Not happy with your purchase?
Simply let us know, and you'll get a full refund, no questions asked. And you don't even need to return anything.
So that means you can say "yes" now and decide later.
Get the only[9] natural[10] pre-workout supplement with clinically effective doses[11] of 6 scientifically proven ingredients[12] for more energy, focus, and strength without the jitters, upset stomach, or post-workout crash.[13]
- 54 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Pulse’s combination of ingredients and doses[14]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[15]
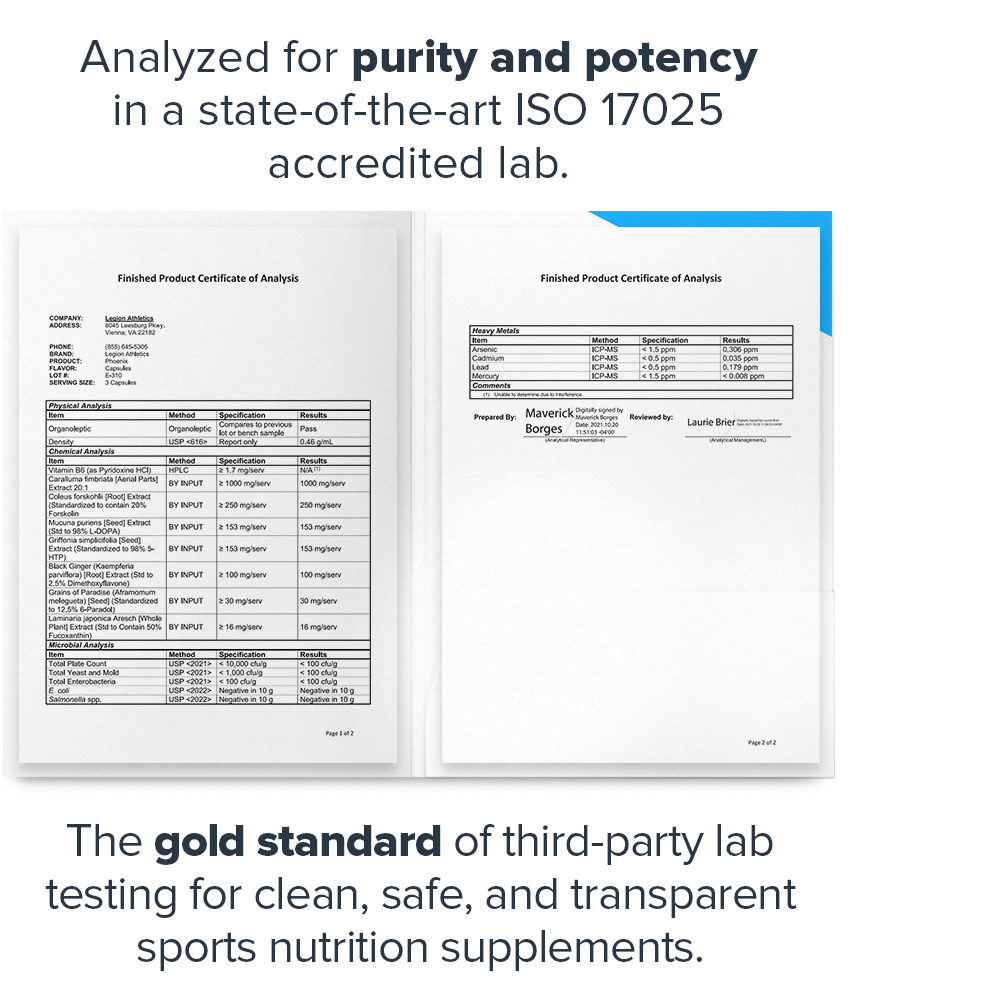
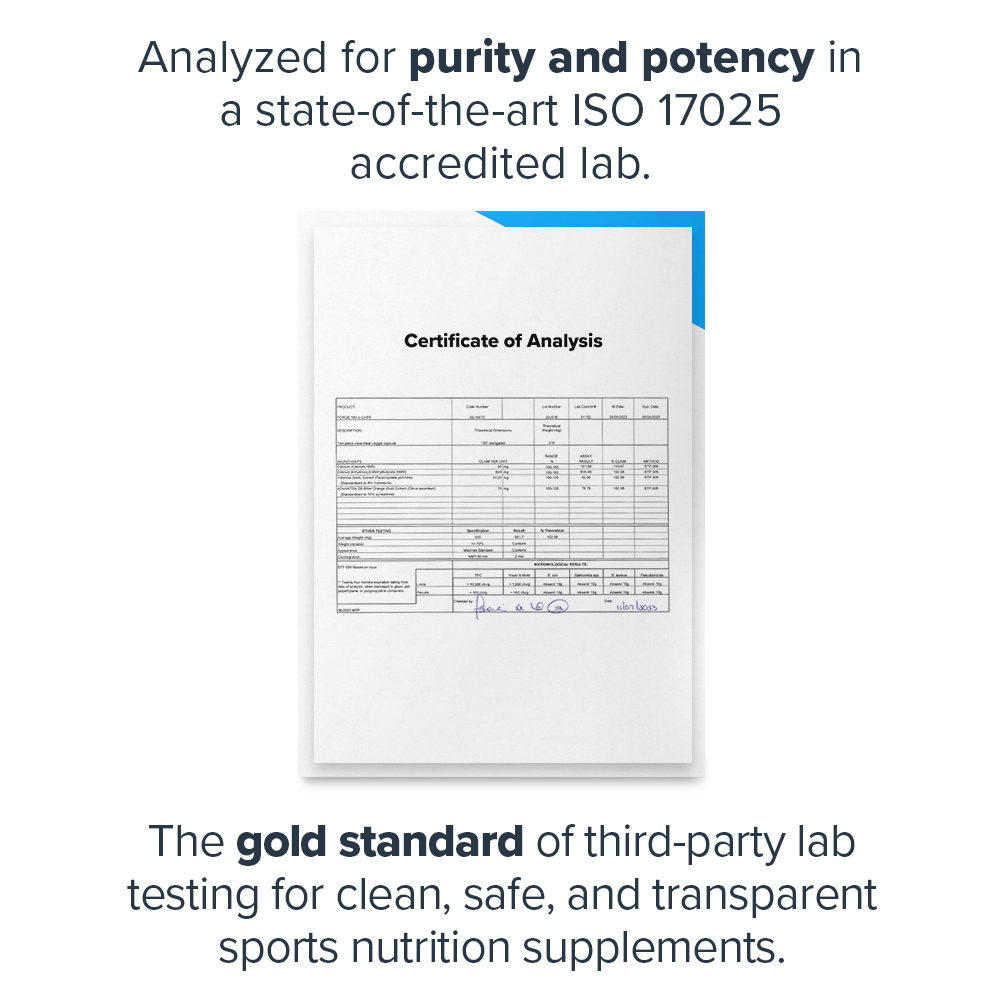
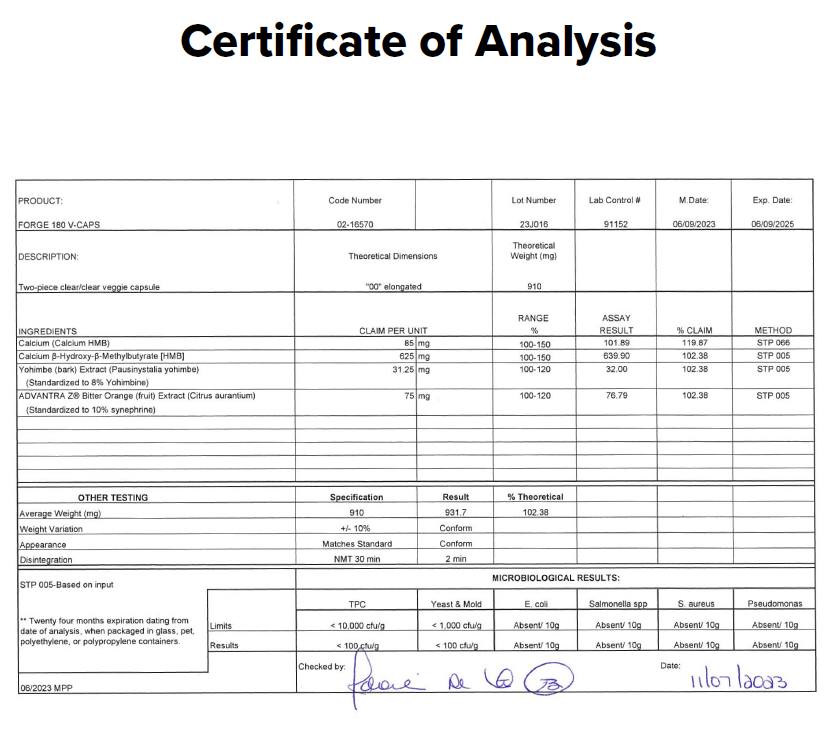
- Tested for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[16]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[17]
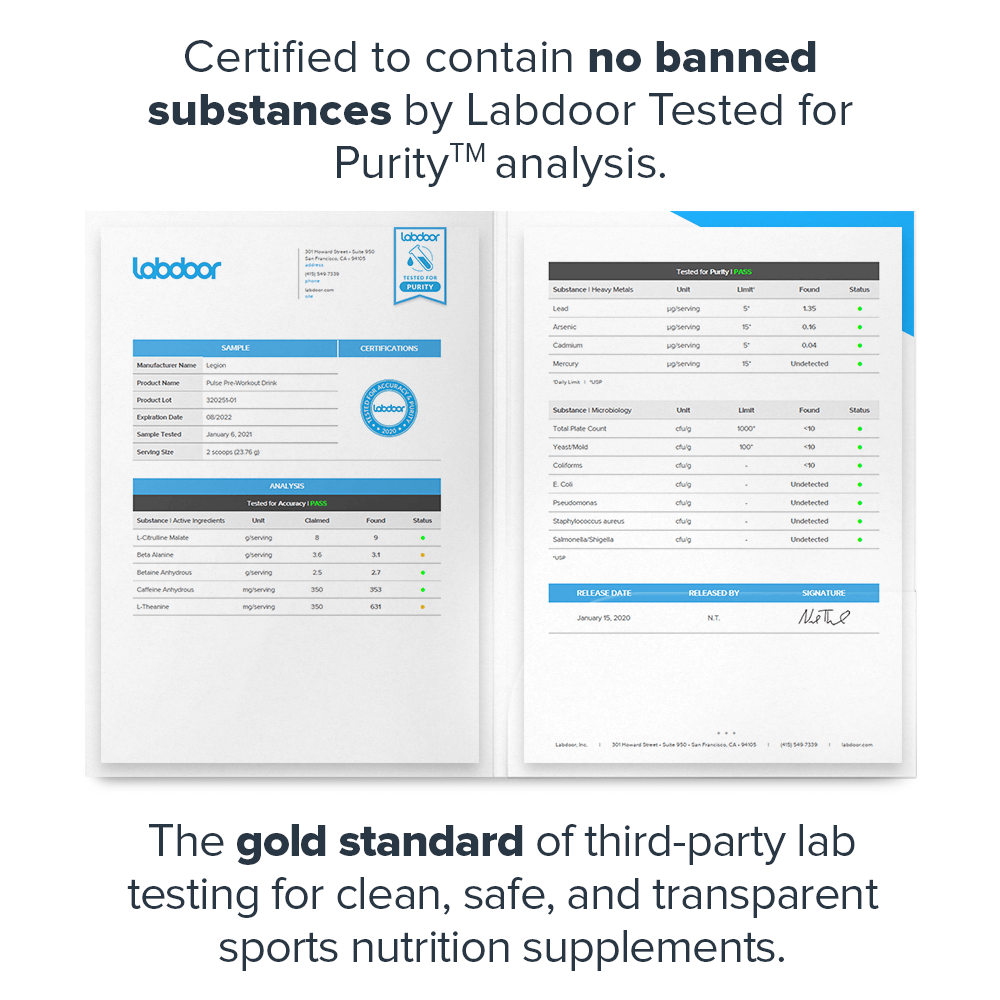
- Certified to contain no banned substances by Labdoor™, the gold standard of third-party lab testing[18]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
Get the only[75] natural[76] stim-free pre-workout supplement with clinically effective doses[77] of 4 scientifically proven ingredients[78] for more strength and stamina and less fatigue without the jitters, upset stomach, or post-workout crash.[79]
- 45 peer-reviewed scientific studies support Pulse’s combination of ingredients and doses[80]
- Contains no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, or other chemical junk[81]
- Tested for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[82]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[83]
- Certified to contain no banned substances by Labdoor™, the gold standard of third-party lab testing[84]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected and cGMP-compliant facilities
Phoenix
Stim-Free Fat Burner
Forge
Pre-Workout Fat Burner
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
See how Legion compares to the rest.
