If you don’t like something of ours, guess what happens next?
No, we don’t request you deliver it to a PO box in the Gobi Desert by carrier pigeon. Nor do we ask you to fill a cursed inkwell with orc’s blood and demon saliva and then use it to complete reams of return forms written in ancient Cyrillic script.
We just . . . wait for it . . . give you every penny of your money back. Holy moo cows. And that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
Legion Vitamin B Complex Ingredients (685.6 milligrams per serving)
8 Essential Vitamin B Vitamins (85.6 milligrams per serving)
Vitamin B Complex contains clinically effective doses of all eight essential B vitamins that are vital for many aspects of health, performance, and wellbeing, including metabolism; brain, nervous, and DNA health and function; cellular growth and repair; hormone production, and more.[7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52][53][54][55][56][57][58][59][60][61]
Choline (250 milligrams per serving)
Choline is an essential nutrient that was formerly considered a B vitamin (B4) but now is recognized as a distinct substance. It’s found in foods like meat, fish, nuts, beans, vegetables, and eggs, and it’s vital for brain, nervous, and liver health and function.
Research shows that supplementation with choline . . .
While it’s possible to get enough choline through your diet to support optimal health, it can be difficult because it requires eating adequate amounts of foods that many people don’t eat, including eggs, liver, and peanuts.
This is why research shows that up to 94% of women and 89% of men in America don’t consume the minimum amount of choline needed to support health.[66]
There is no recommended daily allowance for choline, but the U.S. Food and Nutrition Board has set an Adequate Intake (AI) level of 550 milligrams per day for adult men and 425 milligrams per day for women.
Inositol (250 milligrams per serving)
Inositol, also (now erroneously) known as vitamin B8, is a group of molecules involved in cellular signaling and the health and function of cell membranes.
While it’s possible to get enough inositol through your diet to support optimal health, it can be difficult because it requires eating adequate amounts of foods that many people don’t eat, including citrus fruits, whole grains, beans, nuts, and green leafy vegetables.
Research shows that supplementation with inositol . . .
There is no recommended daily allowance for inositol, but it’s often suggested that adult men and women consume approximately 1-to-4 grams per day to support health.
Coenzyme Q10 (100 milligrams per serving)
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance that helps enzymes perform bodily processes (hence “coenzyme”). It’s found in a variety of foods, especially organ meats such as heart, liver, and kidney.
It’s present in every cell of the body, particularly in the mitochondria (the “powerhouses” of the cells), and it plays a crucial role in the production of cellular energy and functions as an antioxidant.
Moreover, as cellular CoQ10 levels decline with age, scientists believe that this circumstance may contribute to the development of age-related disorders, including the aging process itself.[70][71][72][73]
Research shows that supplementation with CoQ10 . . .
- Reduces oxidative stress[74]
- Enhances antioxidant protection[75]
- Supports healthy inflammation levels[76]
- Boosts physical performance and recovery[77][78][79]
- Improves male fertility[80]
The clinically effective dose of CoQ10 is 50-to-200 milligrams.
No Artificial Food Dyes, Fillers, or Other Unnecessary Junk
Artificial food dyes and fillers may not be as dangerous as some people claim, but studies show they can cause negative effects in some people, including gastrointestinal toxicity and behavioral disorders.[81][82][83][84][85]
That’s why we use natural coloring derived from fruits and other foods as well as naturally derived ingredients for enhancing shelf life and facilitating the manufacturing process.

