions as an antioxidant.
Moreover, as cellular CoQ10 levels decline with age, scientists believe that this circumstance may contribute to the development of age-related disorders, including the aging process itself.[28][29][30][31]
Research shows that supplementation with CoQ10 . . .
- Reduces oxidative stress[32]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[33]
- Supports healthy inflammation levels[34]
- Boosts physical performance and recovery[35][36][37]
- Supports male fertility[38]
The clinically effective dose of CoQ10 is 50-to-200 milligrams.

L-Ergothioneine (10 milligrams per serving)
Ergothioneine is an amino acid found in certain types of mushrooms—the richest dietary source—beans, vegetables, meat, and grains.
It’s present in every cell in the body, particularly those exposed to high levels of oxidative stress or metabolic activity like neurons, cardiac, immune, and liver cells, and it possesses powerful antioxidant properties.
What’s more, as cellular L-ergothioneine levels decline with age, scientists believe that this circumstance may contribute to the development of age-related disorders, including the aging process itself.[39][40][41][42]
Research shows that supplementation with ergothioneine . . .
- Supports cognitive function[43]
- Reduces oxidative stress[44][45][46]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[47][48]
The clinically effective dose of ergothioneine is 10 milligrams.

No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
Artificial food dyes and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, but studies show they can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[49][50][51][52][53]
That’s why we use natural coloring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for enhancing shelf life and facilitating the manufacturing process.

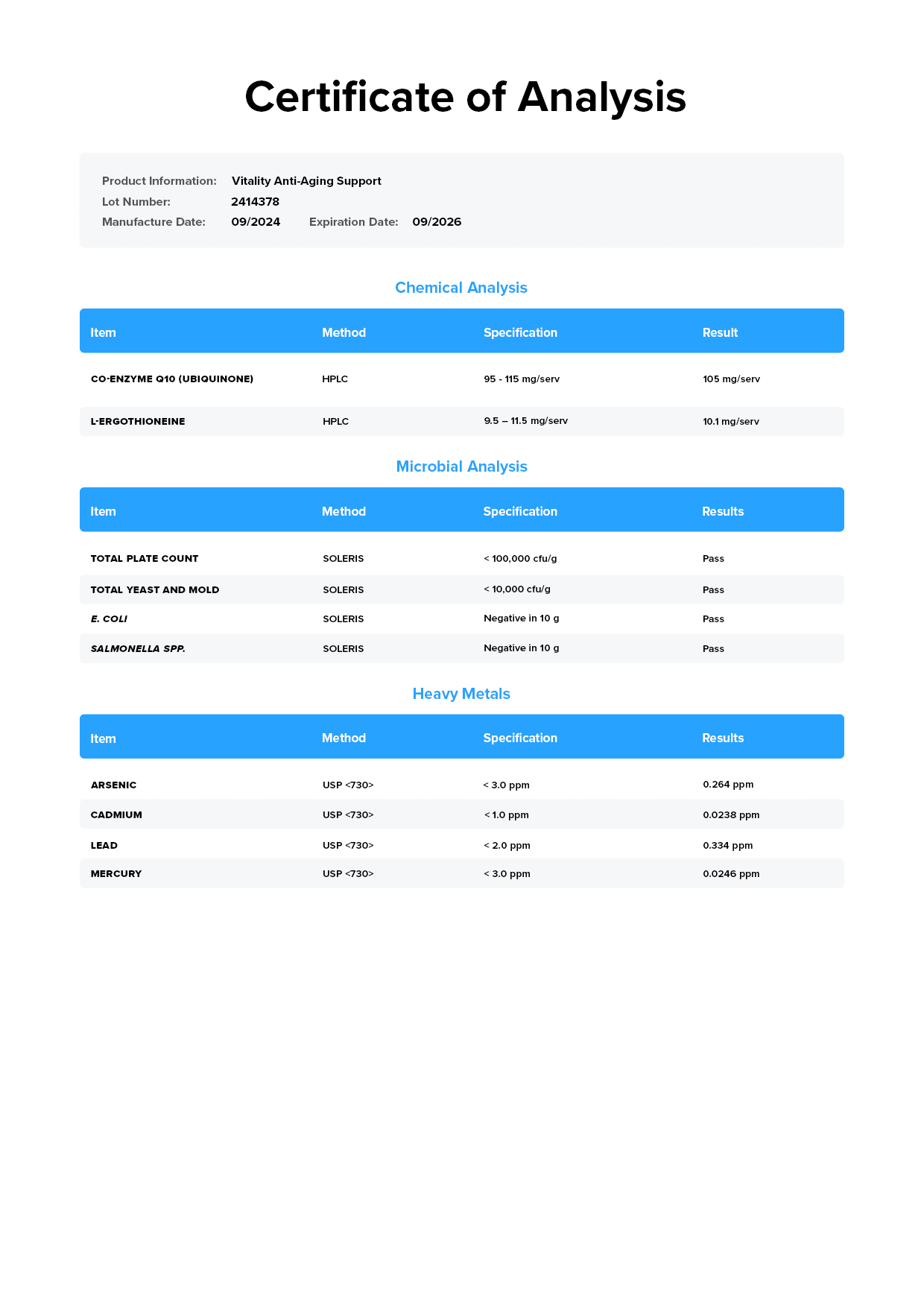
Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Vitality is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA and WADA safety guidelines.[54]
Made in the USA with Globally Sourced Ingredients
If you want to ensure the supplements you’re swallowing every day are safe and effective, you want to buy from a company that:
- Sources ingredients from premium suppliers around the world (great supplements require great raw materials)
- Tests all products for purity and accuracy in accredited laboratories (to conclusively verify safety and efficacy)
- Manufactures in America, which has some of the strictest regulations in the world
And that’s exactly what we do here at Legion.
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in Vitality is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
No Unnecessary Junk
Vitality contains no artificial food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in Vitality on the label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
Vitality is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA and WADA safety guidelines.
Made in the USA
Vitality is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love Vitality, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Some popular vitality supplements contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. Some don’t have any unnecessary junk. But only Vitality checks each of these boxes.↑