- Active Ingredients
- Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
- Caffeine
- Citrulline Malate
- Beta-Alanine
- Betaine
- L-Theanine
- Alpha-GPC
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested by Labdoor™
- Labdoor Ranking
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion Pulse
Pre-Workout
- 15,100 mg
per serving - 350 mg
per serving - 8,000 mg
per serving - 3,600 mg
per serving - 2,500 mg
per serving - 350 mg
per serving - 300 mg
per serving - A-
- $1.80
-
Pre JYM
Pre-Workout
- 20,955 mg
per serving - 300 mg
per serving - 6,000 mg
per serving - 2,000 mg
per serving - 1,500 mg
per serving - 150 mg
per serving - $1.66
-
PEScience
Prolific Pre-Workout
- 10,970 mg
per serving - 320 mg
per seving - 6,000 mg
per serving - 2,500 mg
per serving - 200 mg
per serving - $1.75
-
C4
Pre-Workout
- 4,025 mg
pre serving - 150 mg
per serving - 1,600 mg
per serving - C-
- $1.00
- Active Ingredients
- Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
- Citrulline Malate
- Beta-Alanine
- Betaine
- Alpha-GPC
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested by Labdoor™
- Labdoor Ranking
- Price Per Serving
-
Legion Pulse
Stim-Free Pre-Workout
- 14,400 mg
per serving - 8,000 mg
per serving - 3,600 mg
per serving - 2,500 mg
per serving - 300 mg
per serving - A-
- $1.80
-
Pre-Kaged
Stimulant Free
- 23,050 mg
per serving - 6,500 mg
per serving - 1,600 mg
per serving - 2,500 mg
per serving - $1.99
-
PEScience
High Volume
- 10,750 mg
per serving - 4,000 mg
per serving - $1.94
-
C4
NO3 Ultimate
- 7,180 mg
per serving - 4,000 mg
per serving - $1.99
The #1 brand of naturally sweetened and flavored sports supplements.
We’ve sold over 5 million bags and bottles to over 1 million customers in 169 countries who have left us over 55,000 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every active ingredient, form, and dose in The Fat Loss Stack is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
No Unnecessary Junk
The Fat Loss Stack contains no artificial food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient in The Fat Loss Stack on the labels—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
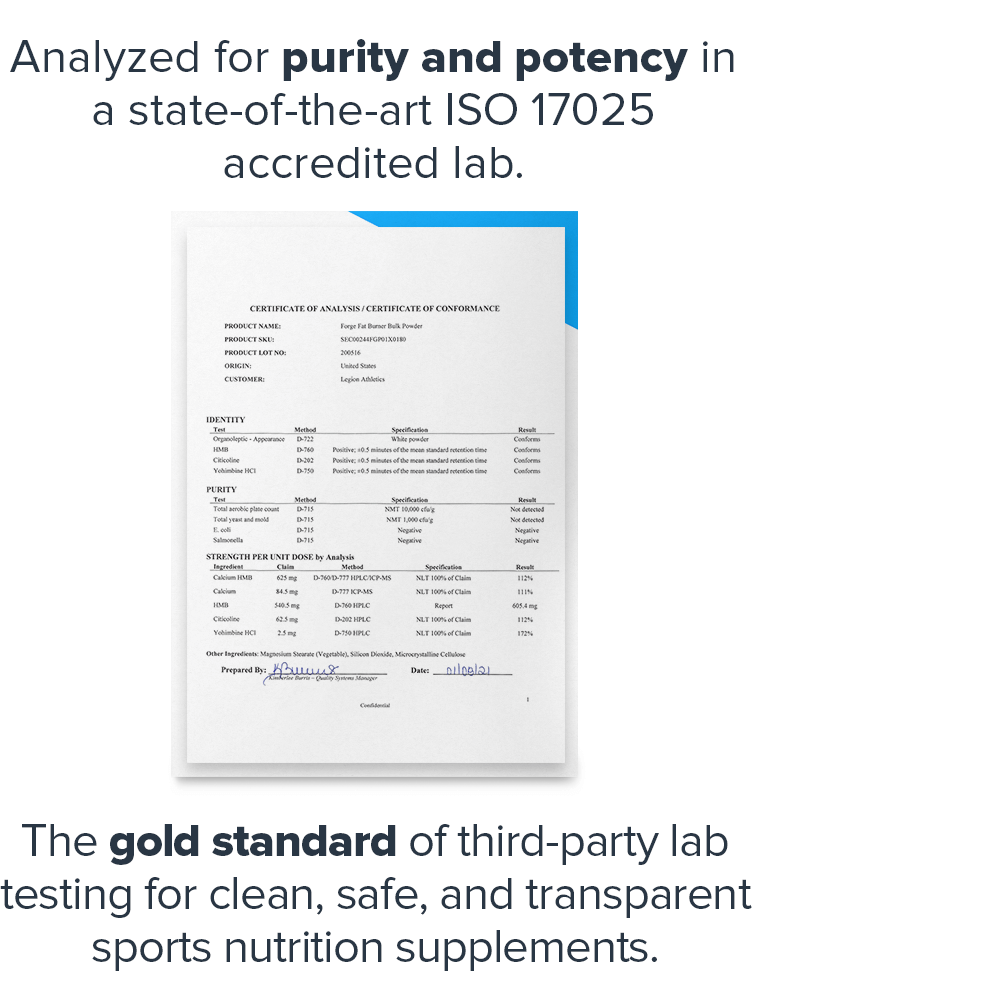
Lab-Tested for Purity and Accuracy
The Fat Loss Stack is lab-tested for purity and accuracy and certified to meet or exceed FDA and WADA safety guidelines.
Made in the USA
The Fat Loss Stack is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
100% Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love The Fat Loss Stack, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Trusted by scientists, doctors, and everyday fitness folk alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
Some popular fat loss supplements contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. Some don’t have any unnecessary junk. But only The Fat Loss Stack checks each of these boxes.↑
Every serving of The Fat Loss Stack contains 19.0918.30 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Each active ingredient in The Fat Loss Stack is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
That’s 1,001929 pages of scientific research that shows The Fat Loss Stack works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in The Fat Loss Stack.↑
Did you know that some supplements contain dangerously high levels of toxins like lead, arsenic, and cadmium?
