The truth is that people who dislike onions have no idea what they’re missing out on. Onions are not only flavorful, they’re also full of healthy nutrients and can be used in countless dishes.
So today we’re going to talk about why you should be eating more onions.
- Onions Are Nutrient-Dense
- History of Onions
- Health Benefits of Onions
- How to Prepare and Eat Onions
- The Drawbacks of Onions
Table of Contents
+Onions Are Nutrient-Dense
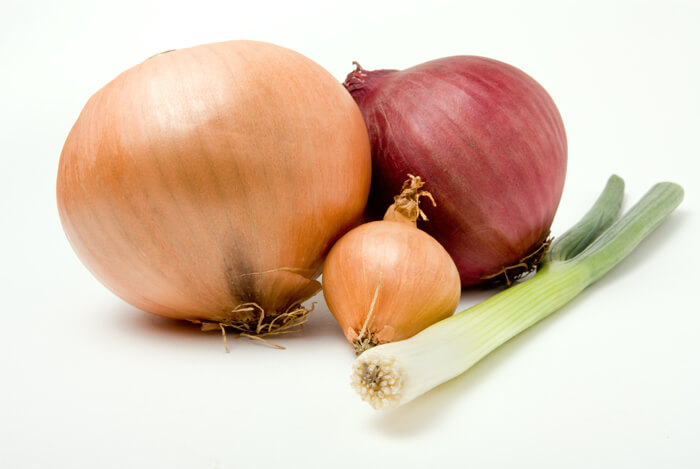

There’s a great reason why onions are a staple food in the cuisine of dozens of cultures worldwide.
Onions are naturally low in calories but high in a multitude of beneficial nutrients. One cup of chopped onion contains approximately:
- 64 calories
- 15 grams of carbohydrate
- 0 grams of fat
- 0 grams of cholesterol
- 3 grams of fiber
- 7 grams of sugar
- 2 grams of protein
Eating onions on a regular basis provides your body with the following nutrients:
- Biotin
- Chromium
- Copper
- Folate
- Manganese
- Phosphorous
- Potassium
- Quercetin
- Vitamin B1
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin C
Quercetin

Quercetin is a powerful antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties found in onions.
Studies have shown quercetin could prevent histamine releases that lead to allergic reactions.
And according to the University of Maryland Medical Center, quercetin could also reduces the symptoms of bladder infections, promotes prostate health, and lowers blood sugar.
History of Onions

There are two main varieties of bulb onions.
First, there are storage onions. These are available year-round and include yellow, white, red, and Spanish onions.
Then you have seasonal onions, which include sweet Vidalia and pearl onions.
Onions were first cultivated in Asia over five thousand years ago, and were common among the ancient Egyptians, Indians, Romans, and Greeks for a number of purposes.
Onions are likely one of the earliest crops because they are less perishable than other foods of the time and are extremely transportable and easy to grow in a variety of soils and climates.
Health Benefits of Onions
Heart Health

A 1987 animal study in the Journal of Hypertension found that sulfur intake may delay or reduced the onset of hypertension.
Onions also may act as anticoagulants, or blood thinners, which can prevent your red blood cells from forming blood clots. Studies have shown can help to improve or prevent cardiovascular diseases.
According to the University of Maryland Medical Center, the quercetin in onions could also help prevent plaque buildup in the arteries, which reduces the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Anti-Cancer

The active compounds in onions may be able to inhibit the development and spread of cancerous cells.
Quercetin – a powerful antioxidant compound – has been linked to the prevention or reduction of the spread of cancer. Because onions are so high in quercetin and other nutrients like vitamin C, they may help nourish the body and ward off potential illness.
Digestion and Stomach Health

Onions are also high in fiber, which promotes good digestion and keeps you regular.
The soluble fiber called oligofructose is found in onions, and it promotes good bacterial growth in your intestines. A 2005 study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology found that oligofructose could help to prevent and treat diarrhea.
Diabetes Management
One relatively unusual mineral found in onions is chromium, which helps the body manage blood sugar levels. Chromium ensures the gradual release of glucose to the muscles and body cells – so eating onions can help modulate your blood sugar levels.
A prebiotic nutrient in onions called inulin has multiple health benefits, which include fighting against diabetes. Women with type 2 diabetes who inulin had improved glycemic control and increased antioxidant activity.
How to Prepare and Eat Onions

The ideal onions are dry and firm with little to no scent before they’re peeled. You should try adding onion for flavor whenever possible because they pair well with most dishes.
You can sauté, roast, grill, or caramelize onions.
You can also use them as a delicious topping for sandwiches, dice them up and toss them into a salad, or add them to salsas or dips like guacamole.
The Drawbacks of Onions

Onions pose a few mild health risks that we should cover briefly.
According to the National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse, the carbohydrates found in onions can cause gas and bloating in certain people.
If you suffer from chronic heartburn or gastric reflux disease, raw onions can actually worsen your heartburn symptoms.
If you take blood-thinning drugs, eating large amounts of green onions can interfere with their effects.