104 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Vitality’s ingredients and doses. That’s 832 pages of scientific research that shows Vitality works the way we say it does.↑
Every serving of Vitality contains 910 milligrams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
View Supplement Facts↑
Each active ingredient in Vitality is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Many supplement ingredients lack scientific validation in humans—we aren't large rodents, after all.
And even when ingredients have proven benefits, they're often used in doses too small to be effective.
That's why we exclusively use ingredients and doses shown to work in peer-reviewed scientific studies on healthy men and women.↑
That’s 952 pages of scientific research that shows Vitality works the way we say it does.↑
The proprietary blend is little more than a sneaky way to use tiny (ineffective) amounts of lots of ingredients and hope customers don’t know any better.
Every dose listed. For every ingredient. In every product. Anything else is unacceptable.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Vitality.↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every batch and guarantee our products provide exactly what the labels claim—and nothing else.
With Legion, you can be certain that what you're putting into your body is truly safe and effective.
↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every ingredient in a third-party lab for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants, ensuring they meet the strict purity standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).↑
Cropley M, Banks AP, Boyle J. Phyther Res. 2015;29(12):1934-1939. doi:10.1002/ptr.5486.↑
Darbinyan V, Aslanyan G, Amroyan E, Gabrielyan E, Malmström C, Panossian A. Nord J Psychiatry. 2007;61(5):343-348. doi:10.1080/08039480701643290.↑
Mao JJ, Xie SX, Zee J, et al. Phytomedicine. 2015;22(3):394-399. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2015.01.010.↑
Olsson EMG, Von Schéele B, Panossian AG. Planta Med. 2009;75(2):105-112. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1088346.↑
Edwards D, Heufelder A, Zimmermann A. Phyther Res. 2012;26(8):1220-1225. doi:10.1002/ptr.3712.↑
Parisi A, Tranchita E, Duranti G, et al. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2010;50(1):57-63.↑
Diwaker D, Mishra KP, Ganju L, Singh SB. Arch Virol. 2014;159(8):1975-1986. doi:10.1007/s00705-014-2028-0.↑
Noreen EE, Buckley JG, Lewis SL, Brandauer J, Stuempfle KJ. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(3):839-847. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31825d9799. ↑
Krikorian R, Shidler MD, Nash TA et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(7):3996-4000. ↑
Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Pouchieu C et al. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1144231. ↑
Kay CD, Holub BJ. Br J Nutr. 2002;88(4):389-98. ↑
Blacker BC, Snyder SM, Eggett DL, Parker TL. Br J Nutr. 2013;109(9):1670-7. ↑
Riso P, Klimis-Zacas D, Del Bo C et al. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52(3):949-61. ↑
Wilms LC, Boots AW, de Boer VC et al. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28(8):1800-6. ↑
Del Bó C, Riso P, Campolo J et al. Nutr Res. 2013;33(3):220-7. ↑
Kay CD, Holub BJ. Br J Nutr. 2002;88(4):389-98. ↑