That’s why we rigorously test every ingredient for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants, ensuring they meet the strict purity standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and World Anti Doping Agency (WADA).↑
Some popular pre-workouts are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Pulse checks each of these boxes.↑
Pulse doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Pulse contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
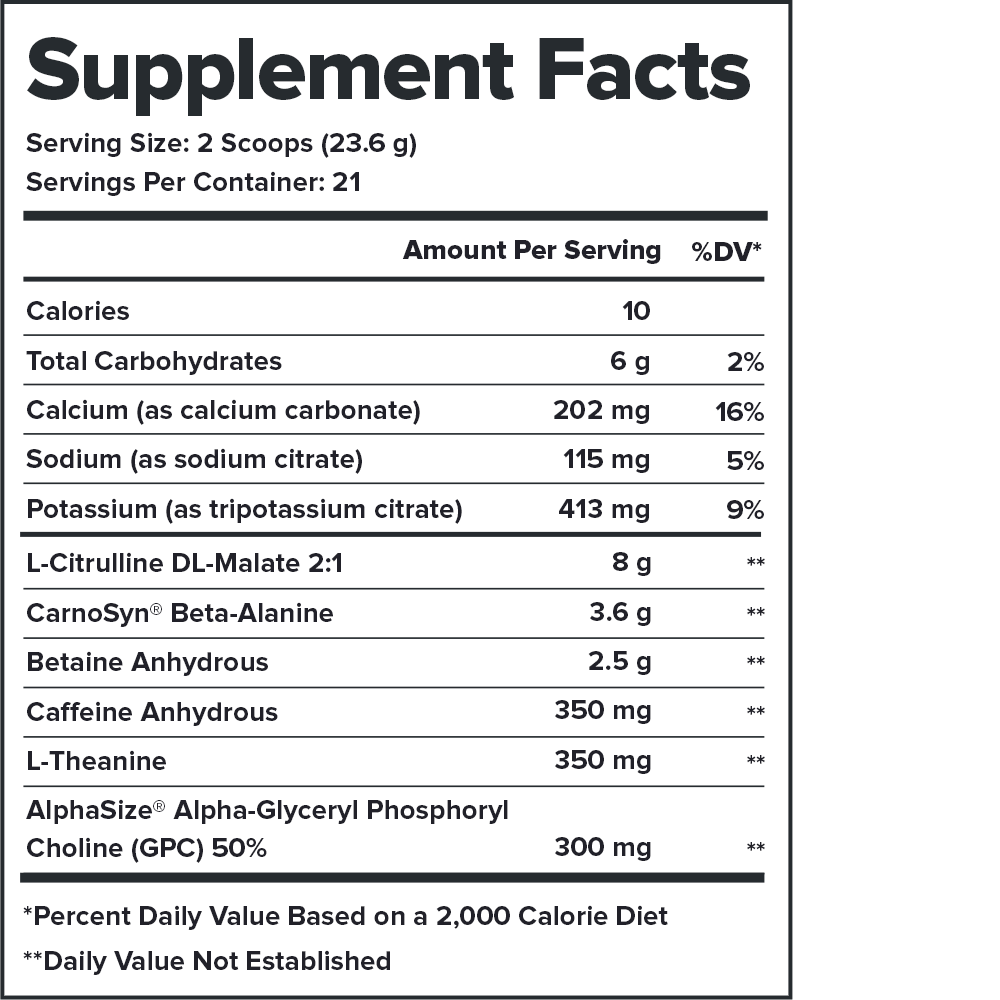
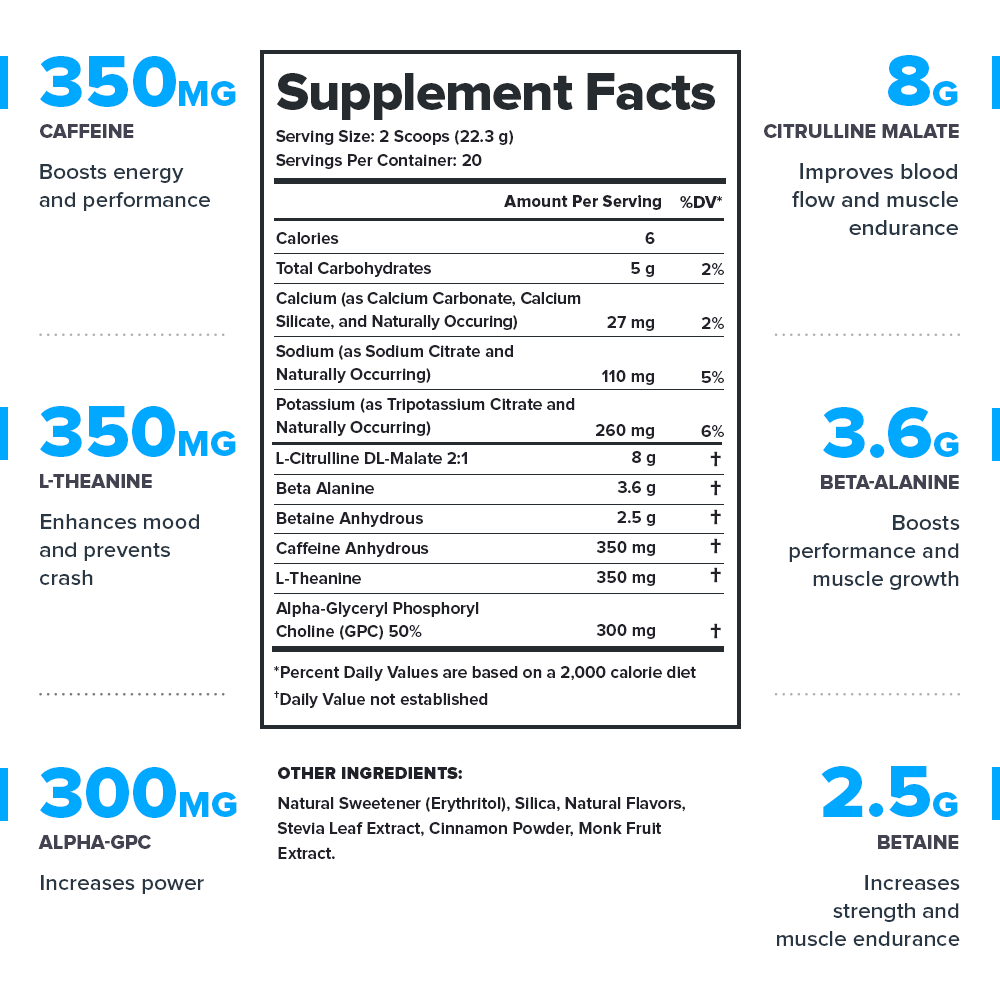
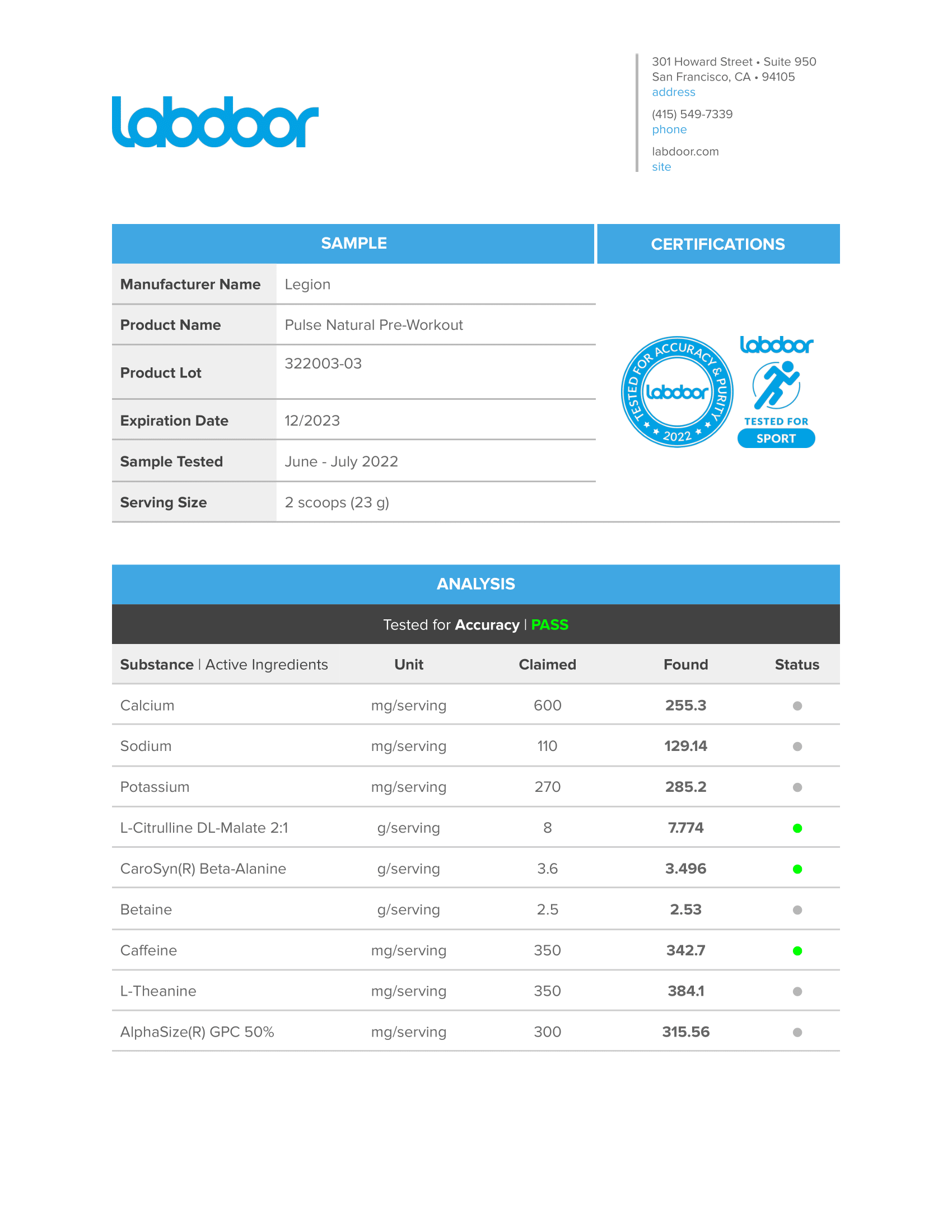
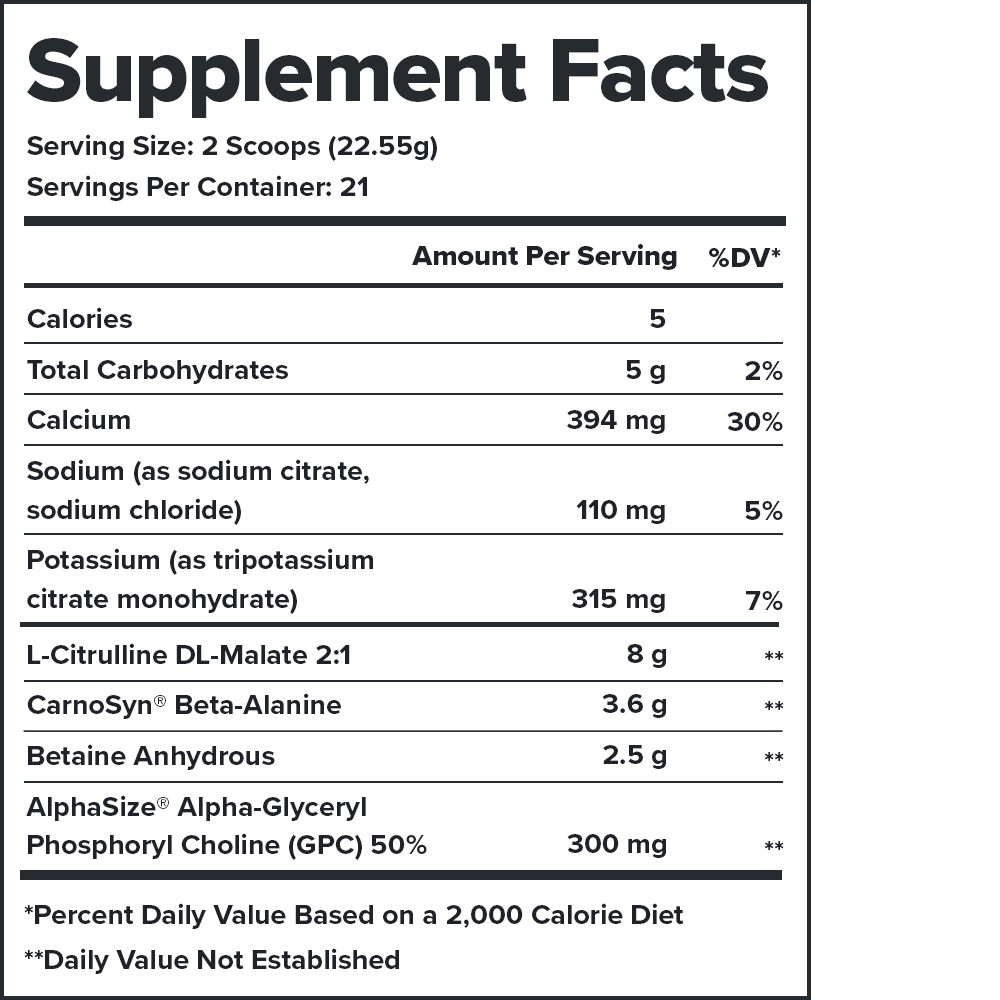
Every serving of Pulse contains 15.1 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Every active ingredient in Pulse is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Pulse contains no harsh stimulants that wind you up and burn you out. Instead, it contains a 1:1 ratio of caffeine and L-theanine, which produces a smooth energy rush and comfortable comedown.↑
That’s 508 pages of scientific research that shows Pulse works the way we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Pulse.↑
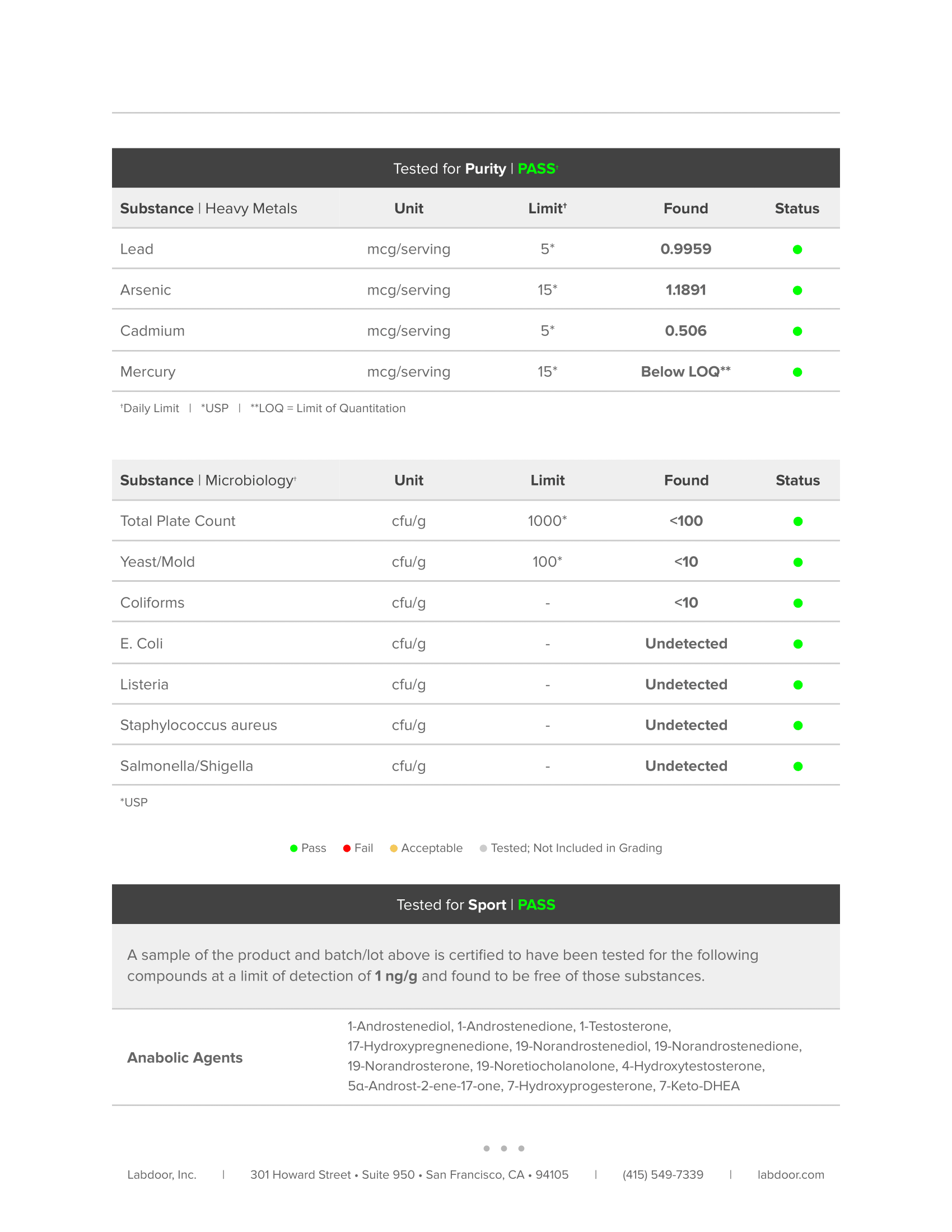
Every bottle of Pulse is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Pulse—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Breum L, Madsen J. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990;51(5):759-767. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.5.759.↑
Astorino TA, Rohmann RL, Firth K. Department of Kinesiology, CSU - San Marcos, San Marcos, CA. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008 Jan;102(2):127-32. ↑
Beck TW, Housh TJ, Schmidt RJ, Johnson GO, Housh DJ, Coburn JW, Malek MH. Department of Nutrition and Health Sciences, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Nebraska-Lincoln. J Strength Cond Res. 2006 Aug;20(3):506-10. ↑
Ganio MS, Klau JF, Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Maresh CM. Department of Kinesiology, Human Performance Laboratory, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Jan;23(1):315-24. ↑
Kimura K, Ozeki M, Juneja LR, Ohira H. Nagoya University Department of Psychology, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, 464-8601, Japan. Biol Psychol. 2007 Jan;74(1):39-45. ↑
Siamwala JH, Dias PM, Majumder S, Joshi MK, Sinkar VP, Banerjee G, Chatterjee S. Vascular Biology Lab, AU-KBC Research Centre, Anna University, MIT Campus, Chennai, India. J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Mar;24(3):595-605. ↑
Bryan J. School of Psychology, University of South Australia, Adelaide, 5001, South Australia, Australia. Nutr Rev. 2008 Feb;66(2):82-90. ↑
Einöther SJ, Martens VE, Rycroft JA, De Bruin EA. Sensation, Perception & Behaviour, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen, Vlaardingen, The Netherlands. Appetite. 2010 Apr;54(2):406-9. ↑
Gomez-Ramirez M, Kelly SP, Montesi JL, Foxe JJ. Program in Cognitive Neuroscience and Schizophrenia, The Cognitive Neurophysiology Laboratory, Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, Orangeburg, NY, USA. Brain Topogr. 2009 Jun;22(1):44-51. ↑
Kahathuduwa CN, Dhanasekara CS, Chin S-H, et al. Nutr Res. 2018;49:67-78. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2017.11.002.↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