Third-Party Lab Tested for Potency & Purity
Vitamin B Complex is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
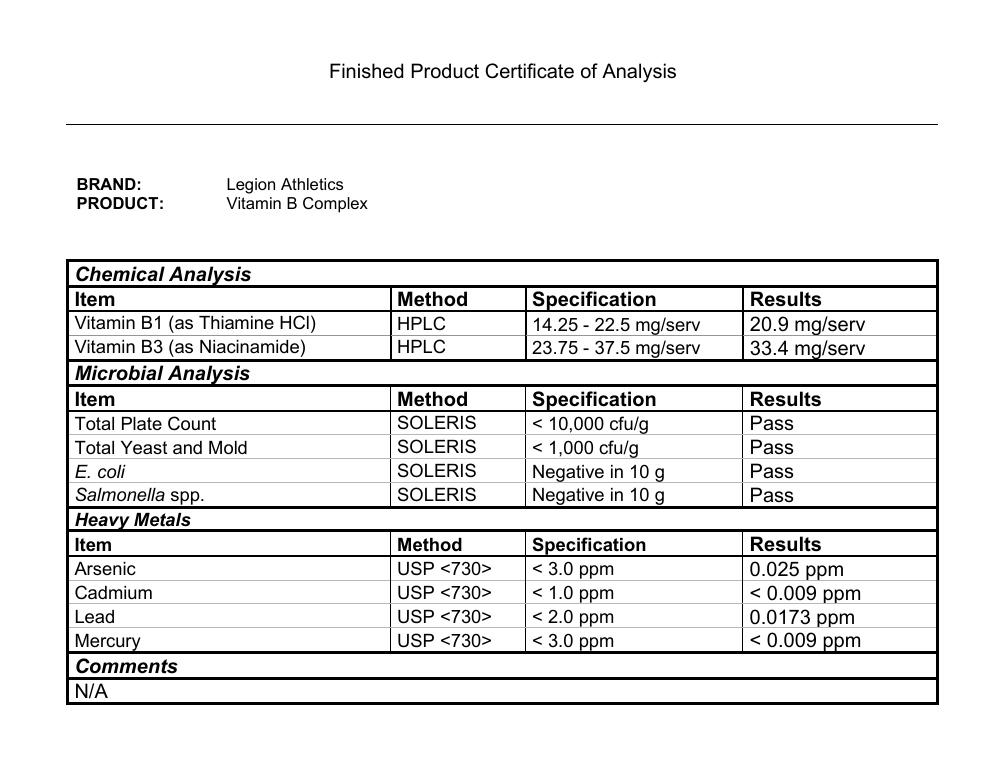
See how Legion Vitamin B Complex compares to the rest.
- Active Ingredients
Per Serving - Clinically Effective Ingredients
& Doses - B Vitamin Complex
- Choline
- Inositol
- Coenzyme Q10
- Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Brand
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion
Vitamin B Complex
- 685.6 mg
per serving - 85.6 mg
per serving - 250 mg
per serving - 250 mg
per serving - 250 mg
per serving - $
-
NOW Foods
Co-Enzyme B-Complex
- 551.9 mg
per serving - 301.9 mg
per serving - 25 mg
per serving - 30 mg
per serving - 10 mg
per serving - $0.43
-
Thorne
Basic B-Complex
- 409.4 mg
per serving - 381.4 mg
per serving - 28 mg
per serving - $0.43
-
Nature Made
B-100 Complex
- 556.8 mg
per serving - 500.8 mg
per serving - $0.35
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in Vitamin B Complex is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
No Unnecessary Junk
Vitamin B Complex contains no artificial food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in Vitamin B Complex on the label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Third-Party Lab Tested for Purity and Potency
Vitamin B Complex is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
Made in the USA
Vitamin B Complex is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love Vitamin B Complex, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Vitamin B Complex doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Vitamin B Complex contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
Every serving of Vitamin B Complex contains 685.6 milligrams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research. ↑
Each active ingredient in Vitamin B Complex is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans. ↑
That’s 1,058 pages of scientific research that shows Vitamin B Complex works exactly like we say it does. ↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Vitamin B Complex. ↑
Every bottle of Vitamin B Complex is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
Seligmann H, Halkin H, Rauchfleisch S, et al. Am J Med. 1991;91(2):151-155. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90007-K.↑
Shimon H, Almog S, Vered Z, et al. Am J Med. 1995;98(5):485-490. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80349-0. ↑
Mimenza Alvarado A, Aguilar Salinas B. Acta Neurol Mex. 2009 Dec;24(4):355-63.↑
Gibson GE, Hirsch JA, Cirio RT, Jordan BD, Fonzetti P, Elder J. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013;55:17-25. doi:10.1016/J.MCN.2012.09.001.↑
Lonsdale D. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3(1):49-59. doi:10.1093/ECAM/NEK009. ↑
Manzetti S, Zhang J, Van Der Spoel D. Biochemistry. 2014;53(5):821-835. doi:10.1021/BI401618Y. ↑
Kuzniarz M, Mitchell P, Cumming RG, Flood VM. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;132(1):19-26. doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(01)00922-9. ↑
Michels AJ, Hagen TM, Frei B. Annu Rev Nutr. 2013;33:45-70. doi:10.1146/ANNUREV-NUTR-071812-161246. ↑
Thompson DF, Saluja HS. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2017;42(4):394-403. doi:10.1111/JCPT.12548. ↑
Boehnke C, Reuter U, Flach U, Schuh-Hofer S, Einhäupl KM, Arnold G. Eur J Neurol. 2004;11(7):475-477. doi:10.1111/J.1468-1331.2004.00813.X.↑
Thakur K, Tomar SK, Singh AK, Mandal S, Arora S. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017;57(17):3650-3660. doi:10.1080/10408398.2016.1145104.↑
Powers HJ. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77(6):1352-1360. doi:10.1093/AJCN/77.6.1352.↑
Altschul R, Hoffer A, Stephen JD. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955;54(2):558-559. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(55)90070-9. ↑