Blacker BC, Snyder SM, Eggett DL, Parker TL. Br J Nutr. 2013;109(9):1670-7. ↑
Riso P, Klimis-Zacas D, Del Bo C et al. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52(3):949-61. ↑
Wilms LC, Boots AW, de Boer VC et al. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28(8):1800-6. ↑
Del Bó C, Riso P, Campolo J et al. Nutr Res. 2013;33(3):220-7. ↑
Pilolla KD, Armendariz J, Burrus BM, Baston DS, McCarthy KA, Bloedon TK. Nutrients [Internet]. 2023. doi:10.3390/nu15061339. ↑
Fernández-Portero C, Amián JG, Bella R, López-Lluch G, Alarcón D. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023;78(1):1-8. doi:10.1093/gerona/glac152. ↑
de la Bella-Garzón R, Fernández-Portero C, Alarcón D, Amián JG, López-Lluch G. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):279. Published 2022 Jan 29. doi:10.3390/antiox11020279. ↑
Hargreaves I, Heaton RA, Mantle D. Published 2020 Sep 13. doi:10.3390/ijms21186695. ↑
Gutierrez-Mariscal FM, Yubero-Serrano EM, Villalba JM, Lopez-Miranda J. 2019;59(14):2240-2257. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1442316. ↑
Sangsefidi ZS, Yaghoubi F, Hajiahmadi S, Hosseinzadeh M. Food Sci Nutr. 2020;8(4):1766-1776. Published 2020 Mar 19. doi:10.1002/fsn3.1492. ↑
Ibid.↑
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH, Lin PT. Nutr J. 2013;12(1):142. Published 2013 Nov 6. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-12-142 ↑
Gökbel H, Gül I, Belviranl M, Okudan N. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(1):97-102. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a61a50. ↑
Gül I, Gökbel H, Belviranli M, Okudan N, Büyükbaş S, Başarali K. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011;51(2):305-312. ↑
Liao P, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Zheng NJ, Zhang X. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2007;23(4):491-494. ↑
Talevi R, Barbato V, Fiorentino I, Braun S, Longobardi S, Gualtieri R. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:81. Published 2013 Aug 16. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-11-81. ↑
Cheah IK, Halliwell B. Redox Biol. 2021;42:101868.↑
Ames BN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(43):10836-44. ↑
Apparoo Y, Phan CW, Kuppusamy UR, Sabaratnam V. Exp Gerontol. 2022;170:111982. ↑
Beelman RB, Kalaras MD, Phillips AT, Richie JP Jr. J Nutr Sci. 2020;9:e52. Published 2020 Nov 11. doi:10.1017/jns.2020.44. ↑
Ishimoto T, Kato Y. FEBS Lett. 2022;596(10):1290-8. ↑
Cheah IK, Tang RM, Yew TS, Lim KH, Halliwell B. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017;26(5):193-206. ↑
Cheah IK, Halliwell B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(5):784-93. ↑
Halliwell B, Cheah IK, Drum CL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;470(2):245-50. ↑
Fu TT, Shen L. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:850813. Published 2022 Mar 18. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.850813. ↑
Chen L, Zhang L, Ye X, Deng Z, Zhao C. Protein Cell. 2024;15(3):191-206. doi:10.1093/PROCEL/PWAD048. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every ingredient in a third-party lab for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants, ensuring they meet the strict purity standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and World Anti Doping Agency (WADA).↑