Some stim-free pre-workouts are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Pulse checks each of these boxes.↑
Pulse doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Pulse contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
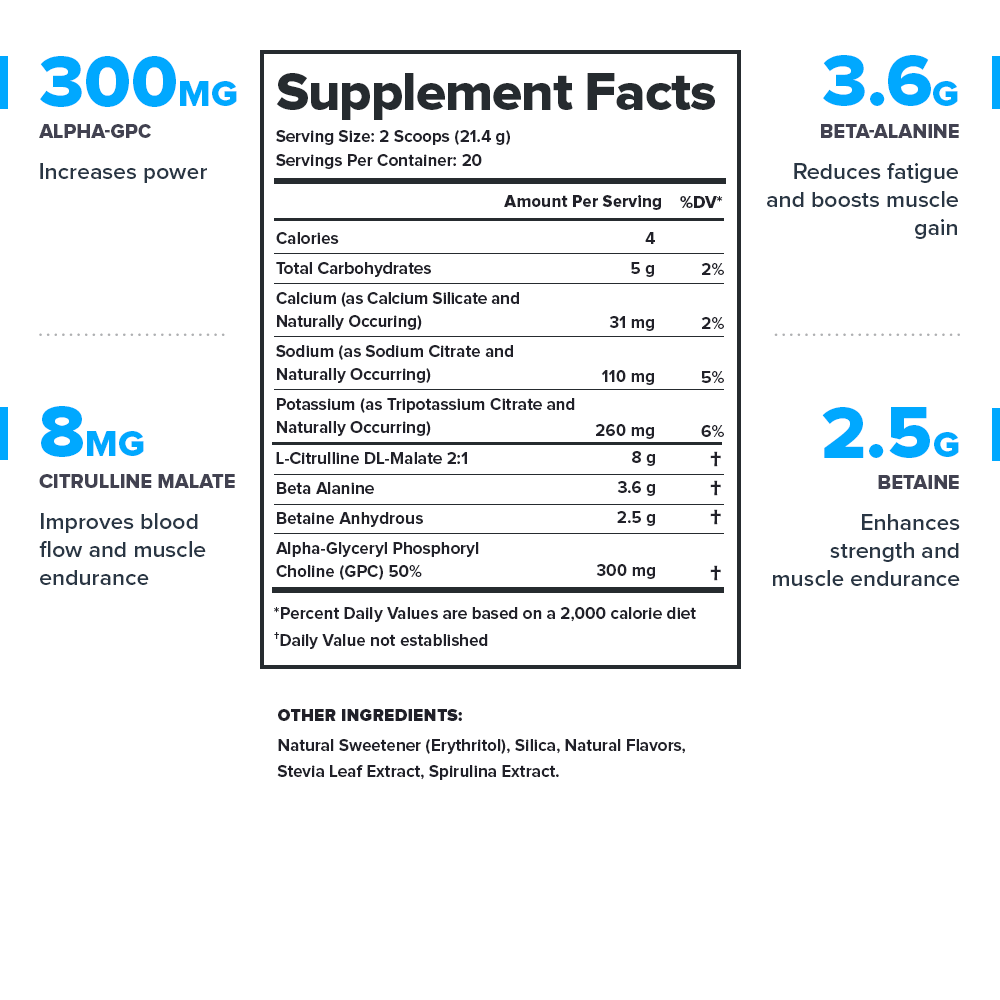
Every serving of Pulse contains 14.4 grams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Every active ingredient in Pulse is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Stim-free Pulse contains no stimulants of any kind, so it won’t wind you up and burn you out.↑
That’s 436 pages of scientific research that shows Pulse works the way we say it does.↑
While these chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why we don’t put any of them into our products.↑
Every bottle of Pulse is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Pulse—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Before you buy a sports supplement, you should know that it's clean, safe, and transparent. And that's exactly what Labdoor's third-party testing and certification means.↑
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(7):829-837, 837a-837d. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304.↑
Zhao Y, Vanhoutte PM, Leung SWS. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;129(2):83-94. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2015.09.002.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Wethington LN, Stone MS, Stewart RW, Moyen NE. Eur J Nutr. 2017;56(2):775-784. doi:10.1007/s00394-015-1124-6.↑
Glenn JM, Gray M, Jensen A, Stone MS, Vincenzo JL. Eur J Sport Sci. 2016;16(8):1095-1103. doi:10.1080/17461391.2016.1158321.↑
Pérez-Guisado J, Jakeman PM. Department of Medicine, University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1215-22. ↑
Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ. Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale, Faculté de Médecine de la Timone, France. Br J Sports Med. 2002 Aug;36(4):282-9. ↑
Suzuki T, Morita M, Kobayashi Y, Kamimura A. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016;13:6. doi:10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z.↑
Dunnett M, Harris RC. Department of Veterinary Basic Sciences, Royal Veterinary College, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1999 Jul;(30):499-504. ↑
Budzeń S, Rymaszewska J. Adv Clin Exp Med. 22(5):739-744.↑
Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris RC, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E. Dept. of Movement and Sport Sciences, Ghent Univ, Belgium. J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;103(5):1736-43. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA. School of Sports, Exercise & Health Sciences, University of Chichester, Chichester, UK. Amino Acids. 2007 Feb;32(2):225-33. ↑
Sale C, Saunders B, Hudson S, Wise JA, Harris RC, Sunderland CD. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, UK. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011 Oct;43(10):1972-8. ↑
Walter AA, Smith AE, Kendall KL, Stout JR, Cramer JT. Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1199-207. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C. Biomedical, Life and Health Sciences Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Clifton Lane, Nottingham, UK. Amino Acids. 2012 Jul;43(1):25-37. ↑