Lavigne PM, Karas RH. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(4):440-446. doi:10.1016/J.JACC.2012.10.030. ↑
PL C, KG B, NK W, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986;8(6):1245-1255. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(86)80293-5. ↑
Kamanna VS, Kashyap ML. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101(8A). doi:10.1016/J.AMJCARD.2008.02.029. ↑
Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(8):1093-1099. doi:10.1136/JNNP.2003.025858. ↑
Foster PP, Rosenblatt KP, Kuljiš RO. Front Neurol. 2011;2. doi:10.3389/FNEUR.2011.00028. ↑
W G. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2004;3(2):88-93. doi:10.1111/J.1473-2130.2004.00115.X.↑
Bissett DL, Oblong JE, Berge CA. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31(7 Pt 2):860-866. doi:10.1111/J.1524-4725.2005.31732. ↑
Kirkland J. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(1):3-11. doi:10.2174/138161209787185823. ↑
Kirkland JB. Mutat Res. 2012;733(1-2):14-20. doi:10.1016/J.MRFMMM.2011.11.008. ↑
Wu BJ, Yan L, Charlton F, Witting P, Barter PJ, Rye KA. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(5):968-975. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.201129. ↑
Sen CK, Khanna S, Gordillo G, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Roy S. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;957:239-249. doi:10.1111/J.1749-6632.2002.TB02920.X. ↑
Gaddi A, Descovich GC, Noseda G, et al. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 1982;53(3-4):137-52.↑
Rumberger JA, Napolitano J, Azumano I, Kamiya T, Evans M. Nutr Res. 2011;31(8):608-615. doi:10.1016/J.NUTRES.2011.08.001. ↑
Trueb RM. Hautarzt. 2007 Aug;58(8):607-14.↑
Rushton DH. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27(5):396-404. doi:10.1046/J.1365-2230.2002.01076.X. ↑
B E-K, J R. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2005;4(1):4-9. doi:10.1111/J.1473-2165.2005.00151.X. ↑
Yang M, Moclair B, Hatcher V, et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2014;4(1):93-101. doi:10.1007/S13555-014-0052-3. ↑
Mooney S, Leuendorf JE, Hendrickson C, Hellmann H. Molecules. 2009;14(1):329-351. doi:10.3390/MOLECULES14010329. ↑
Leklem JE. J Nutr. 1990;120 Suppl 11(4):1503-1507. doi:10.1093/JN/120.SUPPL_11.1503. ↑
Percudani R, Peracchi A. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:273. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-10-273. ↑
Malouf R, Grimley Evans J. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2003;(4). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004393. ↑
Kennedy DO. Nutrients. 2016;8(2):68. doi:10.3390/NU8020068. ↑
Rail LC, Meydani SN. Nutr Rev. 1993;51(8):217-225. doi:10.1111/J.1753-4887.1993.TB03109.X. ↑
Tamura J, Kubota K, Murakami H, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;116(1):28-32. doi:10.1046/J.1365-2249.1999.00870.X. ↑
Scheinfeld N, Dahdah MJ, Scher R. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6(8):782-787. ↑
Trüeb RM. Int J Trichology. 2016;8(2):73-77. doi:10.4103/0974-7753.188040. ↑
Zempleni J, Wijeratne SSK, Kuroishi T. Biotin. In: Erdman JW, Macdonald IA, Zeisel SH, eds. 10th ed. Washington, DC: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012:359-74. ↑
MRC Vitamin Study Research Group. Lancet. 1991;338(8760):131-137. ↑
Czeizel AE, Dudás I. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(26):1832-1835. doi:10.1056/NEJM199212243272602. ↑
Boushey CJ, Beresford SA, Omenn GS, Motulsky AG. JAMA. 1995;274(13):1049-1057. doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03530130055028. ↑
Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK. BMJ. 2002;325(7374):1202. doi:10.1136/bmj.325.7374.1202. ↑
Coppen A, Bolander-Gouaille C. J Psychopharmacol. 2005;19(1):59-65. doi:10.1177/0269881105048899. ↑
Bottiglieri T. Nutr Rev. 1996;54(12):382-390. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.1996.tb03851.x. ↑