Kern BD, Robinson TL. Human Performance and Physical Education Department, Adams State College, Alamosa, Colorado, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jul;25(7):1804-15. ↑
Smith AE, Walter AA, Graef JL, Kendall KL, Moon JR, Lockwood CM, Fukuda DH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Stout JR. Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Feb 11;6:5. ↑
Stout JR, Cramer JT, Zoeller RF, Torok D, Costa P, Hoffman JR, Harris RC, O'Kroy J. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. Amino Acids. 2007;32(3):381-6. ↑
Stout JR, Graves BS, Smith AE, Hartman MJ, Cramer JT, Beck TW, Harris RC. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Nov 7;5:21. ↑
Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Ross R, Kang J, Stout JR, Wise JA. Department of Health and Exercise Science, The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ, USA. Nutr Res. 2008 Jan;28(1):31-5. ↑
Beasley L, Smith L, Antonio J, Gordon D, Johnstone J, Roberts J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Dec 18;15(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0266-3. ↑
Ziegenfuss T, Landis J, Hofheins J. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008;5(Suppl 1):P15. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-5-S1-P15. ↑
De Jesus Moreno Moreno M. Clin Ther. 2003;25(1):178-193. ↑
Kawamura T, Okubo T, Sato K, et al. Nutrition. 2012;28(11-12):1122-1126. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2012.02.011 ↑
Marcus L, Soileau J, Judge LW, Bellar D. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2017;14:39. doi:10.1186/s12970-017-0196-5. ↑
Trepanowski JF, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Schilling BK, Craig SA, Bloomer RJ. Cardiorespiratory/Metabolic Laboratory, The University of Memphis, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):3461-71. ↑
Lee EC, Maresh CM, Kraemer WJ, Yamamoto LM, Hatfield DL, Bailey BL, Armstrong LE, Volek JS, McDermott BP, Craig SA. Department of Kinesiology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010 Jul 19;7:27. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019.↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑
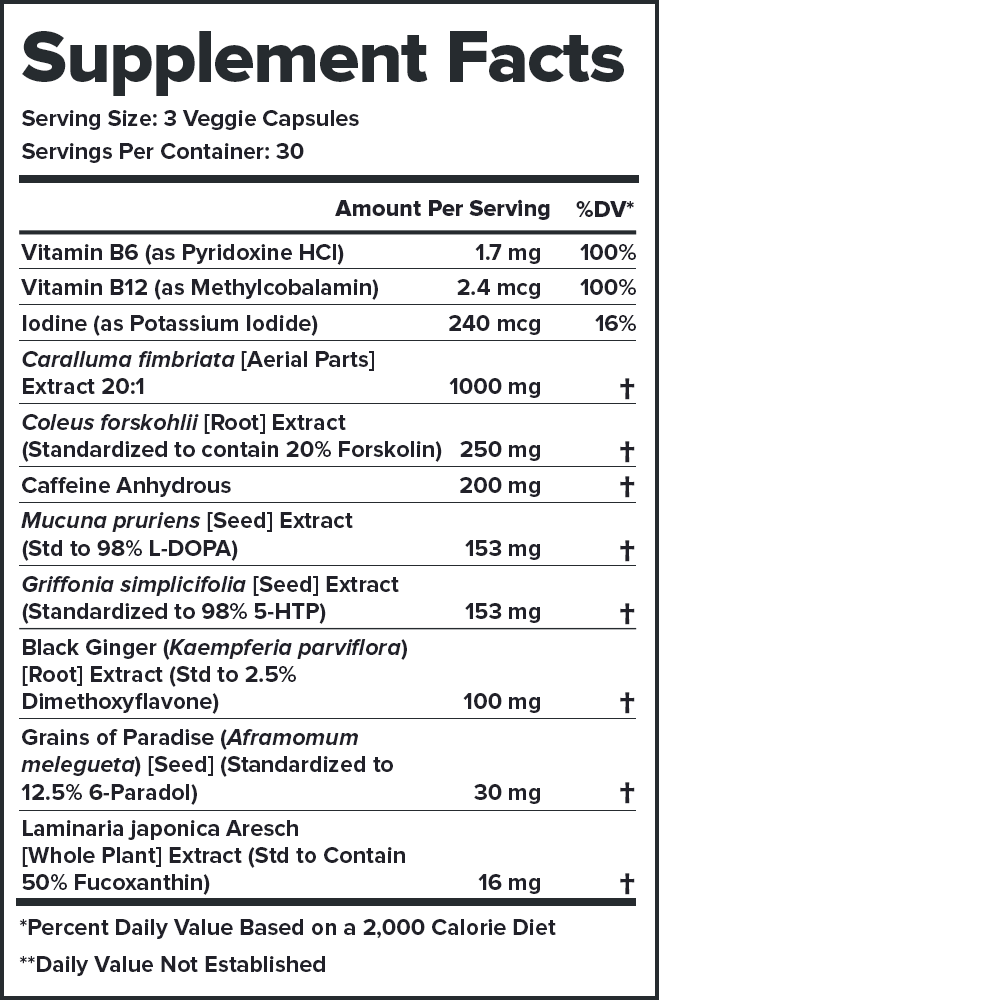
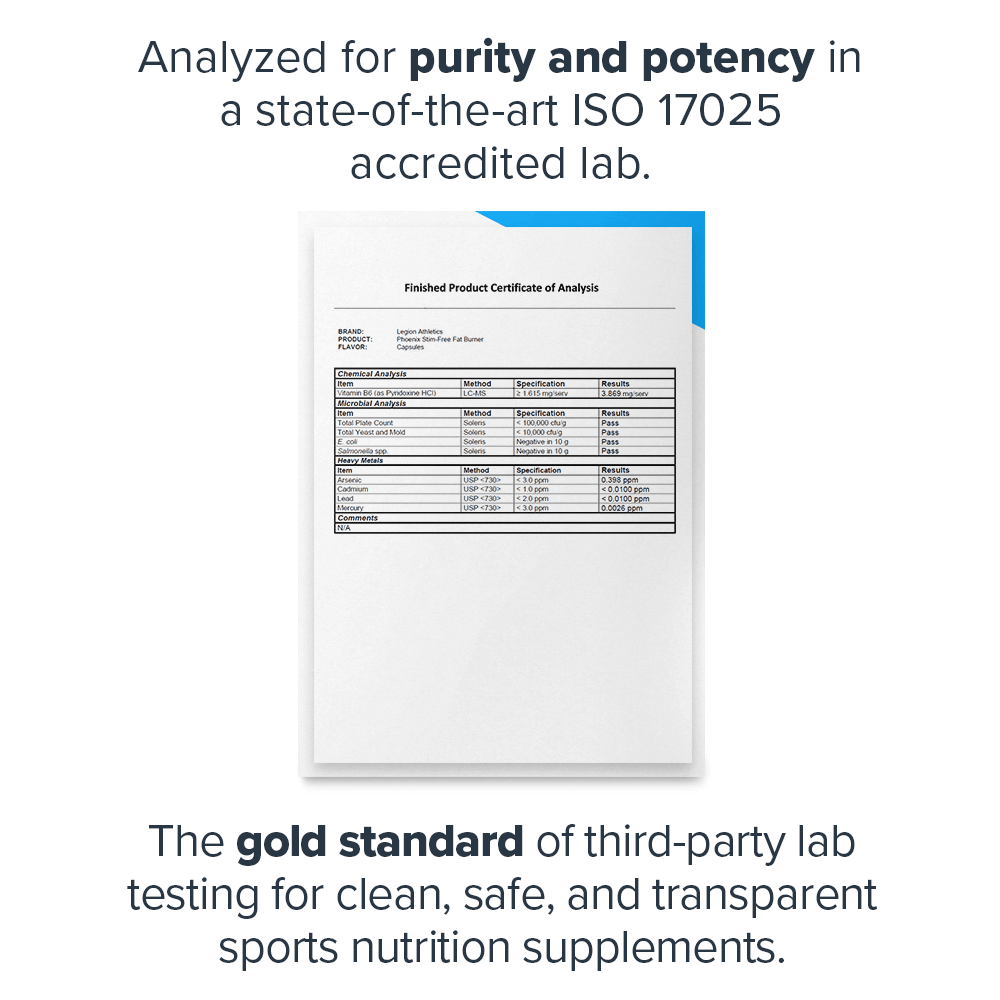
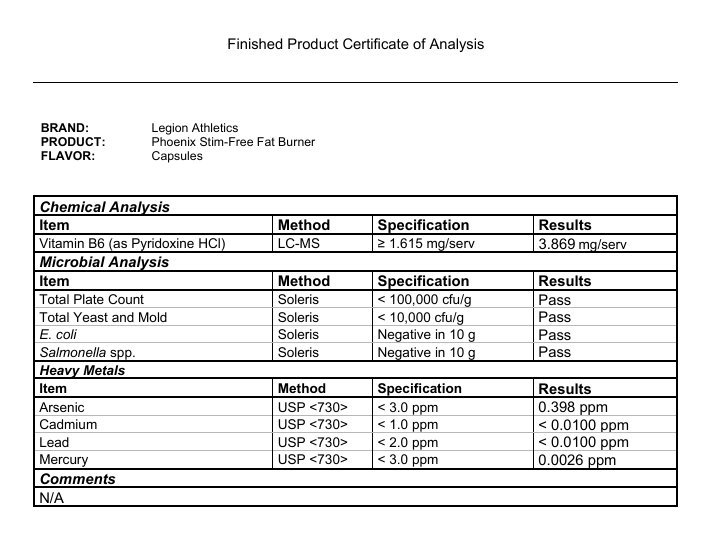
Some popular fat burners are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Phoenix checks each of these boxes. ↑
Every serving of Phoenix contains 1,230 milligrams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Each active ingredient in Phoenix is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
Phoenix contains no stimulants of any kind, so it won't wind you up and burn you out.↑
That's 261 pages of scientific research that shows Phoenix works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that's why you won't find them in Phoenix.↑
Every bottle of Phoenix is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
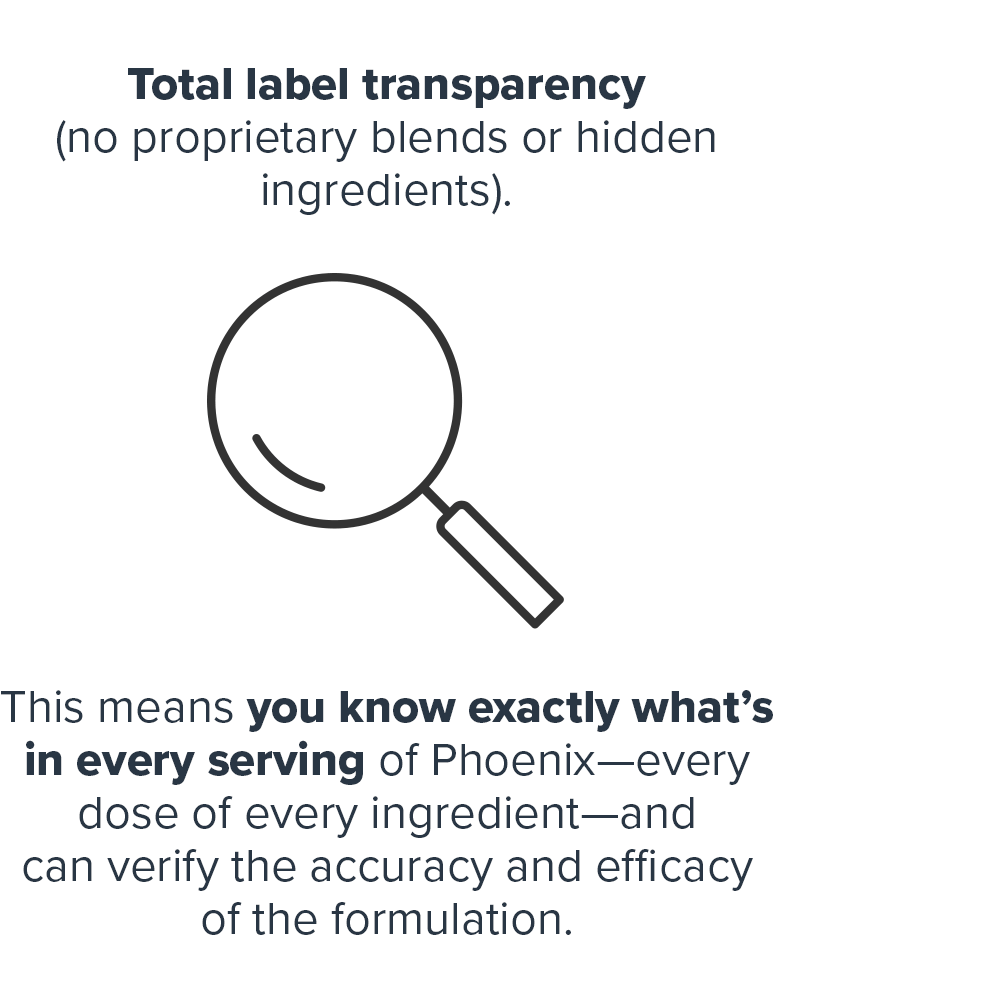
This means you know exactly what's in every serving of Phoenix—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Awwad S, Issa R, Alnsour L, Albals D, Al-Momani I. Molecules. 2021;26(24):7502. Published 2021 Dec 11. doi:10.3390/molecules26247502. ↑
Asbaghi, O., Sadeghian, M., Rahmani, S., Mardani, M., Khodadost, M., Maleki, V., Pirouzi, A., Talebi, S., & Sadeghi, O. (2020). Complementary therapies in medicine, 51, 102424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102424 ↑
Gorji, Z., Varkaneh, H. K., Talaei, S., Nazary-Vannani, A., Clark, C. C. T., Fatahi, S., Rahmani, J., Salamat, S., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology, 63, 153018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153018. ↑
Lee, J., Chung, M., Fu, Z., Choi, J., & Lee, H. J. (2020). Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 39(5), 388–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2019.1691956. ↑
Azantsa B, Kuate D, Chakokam R, Paka G, Bartholomew B, Nash R. Funct Foods Heal Dis. 2015;5(6):200-208. doi:10.31989/FFHD.V5I6.184. ↑
Lee, J., Chung, M., Fu, Z., Choi, J., & Lee, H. J. (2020). Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 39(5), 388–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2019.1691956. ↑
Méndez-Del Villar, M., González-Ortiz, M., Martínez-Abundis, E., Pérez-Rubio, K. G., & Cortez-Navarrete, M. (2018). Journal of medicinal food, 21(6), 568–574. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.0092 ↑
Ngondi, J. L., Oben, J. E., & Minka, S. R. (2005). Lipids in health and disease, 4, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-4-12. ↑
Ngondi JL, Etoundi BC, Nyangono CB, Mbofung CM, Oben JE. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:7. Published 2009 Mar 2. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-8-7. ↑
Yang, C. S., Lambert, J. D., & Sang, S. (2009). Archives of toxicology, 83(1), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0372-0. ↑
Dulloo, A. G., Seydoux, J., Girardier, L., Chantre, P., & Vandermander, J. (2000). International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders : journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 24(2), 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801101. ↑
Dulloo, A. G., Duret, C., Rohrer, D., Girardier, L., Mensi, N., Fathi, M., Chantre, P., & Vandermander, J. (1999). The American journal of clinical nutrition, 70(6), 1040–1045. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/70.6.1040. ↑
Kapoor, M. P., Sugita, M., Fukuzawa, Y., & Okubo, T. (2017). The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 43, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.10.013. ↑
Auvichayapat P, Prapochanung M, Tunkamnerdthai O, et al. Physiol Behav. 2008;93(3):486-491. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.10.009. ↑
Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Lejeune MP, Kovacs EM. Obes Res. 2005;13(7):1195-1204. doi:10.1038/oby.2005.142. ↑
Maki KC, Reeves MS, Farmer M, et al. J Nutr. 2009;139(2):264-270. doi:10.3945/jn.108.098293 ↑
Venables MC, Hulston CJ, Cox HR, Jeukendrup AE. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(3):778-784. doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.3.778. ↑
Maki KC, Reeves MS, Farmer M, et al. J Nutr. 2009;139(2):264-270. doi:10.3945/jn.108.098293. ↑
Cardoso GA, Salgado JM, Cesar Mde C, Donado-Pestana CM. J Med Food. 2013;16(2):120-127. doi:10.1089/jmf.2012.0062. ↑
Willems MET, Şahin MA, Cook MD. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018;28(5):536-541. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2017-0237. ↑
Bagheri R, Rashidlamir A, Ashtary-Larky D, et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;86(4):753-762. doi:10.1111/bcp.14176. ↑