Clarke R, Birks J, Nexo E, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86(5):1384-1391. doi:10.1093/ajcn/86.5.1384. ↑
Tangney CC, Aggarwal NT, Li H, et al. [published correction appears in Neurology. 2011 Nov 8;77(19):1773]. Neurology. 2011;77(13):1276-1282. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182315a33. ↑
Voutilainen S, Lakka TA, Porkkala-Sarataho E, Rissanen T, Kaplan GA, Salonen JT. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000;54(5):424-428. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600991. ↑
Sen CK, Khanna S, Gordillo G, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Roy S. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;957:239-249. doi:10.1111/J.1749-6632.2002.TB02920.X. ↑
Gaddi A, Descovich GC, Noseda G, et al. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 1982;53(3-4):137-52.↑
Rumberger JA, Napolitano J, Azumano I, Kamiya T, Evans M. Nutr Res. 2011;31(8):608-615. doi:10.1016/J.NUTRES.2011.08.001. ↑
Trueb RM. Hautarzt. 2007 Aug;58(8):607-14.↑
Rushton DH. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002;27(5):396-404. doi:10.1046/J.1365-2230.2002.01076.X. ↑
Cohen BM, Renshaw PF, Stoll AL, Wurtman RJ, Yurgelun-Todd D, Babb SM. JAMA. 1995;274(11):902-907. ↑
Wurtman RJ. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15(4):117-122. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(92)90351-8. ↑
Li Z, Vance DE. J Lipid Res. 2008;49(6):1187-1194. doi:10.1194/jlr.R700019-JLR200. ↑
Resseguie ME, da Costa KA, Galanko JA, Patel M, Davis IJ, Zeisel SH. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(2):1649-1658. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.106922. ↑
United States Department of Agriculture. ↑
Levine J, Barak Y, Gonzalves M, et al. Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152(5):792-794. doi:10.1176/AJP.152.5.792. ↑
Benjamin J, Levine J, Fux M, Aviv A, Levy D, Belmaker RH. Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152(7):1084-1086. doi:10.1176/AJP.152.7.1084.↑
Eisenberg DP, Ianni AM, Wei SM, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(6):713. doi:10.1038/MP.2012.187. ↑
Fernández-Portero C, Amián JG, Bella R, López-Lluch G, Alarcón D. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023;78(1):1-8. doi:10.1093/gerona/glac152. ↑
de la Bella-Garzón R, Fernández-Portero C, Alarcón D, Amián JG, López-Lluch G. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):279. Published 2022 Jan 29. doi:10.3390/antiox11020279. ↑
Hargreaves I, Heaton RA, Mantle D. Published 2020 Sep 13. doi:10.3390/ijms21186695. ↑
Gutierrez-Mariscal FM, Yubero-Serrano EM, Villalba JM, Lopez-Miranda J. 2019;59(14):2240-2257. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1442316. ↑
Sangsefidi ZS, Yaghoubi F, Hajiahmadi S, Hosseinzadeh M. Food Sci Nutr. 2020;8(4):1766-1776. Published 2020 Mar 19. doi:10.1002/fsn3.1492. ↑
Ibid.↑
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH, Lin PT. Nutr J. 2013;12(1):142. Published 2013 Nov 6. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-12-142 ↑
Gökbel H, Gül I, Belviranl M, Okudan N. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(1):97-102. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a61a50. ↑
Gül I, Gökbel H, Belviranli M, Okudan N, Büyükbaş S, Başarali K. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011;51(2):305-312. ↑
Liao P, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Zheng NJ, Zhang X. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2007;23(4):491-494. ↑
Talevi R, Barbato V, Fiorentino I, Braun S, Longobardi S, Gualtieri R. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:81. Published 2013 Aug 16. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-11-81. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8.↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7.↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9.↑
