Wolfram S, Wang Y, Thielecke F. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2006;50(2):176-187. doi:10.1002/MNFR.200500102. ↑
Rondanelli M, Riva A, Petrangolini G, et al. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):644. Published 2021 Feb 17. doi:10.3390/nu13020644. ↑
Thielecke F, Rahn G, Böhnke J, et al. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010;64(7):704-713. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2010.47. ↑
Sugita J, Yoneshiro T, Sugishima Y, et al. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2014;60(1):22-27. doi:10.3177/jnsv.60.22. ↑
Sugita J, Yoneshiro T, Hatano T, et al. Br J Nutr. 2013;110(4):733-738. doi:10.1017/S0007114512005715. ↑
Ceci F, Cangiano C, Cairella M, et al. J Neural Transm. 1989;76(2):109-117. doi:10.1007/BF01578751. ↑
Birdsall TC. Altern Med Rev. 1998;3(4):271-280. ↑
Wurtman RJ, Wurtman JJ. Obes Res. 1995;3 Suppl 4:477S-480S. doi:10.1002/j.1550-8528.1995.tb00215.x. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4(2):568-586. Published 2012 Jan 1. doi:10.2741/e400 ↑
Kanarek RB. Nutr Rev. 2011;69(7):385-391. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00385.x ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012;51(1):86-97.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.10.015 ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, et al. [published correction appears in Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1542]. Lancet. 2007;370(9598):1560-1567. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3 ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. J Food Sci. 2011;76(6):T125-T129. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02267.x ↑
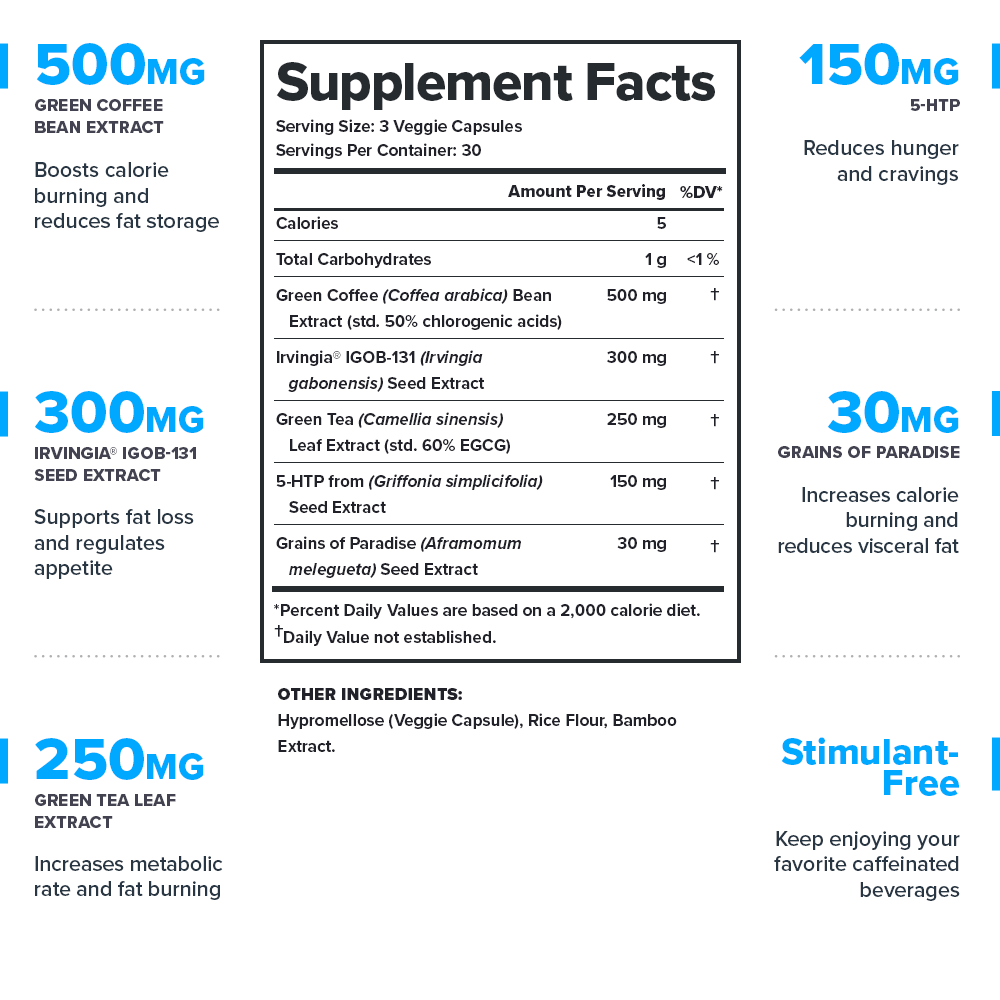
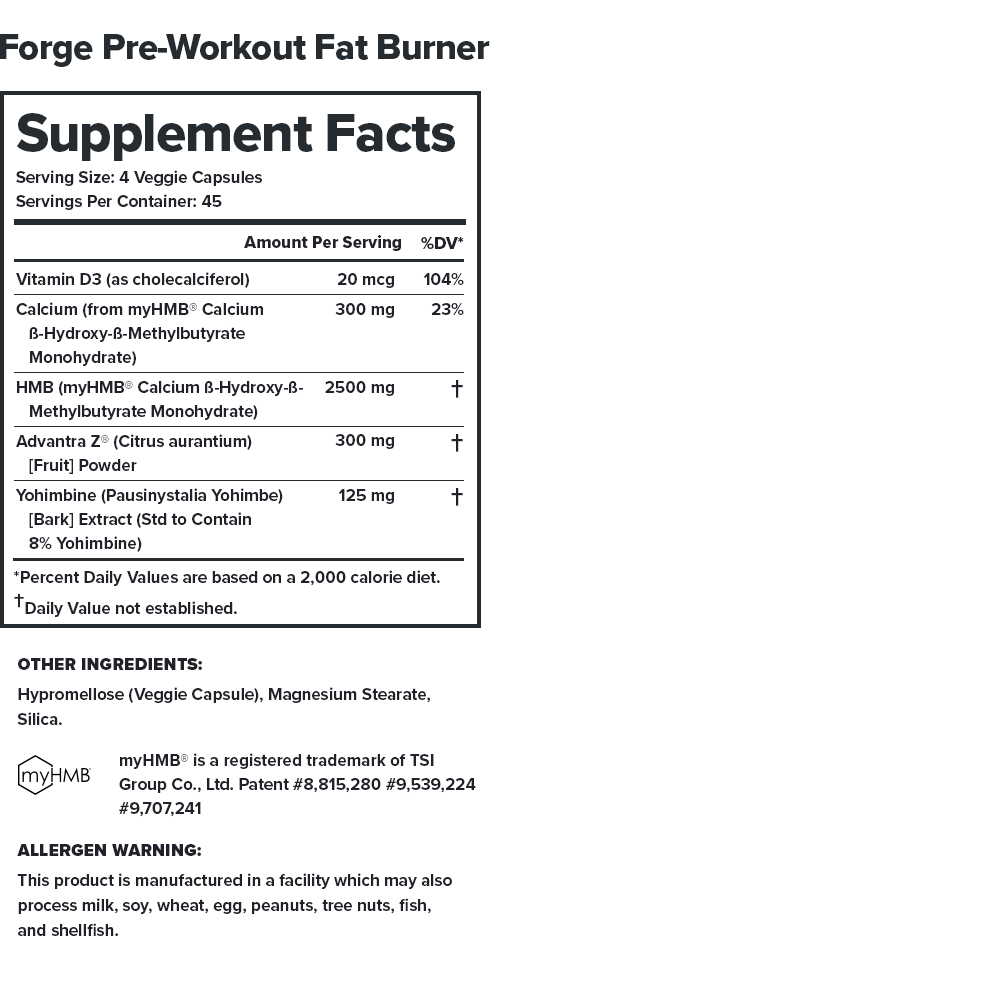
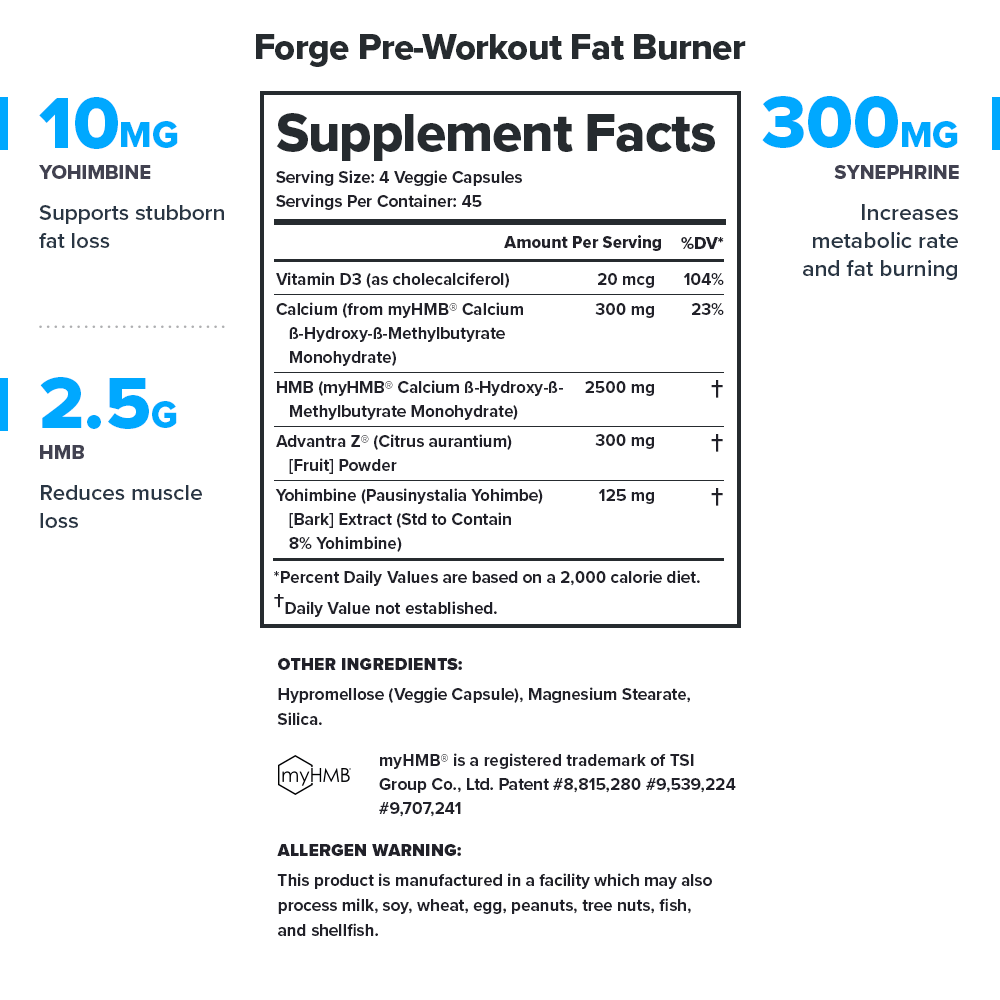
Some popular pre-workout fat burners are all-natural. Some contain the right mix of high-quality ingredients. Some provide clinically effective doses. But only Forge checks each of these boxes.↑
Forge doesn’t just “contain natural ingredients''—every ingredient is naturally sourced from plants and animals. Forge contains no artificial or synthetic substances of any kind.↑
Every serving of Forge contains 2,760 milligrams of active ingredients that have been shown to be safe and effective in peer-reviewed scientific research.↑
Each active ingredient in Forge is backed by published scientific studies that show benefits in healthy humans.↑
That’s 159 pages of scientific research that shows Forge works exactly like we say it does.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Forge.↑
Every bottle of Forge is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
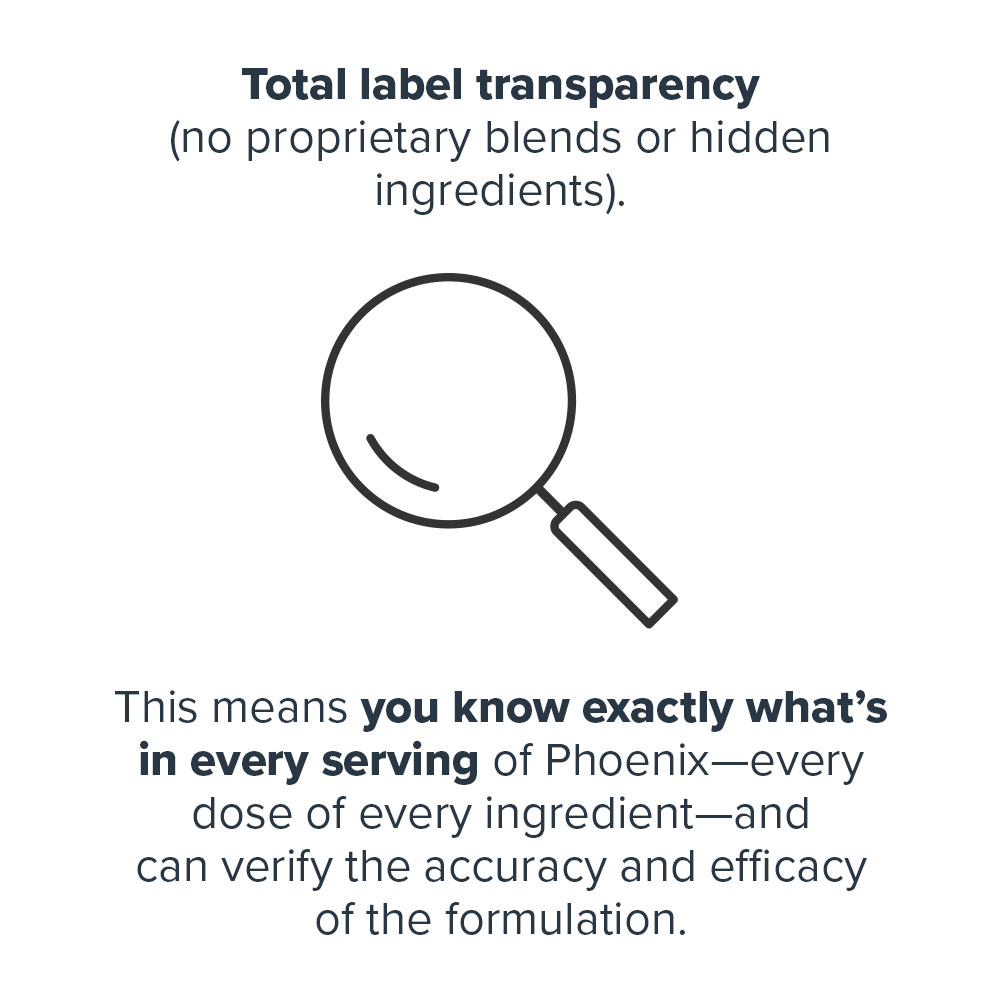
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Forge—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Ostojic SM. Res Sports Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;14(4):289-99. doi: 10.1080/15438620600987106. ↑
Callahan MF, Beales M, Oltmans GA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 Apr;20(4):591-9. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(84)90309-5. ↑
Lafontan M, Berlan M, Galitzky J, Montastruc JL. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Jan;55(1 Suppl):219S-227S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.1.219s. ↑
Ostojic SM. Res Sports Med. 2006 Oct-Dec;14(4):289-99. doi: 10.1080/15438620600987106. ↑
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Cussac D, Lejeune F, Nicolas JP, Cogé F, Galizzi JP, Boutin JA, Rivet JM, Dekeyne A, Gobert A. Psychopharmacology Department, Institut de Recherches Servier, Centre de Recherches de Croissy, 125, Chemin de Ronde, 78290-Croissy-sur-Seine, Paris, France. Synapse. 2000 Feb;35(2):79-95. ↑
Hayder M. Al-Kuraishy, Haidar A. N. Abood, Ali Ismail A. Al-Gareeb. 1. Department of Pharmacology/College of Medicine/ Al-Mustansiriya University/Baghdad/Iraq 2. Department of Pharmacology/College of Medicine/Kerbala University/Kerbala/ Iraq. Karbala J. Med 01/2015; 7(2). ↑
Galitzky J, Taouis M, Berlan M, Rivière D, Garrigues M, Lafontan M. Laboratoire de Pharmacologie Clinique et Médicale, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France. Eur J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;18(6):587-94. ↑
McCarty MF. Pantox Laboratories, California 92109, USA Med Hypotheses. 2002 Jun;58(6):491-5. ↑
Cimolai N, Cimolai T. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. J Diet Suppl. 2011 Dec;8(4):346-54. doi: 10.3109/19390211.2011.615806. Epub 2011 Oct 21. ↑
Kimball SR, Jefferson LS. Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA. J Nutr. 2006 Jan;136(1 Suppl):227S-31S. ↑
Rowlands DS, Thomson JS. Exercise and Sport Sciences, Institute of Food, Nutrition and Human Health, Massey University, Wellington, New Zealand. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 May;23(3):836-46. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a00c80. ↑
Wilson JM, Lowery RP, Joy JM, et al. Br J Nutr. 2013 Aug 28;110(3):538-44. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512005387. Epub 2013 Jan 3. ↑
Wilson JM, Lowery RP, Joy JM, et al. Br J Nutr. 2013 Aug 28;110(3):538-44. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512005387. Epub 2013 Jan 3. ↑
Wilkinson DJ, Hossain T, Hill DS, Phillips BE, Crossland H, Williams J, Loughna P, Churchward-Venne TA, Breen L, Phillips SM, Etheridge T, Rathmacher JA, Smith K, Szewczyk NJ, Atherton PJ. Metabolic and Molecular Physiology Research Group, MRC-ARUK Centre of Excellence for Musculoskeletal Ageing Research, School of Graduate Entry Medicine and Health, Derby DE22 3DT, UK. J Physiol. 2013 Jun 1;591(Pt 11):2911-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.253203. Epub 2013 Apr 3. ↑
Doi M, Yamaoka I, Nakayama M, Sugahara K, Yoshizawa F. Division of Pharmacology, Drug Safety and Metabolism, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Factory, Inc., Naruto, Tokushima 772-8601, Japan. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jun;292(6):E1683-93. Epub 2007 Feb 13. ↑
Staten MA, Bier DM, Matthews DE. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Dec;40(6):1224-34. ↑
Haaz S, Fontaine KR, Cutter G, Limdi N, Perumean-Chaney S, Allison DB. Obes Rev. 2006;7(1):79-88. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2006.00195.x. ↑
Stohs SJ, Preuss HG, Keith SC, Keith PL, Miller H, Kaats GR. Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(4):295-301. Published 2011 Apr 28. doi:10.7150/ijms.8.295.↑
Brown CM, McGrath JC, Midgley JM, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 1988;93(2):417-429. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11449.x. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